Appendix B: Advanced network scenarios¶
Let’s see how to deploy network scenarios somewhat more complex than just a virtual machine with Internet access through Bridged Adapter mode.
Scenario 1: Virtualized Zentyal server with Internet connection and access from the host machine and other client¶
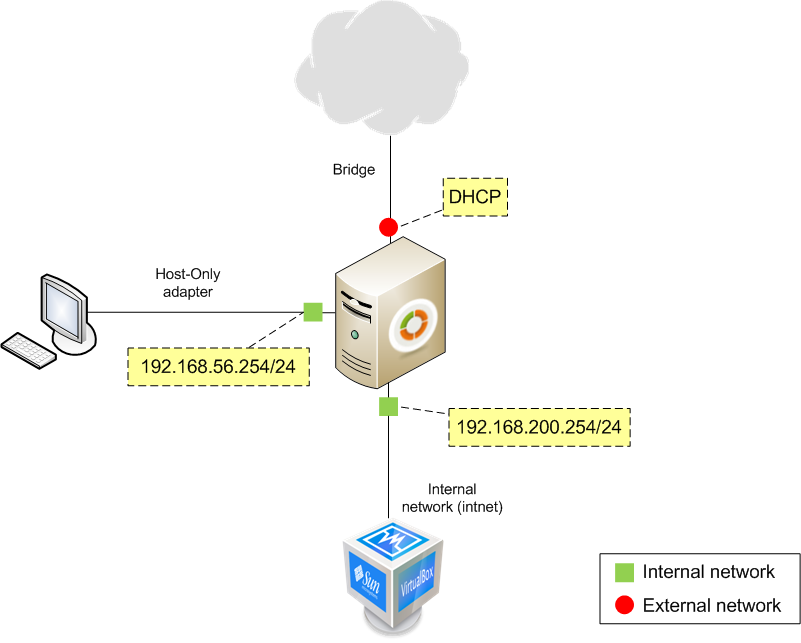
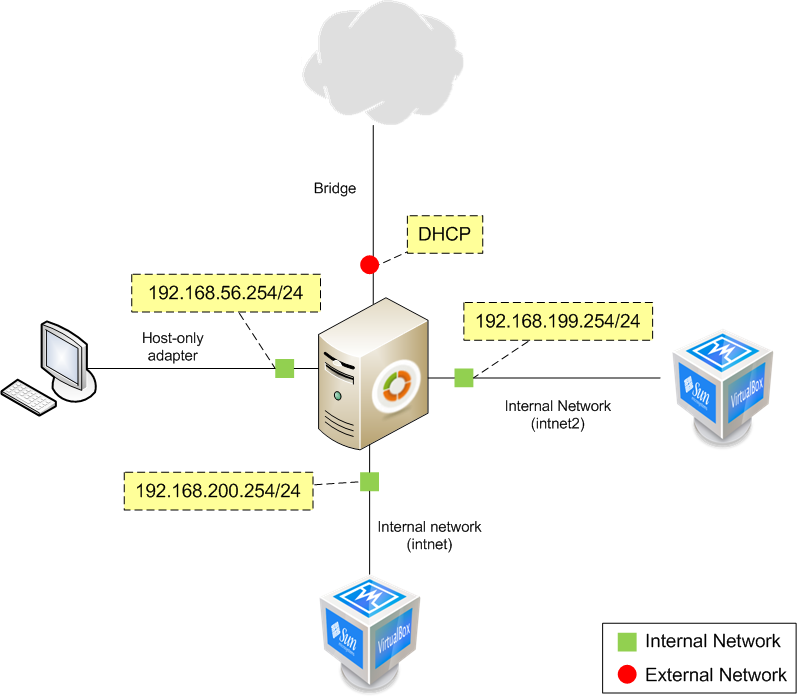
This first scenario consists on a virtualized Zentyal server with three networks. One is a Host interface type connecting with the host server. This network will work on the vboxnet0 interface (Default). A second network will connect the server with a virtual client, using an Internal nework type connection. The third connection will link the server with Internet, using a Bridged adapter connection with DHCP resolution.
The first network will use the vboxnet0 interface, using the 192.168.56.0/24 range. This network is considered internal and Zentyal will use it to connect with the Host. The second network will use the intnet interface using the 192.168.200.0/24 range and it will be considered internal, to access internal services. The third network will connect the server to the Internet and the address will be assigned by DHCP. You must check that these ranges do not clash with any other network you are connected to. If that is the case, change the example ranges to different ones. You may check the scenario in the following figure:
The first step is to create the vboxnet network interface on the host using a Host interface type.
Note: In modern versions of VirtualBox, the interface vboxnet is created by default on the host, so we only need to configure the virtualized machine to use one of the interfaces in mode host-only and connect this interface to vboxnet. If this is your case, you can skip directly to the step corresponding to the figure ‘VirtualBox Settings Network 1’.
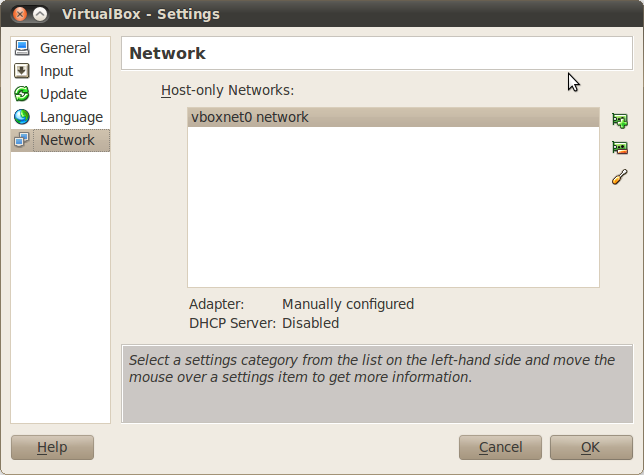
You also need to set up the virtual network. In VirtualBox menu select :menuselection: File –> Preferences, with a window similar to the following figure:
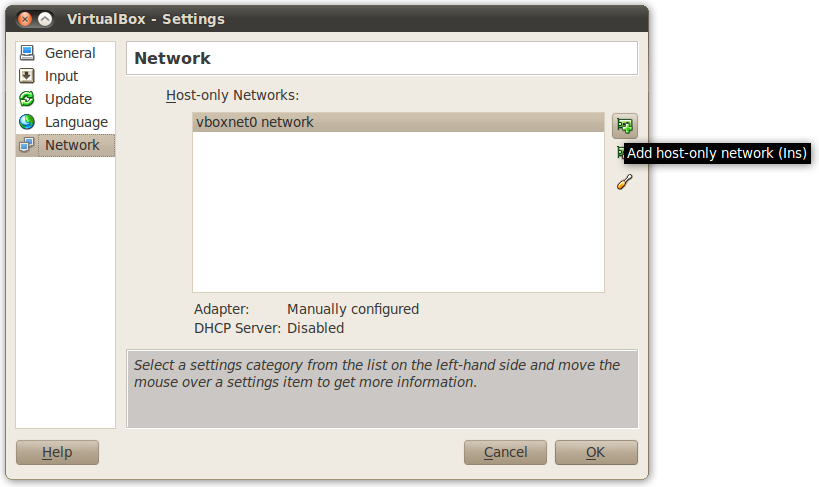
In order to add new networks, click on the Add host-only network button.
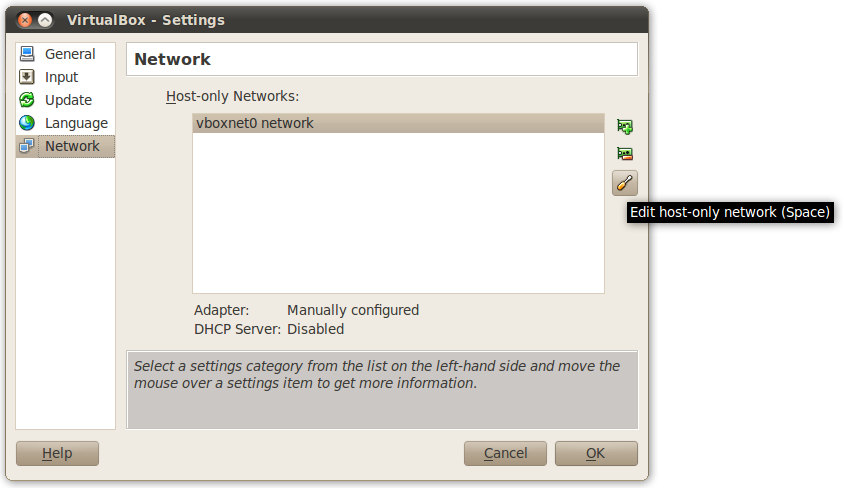
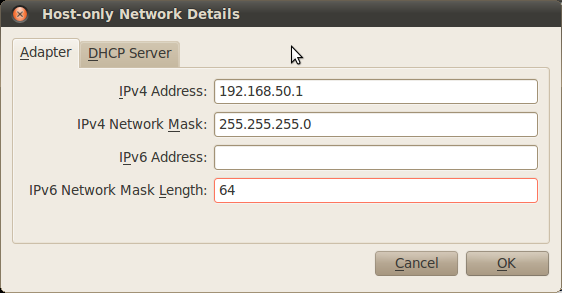
Once you have created the network, just assign a network address within its IP range. In order to configure the network, click on the Edit host-only network button.
You will see a window similar to the following:
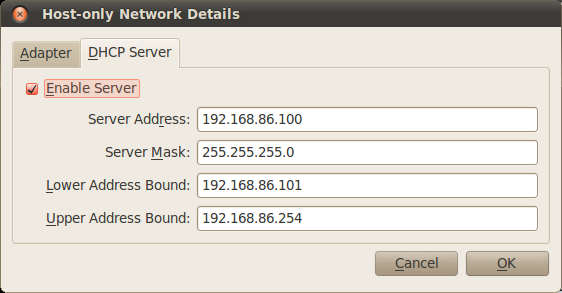
In this window you can set the host machine’s IP and its netmask. If required, you can set up a DHCP server for the host-only network, but in this case this is not necessary.
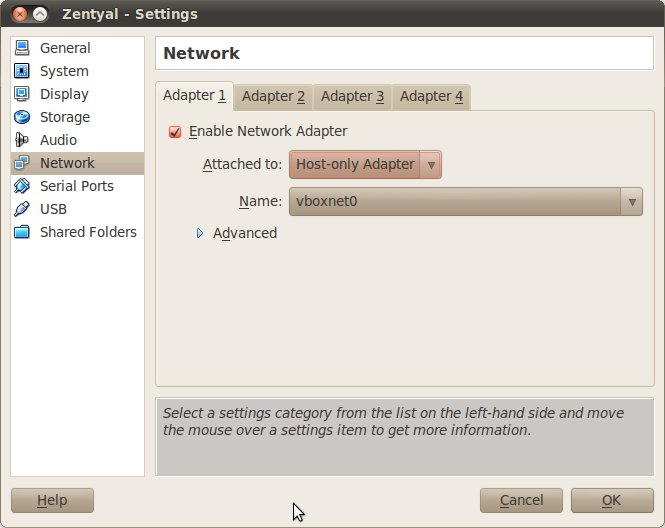
From Settings –> Network on the virtual machine where you intend to install Zentyal, connect the interfaces to vboxnet0.
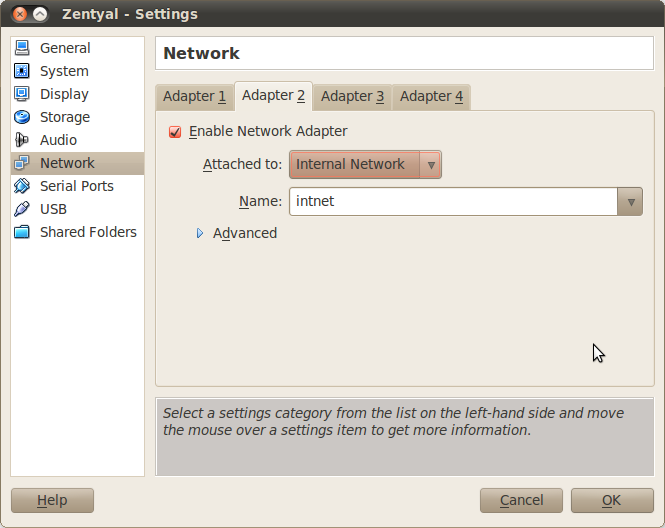
Set the second interface as internal network, as intnet.
Set the third interface as Bridged Adapter, choosing the interface you are effectively using to access Internet on the Host machine. Now you can reboot your Zentyal server and configure its interfaces.
It is recommended to allocate a minimal amount of resources for client machines, particularly concerning RAM memory. This is why, although you can use any operative system for the client machine, we recommend using a specific Linux distribution called grml [1], which is a Debian based Live CD oriented for system administrators. 92 MB of memory should be enough and the network will be automatically configured when booting.
| [1] | grml <http://grml.org/> |
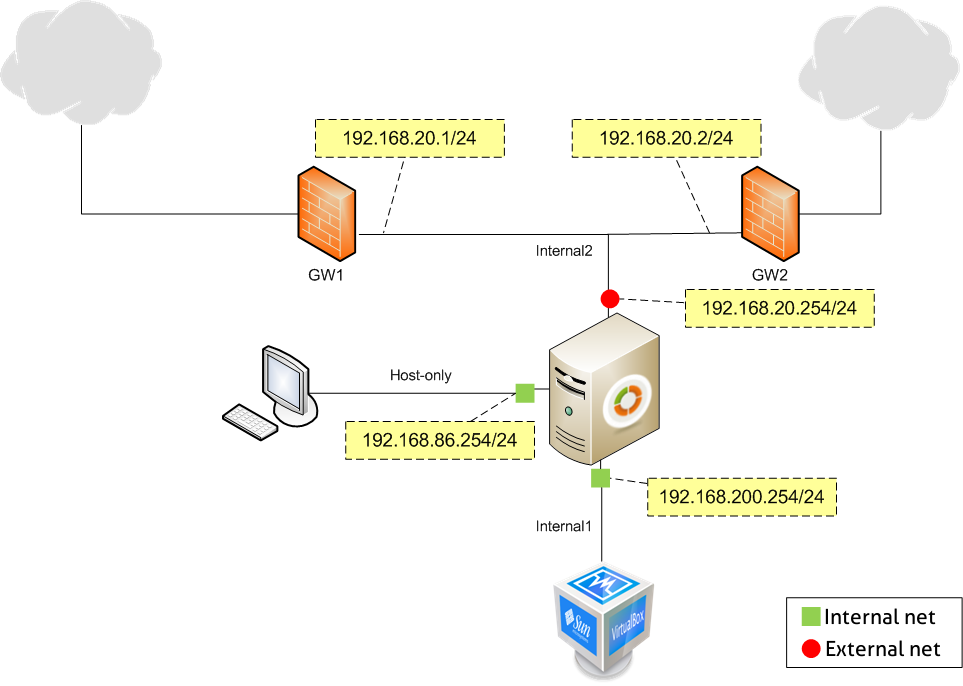
Scenario 2: Virtualized Zentyal server with access from the host and another client with Internet connection through two gateways¶
The following scenario has the two first interfaces exactly the same as in the previous scenario, but now the third one is connected to an external network through two gateways managing the traffic to Internet.
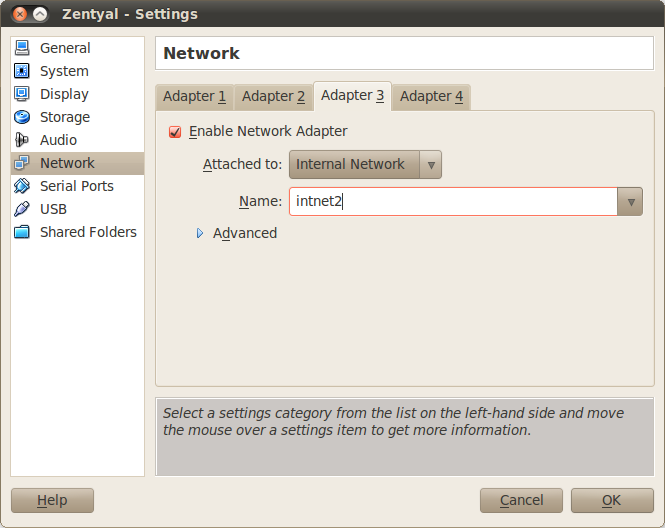
In order to configure that, you need to use an internal network type of connection. As it has to be a different network, you can name it as intnet2 with an IP range 192.168.20.0/24. You need to shutdown the machine before adding this new interface. Similarly as before, go to Settings ‣ Network, in the tab for the third adapter select Internal network and set the name to intnet2.
You should connect the two machines acting as gateways to the same internal network.
Scenario 3: Virtualized Zentyal server with Internet connection and access from the host and two clients¶
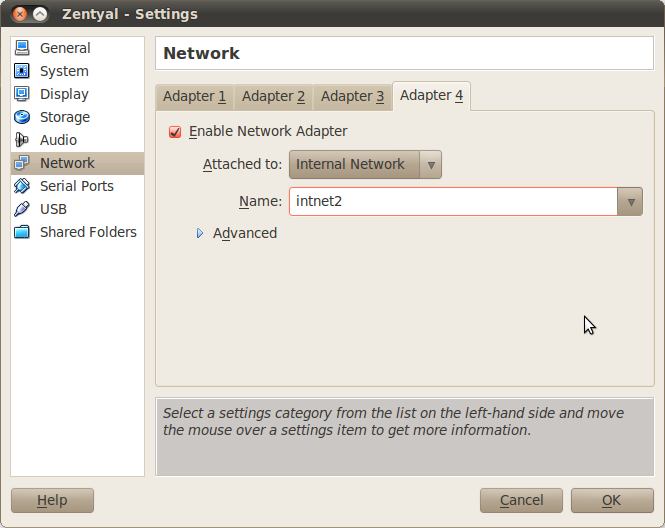
This scenario is similar to the first one but adding another virtual network with the range 192.168.199.0/24.
This interface is internal and you can create it in a similar way as in the previous scenario, but linked to a fourth interface.
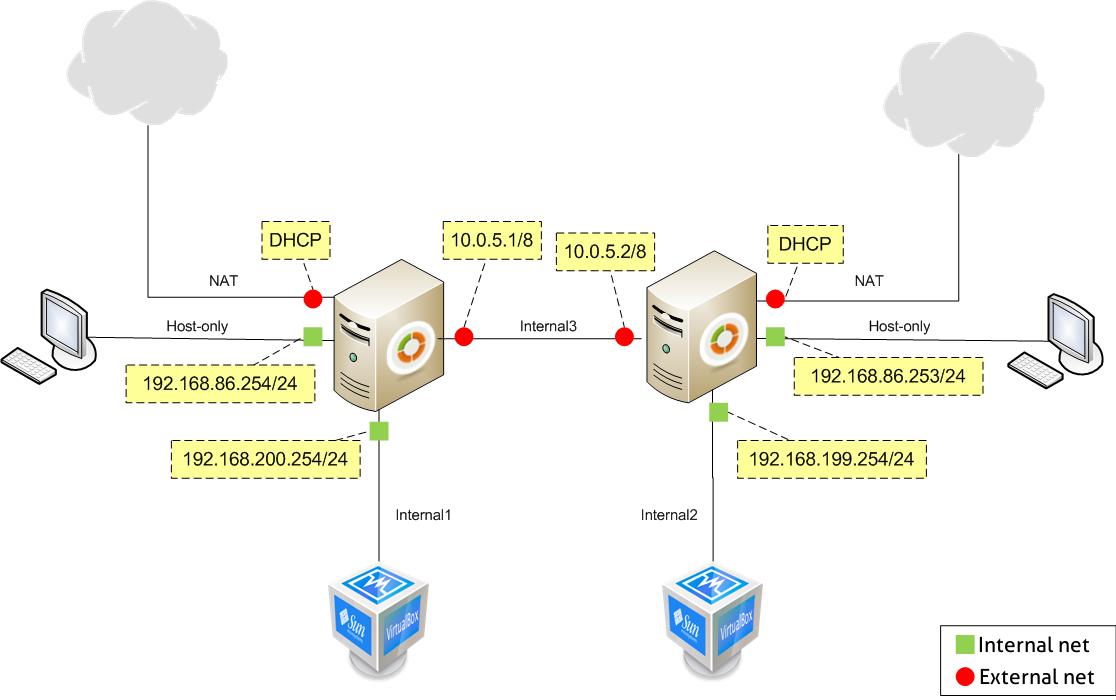
Scenario 4: Virtualized Zentyal server connected to another virtualized Zentyal linking two separate networks¶
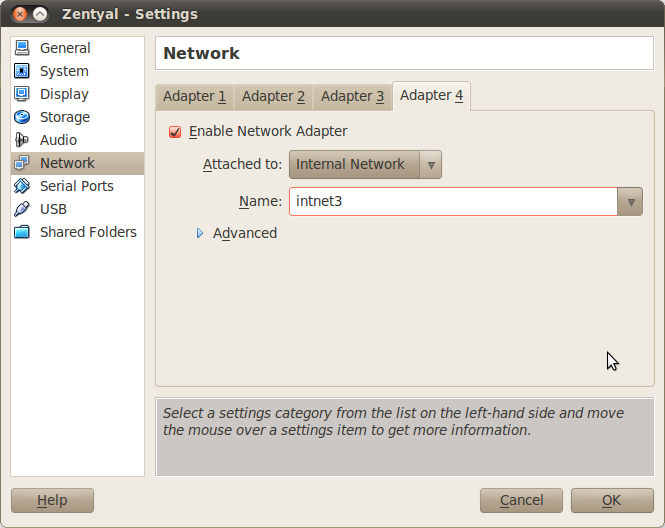
In order to build this scenario, you need to duplicate the first one, and connect them through an internal network connection, intnet3. Take into account in the diagram that you need to create an internal network intnet2 with IP range 192.168.199.0/24, as you cannot use intnet1 to connect that client. Moreover, for the second connection of the host you will need to assign another IP.
Set the fourth interface of each server as belonging to that network.
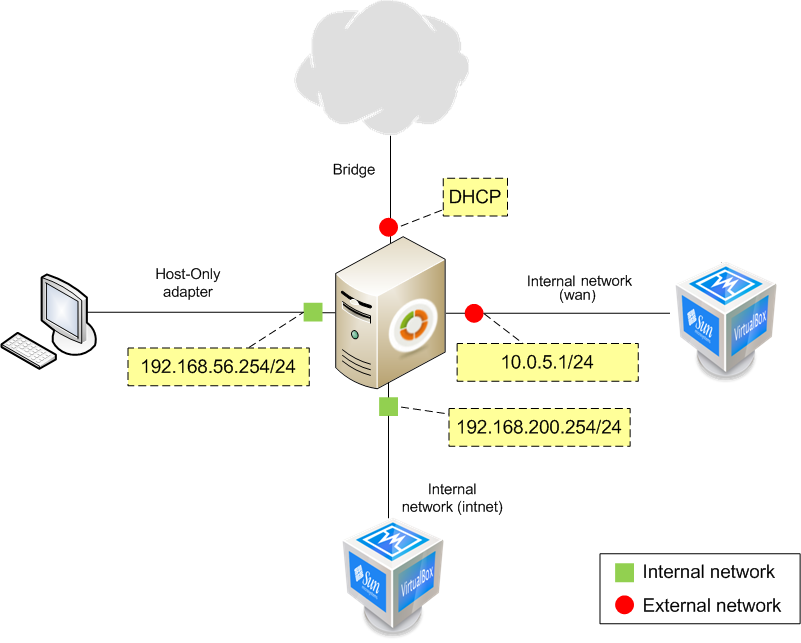
Scenario 5: Virtualized Zentyal server with Internet access, access from the host machine, clients in Internal and External networks¶
This scenario is similar to the first one, but we will add a fourth network interface. In VirtualBox, we will configure it as an ‘Internal Network’, named ‘wan’. In Zentyal, we will configure this new interface as ‘External network’ and then, we will configure it manually with IP and netmask 10.0.5.1/24.
We will add a new virtualized client as well, this client will have a single interface, that we have to configure manually to with IP and netmask 10.0.5.2/24. This way, both the Zentyal and the client should be in the same external network.
Note: Zentyal’s firewall blocks ping requests (ICMP service) from external networks by default.