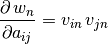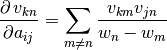tensor.nlinalg – Linear Algebra Ops Using Numpy¶
Note
This module is not imported by default. You need to import it to use it.
API¶
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.AllocDiag[source]¶ Allocates a square matrix with the given vector as its diagonal.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.Eig[source]¶ Compute the eigenvalues and right eigenvectors of a square array.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.Eigh(UPLO='L')[source]¶ Return the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a Hermitian or symmetric matrix.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.EighGrad(UPLO='L')[source]¶ Gradient of an eigensystem of a Hermitian matrix.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.ExtractDiag(view=False)[source]¶ Return the diagonal of a matrix.
Notes
Works on the GPU.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.MatrixInverse[source]¶ Computes the inverse of a matrix
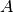 .
.Given a square matrix
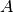 ,
, matrix_inversereturns a square matrix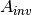 such that the dot product
such that the dot product 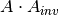 and
and 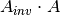 equals the identity matrix
equals the identity matrix 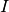 .
.Notes
When possible, the call to this op will be optimized to the call of
solve.-
R_op(inputs, eval_points)[source]¶ The gradient function should return
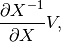
where
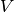 corresponds to
corresponds to g_outputsand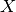 to
to
inputs. Using the matrix cookbook, one can deduce that the relation corresponds to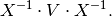
-
grad(inputs, g_outputs)[source]¶ The gradient function should return
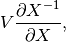
where
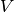 corresponds to
corresponds to g_outputsand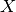 to
to
inputs. Using the matrix cookbook, one can deduce that the relation corresponds to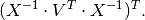
-
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.MatrixPinv[source]¶ Computes the pseudo-inverse of a matrix
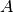 .
.The pseudo-inverse of a matrix
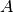 , denoted
, denoted 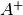 , is
defined as: “the matrix that ‘solves’ [the least-squares problem]
, is
defined as: “the matrix that ‘solves’ [the least-squares problem]
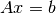 ,” i.e., if
,” i.e., if 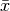 is said solution, then
is said solution, then
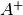 is that matrix such that
is that matrix such that 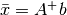 .
.Note that
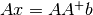 , so
, so 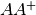 is close to the identity matrix.
This method is not faster than matrix_inverse. Its strength comes from
that it works for non-square matrices.
If you have a square matrix though, matrix_inverse can be both more
exact and faster to compute. Also this op does not get optimized into a
solve op.
is close to the identity matrix.
This method is not faster than matrix_inverse. Its strength comes from
that it works for non-square matrices.
If you have a square matrix though, matrix_inverse can be both more
exact and faster to compute. Also this op does not get optimized into a
solve op.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.QRFull(mode)[source]¶ Full QR Decomposition.
Computes the QR decomposition of a matrix. Factor the matrix a as qr, where q is orthonormal and r is upper-triangular.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.QRIncomplete(mode)[source]¶ Incomplete QR Decomposition.
Computes the QR decomposition of a matrix. Factor the matrix a as qr and return a single matrix.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.SVD(full_matrices=True, compute_uv=True)[source]¶ Parameters: - full_matrices (bool, optional) – If True (default), u and v have the shapes (M, M) and (N, N), respectively. Otherwise, the shapes are (M, K) and (K, N), respectively, where K = min(M, N).
- compute_uv (bool, optional) – Whether or not to compute u and v in addition to s. True by default.
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.TensorInv(ind=2)[source]¶ Class wrapper for tensorinv() function; Theano utilization of numpy.linalg.tensorinv;
-
class
theano.tensor.nlinalg.TensorSolve(axes=None)[source]¶ Theano utilization of numpy.linalg.tensorsolve Class wrapper for tensorsolve function.
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.diag(x)[source]¶ Numpy-compatibility method If x is a matrix, return its diagonal. If x is a vector return a matrix with it as its diagonal.
- This method does not support the k argument that numpy supports.
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.matrix_dot(*args)[source]¶ Shorthand for product between several dots.
Given
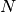 matrices
matrices 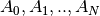 ,
, matrix_dotwill generate the matrix product between all in the given order, namely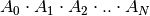 .
.
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.matrix_power(M, n)[source]¶ Raise a square matrix to the (integer) power n.
Parameters: - M (Tensor variable) –
- n (Python int) –
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.qr(a, mode='reduced')[source]¶ Computes the QR decomposition of a matrix. Factor the matrix a as qr, where q is orthonormal and r is upper-triangular.
Parameters: - a (array_like, shape (M, N)) – Matrix to be factored.
- mode ({'reduced', 'complete', 'r', 'raw'}, optional) –
If K = min(M, N), then
- ‘reduced’
- returns q, r with dimensions (M, K), (K, N)
- ‘complete’
- returns q, r with dimensions (M, M), (M, N)
- ‘r’
- returns r only with dimensions (K, N)
- ‘raw’
- returns h, tau with dimensions (N, M), (K,)
Note that array h returned in ‘raw’ mode is transposed for calling Fortran.
Default mode is ‘reduced’
Returns: - q (matrix of float or complex, optional) – A matrix with orthonormal columns. When mode = ‘complete’ the result is an orthogonal/unitary matrix depending on whether or not a is real/complex. The determinant may be either +/- 1 in that case.
- r (matrix of float or complex, optional) – The upper-triangular matrix.
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.svd(a, full_matrices=1, compute_uv=1)[source]¶ This function performs the SVD on CPU.
Parameters: - full_matrices (bool, optional) – If True (default), u and v have the shapes (M, M) and (N, N), respectively. Otherwise, the shapes are (M, K) and (K, N), respectively, where K = min(M, N).
- compute_uv (bool, optional) – Whether or not to compute u and v in addition to s. True by default.
Returns: U, V, D
Return type: matrices
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.tensorinv(a, ind=2)[source]¶ Does not run on GPU; Theano utilization of numpy.linalg.tensorinv;
Compute the ‘inverse’ of an N-dimensional array. The result is an inverse for a relative to the tensordot operation
tensordot(a, b, ind), i. e., up to floating-point accuracy,tensordot(tensorinv(a), a, ind)is the “identity” tensor for the tensordot operation.Parameters: - a (array_like) – Tensor to ‘invert’. Its shape must be ‘square’, i. e.,
prod(a.shape[:ind]) == prod(a.shape[ind:]). - ind (int, optional) – Number of first indices that are involved in the inverse sum. Must be a positive integer, default is 2.
Returns: b – a‘s tensordot inverse, shape
a.shape[ind:] + a.shape[:ind].Return type: ndarray
Raises: LinAlgError– If a is singular or not ‘square’ (in the above sense).- a (array_like) – Tensor to ‘invert’. Its shape must be ‘square’, i. e.,
-
theano.tensor.nlinalg.tensorsolve(a, b, axes=None)[source]¶ Theano utilization of numpy.linalg.tensorsolve. Does not run on GPU!
Solve the tensor equation
a x = bfor x. It is assumed that all indices of x are summed over in the product, together with the rightmost indices of a, as is done in, for example,tensordot(a, x, axes=len(b.shape)).Parameters: - a (array_like) – Coefficient tensor, of shape
b.shape + Q. Q, a tuple, equals the shape of that sub-tensor of a consisting of the appropriate number of its rightmost indices, and must be such thatprod(Q) == prod(b.shape)(in which sense a is said to be ‘square’). - b (array_like) – Right-hand tensor, which can be of any shape.
- axes (tuple of ints, optional) – Axes in a to reorder to the right, before inversion. If None (default), no reordering is done.
Returns: x
Return type: ndarray, shape Q
Raises: LinAlgError– If a is singular or not ‘square’ (in the above sense).- a (array_like) – Coefficient tensor, of shape
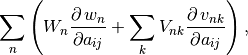
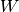 ,
,  to
to 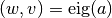 .
.