Copyright © 2003, 2005 Thomas M. Eastep
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, with no Front-Cover, and with no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”.
2009/10/16
Table of Contents
Netfilter consists of three tables: Filter, Nat and Mangle. Each table has a number of build-in chains: PREROUTING, INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT and POSTROUTING.
Rules in the various tables are used as follows:
- Filter
Packet filtering (rejecting, dropping or accepting packets)
- Nat
Network Address Translation including DNAT, SNAT and Masquerading
- Mangle
General packet header modification such as setting the TOS value or marking packets for policy routing and traffic shaping.
The following diagram shows how packets traverse the various builtin chains within Netfilter. Note that not all table/chain combinations are used.
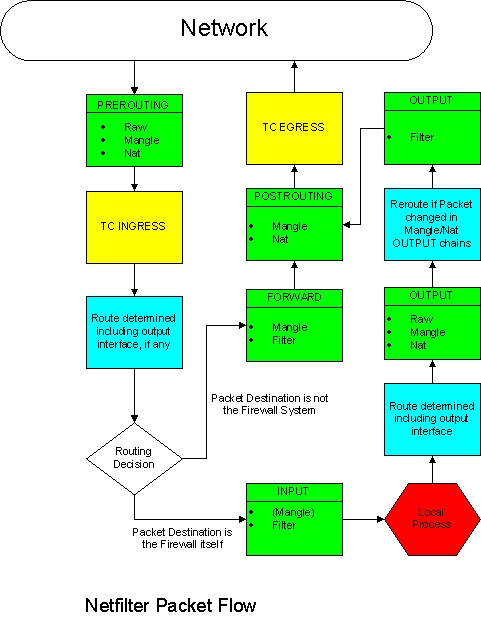
“Local Process” means a process running on the Shorewall system itself.
A more elaborate version of this flow is available here and this one contrasts the Netfilter flow with that of ipchains.
In the above diagram are boxes similar to this:

The above box gives the name of the built-in chain (INPUT) along with the names of the tables (Mangle and Filter) that the chain exists in and in the order that the chains are traversed. The above sample indicates that packets go first through the INPUT chain of the Mangle table then through the INPUT chain of the Filter table. When a chain is enclosed in parentheses, Shorewall does not use the named chain (INPUT) in that table (Mangle).
Important
Keep in mind that chains in the Nat table are only traversed for new connection requests (including those related to existing connections) while the chains in the other tables are traversed on every packet.
The above diagram should help you understand the output of “shorewall dump”. You may also wish to refer to this article that describes the flow of packets through a Shorewall-generated firewall.
Here are some excerpts from “shorewall dump” on a server with one interface (eth0):
[root@tipper ~]# shorewall dump Shorewall 4.4.2.2 Dump at tipper - Fri Oct 16 07:38:16 PDT 2009 Counters reset Thu Oct 8 00:38:06 PDT 2009
The first table shown is the Filter table.
Chain INPUT (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
6428 1417K dynamic all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state INVALID,NEW
967K 629M eth0_in all -- eth0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
49 3896 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHEDThe “dynamic” chain above is where dynamic blacklisting is done.
The following rule indicates that all traffic destined for the firewall that comes into the firewall on eth0 is passed to a chain called “eth0_in”. That chain will be shown further down.
785K 93M eth0_in all -- eth0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 Reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 LOG all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 LOG flags 0 level 6 prefix `Shorewall:INPUT:REJECT:'
0 0 reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain FORWARD (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 accounting all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DROP !icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state INVALID
0 0 eth0_fwd all -- eth0 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 Reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 LOG all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 LOG flags 0 level 6 prefix `Shorewall:FORWARD:REJECT:'
0 0 reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain OUTPUT (policy DROP 1 packets, 60 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
895K 181M fw2net all -- * eth0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
49 3896 ACCEPT all -- * lo 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 Reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 LOG all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 LOG flags 0 level 6 prefix `Shorewall:OUTPUT:REJECT:'
0 0 reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
Here is the eth0_in chain:
Chain eth0_in (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
49 3896 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 Reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 LOG all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 LOG flags 0 level 6 prefix `Shorewall:INPUT:REJECT:'
0 0 reject all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
Next comes the Nat table:
NAT Table Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 5593 packets, 1181K bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 11579 packets, 771K bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 11579 packets, 771K bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Next, the Mangle table:
Mangle Table
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 967K packets, 629M bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
967K 629M tcpre all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 967K packets, 629M bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 tcfor all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 895K packets, 181M bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
895K 181M tcout all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 895K packets, 181M bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
895K 181M tcpost all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain tcfor (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain tcout (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain tcpost (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain tcpre (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destinationAnd finally, the Raw table:
Raw Table Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 1004K packets, 658M bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 926K packets, 186M bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination