

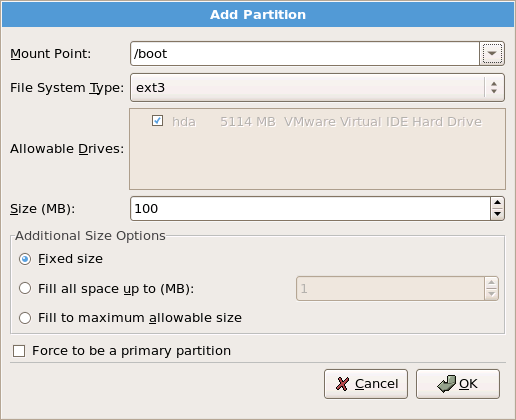
/; enter /boot for the /boot partition, and so on. You can also use the pull-down menu to choose the correct mount point for your partition. For a swap partition the mount point should not be set — setting the filesystem type to swap is sufficient.
fsck [7] the file system.
btrfs. Refer to Chapter 28, Boot Options for instructions.
[7]
The fsck application is used to check the file system for metadata consistency and optionally repair one or more Linux file systems.