Illustration of Gaussian process classification (GPC) on the XOR dataset¶
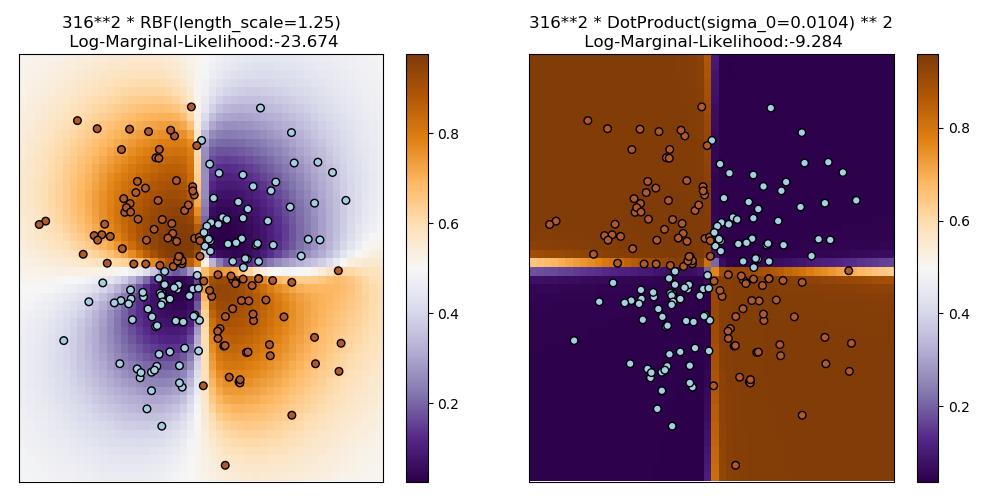
This example illustrates GPC on XOR data. Compared are a stationary, isotropic kernel (RBF) and a non-stationary kernel (DotProduct). On this particular dataset, the DotProduct kernel obtains considerably better results because the class-boundaries are linear and coincide with the coordinate axes. In general, stationary kernels often obtain better results.
print(__doc__)
# Authors: Jan Hendrik Metzen <[email protected]>
#
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF, DotProduct
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-3, 3, 50),
np.linspace(-3, 3, 50))
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
X = rng.randn(200, 2)
Y = np.logical_xor(X[:, 0] > 0, X[:, 1] > 0)
# fit the model
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
kernels = [1.0 * RBF(length_scale=1.0), 1.0 * DotProduct(sigma_0=1.0)**2]
for i, kernel in enumerate(kernels):
clf = GaussianProcessClassifier(kernel=kernel, warm_start=True).fit(X, Y)
# plot the decision function for each datapoint on the grid
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.vstack((xx.ravel(), yy.ravel())).T)[:, 1]
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
image = plt.imshow(Z, interpolation='nearest',
extent=(xx.min(), xx.max(), yy.min(), yy.max()),
aspect='auto', origin='lower', cmap=plt.cm.PuOr_r)
contours = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2,
linetypes='--')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=30, c=Y, cmap=plt.cm.Paired,
edgecolors=(0, 0, 0))
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.axis([-3, 3, -3, 3])
plt.colorbar(image)
plt.title("%s\n Log-Marginal-Likelihood:%.3f"
% (clf.kernel_, clf.log_marginal_likelihood(clf.kernel_.theta)),
fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.669 seconds)

