Geospatial queries
Geospatial coordinates consisting of a latitude and longitude value can be stored either as two separate attributes, or as a single attribute in the form of an array with both numeric values. ArangoDB can index such coordinates for fast geospatial queries.
Locations data
Let us insert some filming locations into a new collection Locations, which you need to create first, then run below AQL query:
LET places = [
{ "name": "Dragonstone", "coordinate": [ 55.167801, -6.815096 ] },
{ "name": "King's Landing", "coordinate": [ 42.639752, 18.110189 ] },
{ "name": "The Red Keep", "coordinate": [ 35.896447, 14.446442 ] },
{ "name": "Yunkai", "coordinate": [ 31.046642, -7.129532 ] },
{ "name": "Astapor", "coordinate": [ 31.50974, -9.774249 ] },
{ "name": "Winterfell", "coordinate": [ 54.368321, -5.581312 ] },
{ "name": "Vaes Dothrak", "coordinate": [ 54.16776, -6.096125 ] },
{ "name": "Beyond the wall", "coordinate": [ 64.265473, -21.094093 ] }
]
FOR place IN places
INSERT place INTO Locations
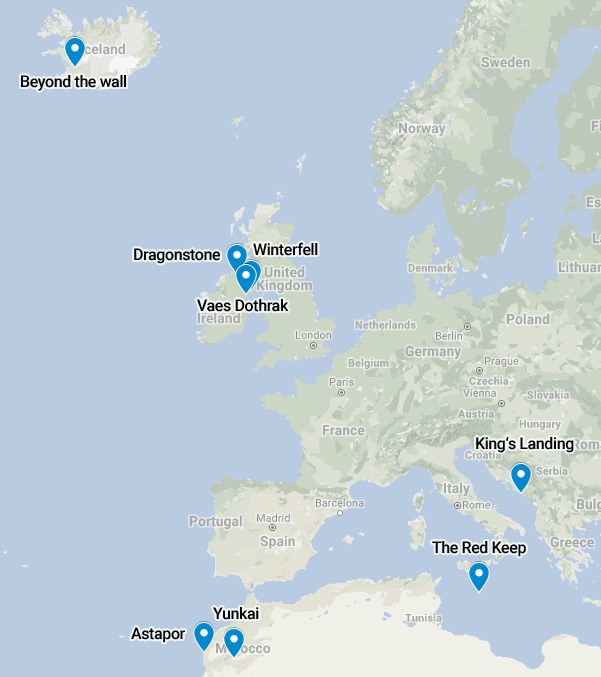
Visualization of the coordinates on a map with their labels:
Geospatial index
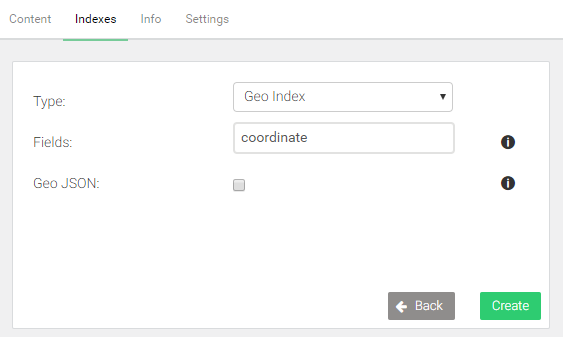
To query based on coordinates, a geo index is required. It determines which fields contain the latitude and longitude values.
- Go to COLLECTIONS
- Click on the Locations collection
- Switch to the Indexes tab at top
- Click the green button with a plus on the right-hand side
- Change the type to Geo Index
- Enter
coordinateinto the Fields field - Click Create to confirm
Find nearby locations
A FOR loop is used again, but this time to iterate over the results of a
function call to NEAR() to find the n closest coordinates to a reference
point, and return the documents with the nearby locations. The default for
n is 100, which means 100 documents are returned at most, the closest
matches first.
In below example, the limit is set to 3. The origin (the reference point) is a coordinate somewhere downtown in Dublin, Ireland:
FOR loc IN NEAR(Locations, 53.35, -6.26, 3)
RETURN {
name: loc.name,
latitude: loc.coordinate[0],
longitude: loc.coordinate[1]
}
[
{
"name": "Vaes Dothrak",
"latitude": 54.16776,
"longitude": -6.096125
},
{
"name": "Winterfell",
"latitude": 54.368321,
"longitude": -5.581312
},
{
"name": "Dragonstone",
"latitude": 55.167801,
"longitude": -6.815096
}
]
The query returns the location name, as well as the coordinate. The coordinate
is returned as two separate attributes. You may use a simpler RETURN loc
instead if you want.
Find locations within radius
NEAR() can be swapped out with WITHIN(), to search for locations within a
given radius from a reference point. The syntax is the same as for NEAR(),
except for the fourth parameter, which specifies the radius instead of a limit.
The unit for the radius is meters. The example uses a radius of 200,000
meters (200 kilometers):
FOR loc IN WITHIN(Locations, 53.35, -6.26, 200 * 1000)
RETURN {
name: loc.name,
latitude: loc.coordinate[0],
longitude: loc.coordinate[1]
}
[
{
"name": "Vaes Dothrak",
"latitude": 54.16776,
"longitude": -6.096125
},
{
"name": "Winterfell",
"latitude": 54.368321,
"longitude": -5.581312
}
]
Return the distance
Both NEAR() and WITHIN() can return the distance to the reference point
by adding an optional fifth parameter. It has to be a string, which will be
used as attribute name for an additional attribute with the distance in meters:
FOR loc IN NEAR(Locations, 53.35, -6.26, 3, "distance")
RETURN {
name: loc.name,
latitude: loc.coordinate[0],
longitude: loc.coordinate[1],
distance: loc.distance / 1000
}
[
{
"name": "Vaes Dothrak",
"latitude": 54.16776,
"longitude": -6.096125,
"distance": 91.56658640314431
},
{
"name": "Winterfell",
"latitude": 54.368321,
"longitude": -5.581312,
"distance": 121.66399816395028
},
{
"name": "Dragonstone",
"latitude": 55.167801,
"longitude": -6.815096,
"distance": 205.31879386198324
}
]
The extra attribute, here called distance, is returned as part of the loc variable, as if it was part of the location document. The value is divided by 1000 in the example query, to convert the unit to kilometers, simply to make it better readable.