Instead of instructing you to modify the settings here and there, I thought it might be better to explain the Yafray light types one by one. This will enable you to make informed decisions.
There are five light types used in Blender and of them only four
are directly supported in Yafray. On enabling Yafray raytracer from the
Render tab, you initially see six lamp types (in the
lamp options window, F5), of which Yafray makes use of
Blender's lamp, area, spot and sun. I will come later to the other two
lamps listed, Hemi and Photons later.
The scene description: The current scene has
two light sources. One is a helper light (Sun,
without shadow and at value .200), which is used to provide
non-directional light to increase the ambience for the scene. The other
is the lamp source (or light source), which is a
placeholder for every light type explained. The lamp positions are
static throughout, and Ray Shadow (shadow casting)
is enabled for all the lamp sources that are being used (see Figure 28.8, “The scene as seen in the Viewport.”).
Note
The suggested uses for the light types defined here are general in the usability approach. They are not to be taken as the absolute word for lighting your scene. The lighting varies depending on the scene and the artists own vision for the scene. For best results experiment with the lights in your scene to find which works best for you.
Important
The mention of render times in the images is rounded off, it is relative and is used just to give the idea of typical render times for same scene by different lights and settings.
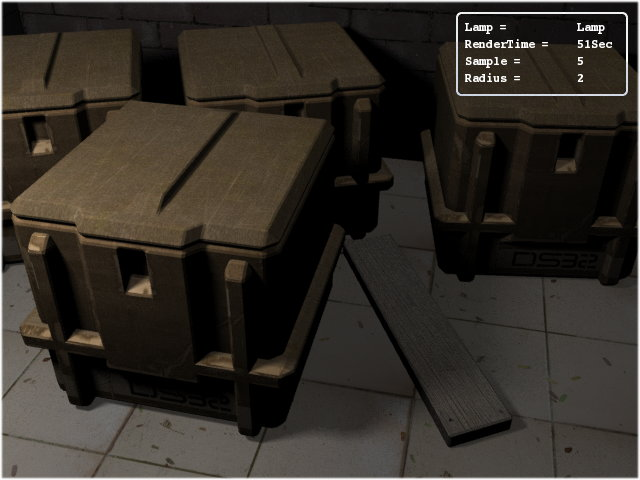
This is the simplest light source available, in some ways it is like sun, as it is omni-directional (i.e. shoots light in all directions from the point of its origin) and is spherical in nature. Since it shoots light rays in every direction, that means the ray going away from the scene will not make any visible changes in the scene, the light rays will be lost and thus are waste of computation. Although Ray tracers use a variety of hacks by cutting off the unwanted computations, it is a bit slower than other directional light sources if bigger parts of the light shot come inside the scene view.
The general use of Lamp is for indoor lighting, like rooms and halls, but it is not limited to this use, it is also more commonly used as filler light or helper light in the scene.
Values: When a single lamp is used for the scene in Yafray (through-out the tutorial when I say Yafray I mean Blender-Yafray), it will generally not provide sufficient lighting to light up the scene unless it is kept at a higher value. For the sample scene, the value of Lamp was set at 10 (maximum) but still there seems to be the need for additional lighting (but we are sticking to it for the sake of understanding). See Figure 28.9, “Rendered with Lamp at default settings.”.
The Lamp will cast sharper shadows at default (zero) radius. The radius setting in Lamp is used to increase the area size for shooting the light. If the size of Lamp is bigger than the objects, then the light shot from some parts of the lamp could directly reach to the parts of the scene where the other part of the lamp casts a shadow. This intersection results in the shadow being diluted for that part, thus getting blurred (also called partial shadows). You can observe this phenomenon in real world (sun light).
LINK: for more info on shadow dilution or Partial shadows go to Ditto head's Light tutorial.
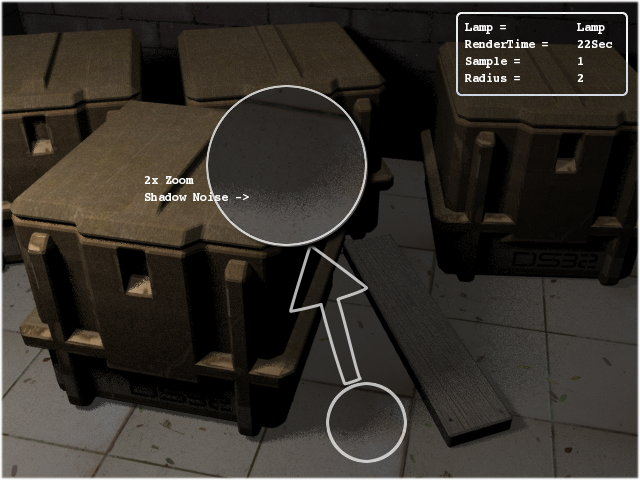
The scene above (Figure 28.10, “The noise
comes when sampling values is low.”) was rendered at radius
2 with a sampling value at 1, as can be seen the scene has grainy
partial shadows. The use of samples button is only to reduce the
grain in shadows, the sampling buttons control the number of
samples used in shadow calculations, increasing the sampling results
in smoother shadows. The sampling button is only available in Lamp
and Area Light and functions the same for both.
The Area Light is a directional source. The
shape of Area Light can be varied from square to rectangular from
the drop down list in the Lamp tab. Below the
shape selection there is also an option to increase the size of the
Area Light.
Values: For Area Lamp you will need lower light intensity values for rendering a scene with Yafray. The sample scene is lit by light value at 4, it is brighter than the one rendered by Lamp at value 10. This is because it is shooting all the light towards a direction from a plane while the Lamp shoots the light in every direction distributing energy where it may not be required.
Figure 28.13. Although the scene looks similar to Figure 28.11, “The increase in sampling to 5 remove the noise.” but is brighter and have better shadows.
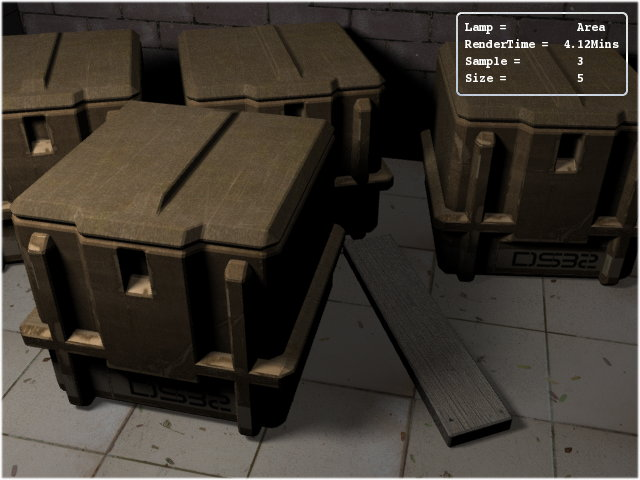

Note
One important point to remember is that in the official Build of Blender 2.34 using two or more Area Lights results in error in the renderings, it is a recognized bug and has been patched in some more recent builds.
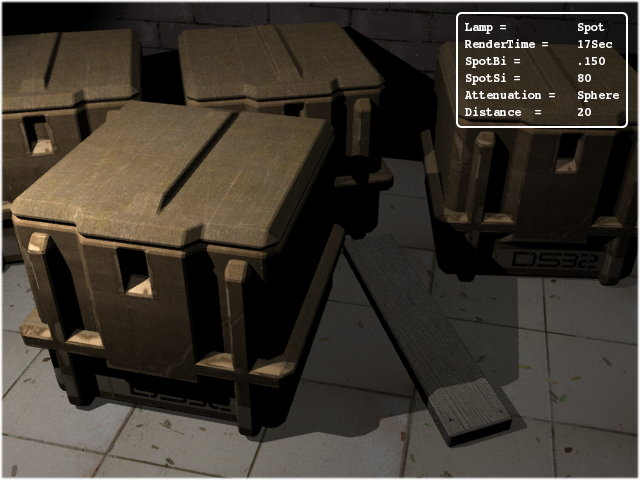
The Spot is also a directional light source
and as the name suggests it provides a circular spot of light or
more appropriately a cone of light. The size of cone can be
controlled by the SpotSi or angle of spotlight
beam. The higher the angle the more nearer it behaves like an area
light, but with one major difference. It cannot cast partial
shadows. Spot light has a parameter to control the
SpotBi or Spot's edge smoothness only. It can be
seen only if the Spot light is inside the scene view, otherwise you
will not notice any difference in Spot or other lights.
Notice the increased brightness at the portion nearer to the
lamp in the Figure 28.15, “Spot lamp
with spherical light attenuation.” while
using the Spherical light attenuation (Quad is not supported in
Yafray). Increase in the distance value the
spherical attenuation also increases in radius, for example the
Figure 28.15, “Spot lamp
with spherical light attenuation.” has a default
distance value of 20 while Figure 28.16, “Spot lamp
with Spherical attenuation enabled.” has the
distance value at 30. The effect looks like that
of typical household lamps where the attenuation is sharper.
Note
The light attenuation in Yafray has only quadratic falloff, while Blender can have linear, cubic and the mix of these also. That explains relatively sharper light intensity falloff in Yafray renders.
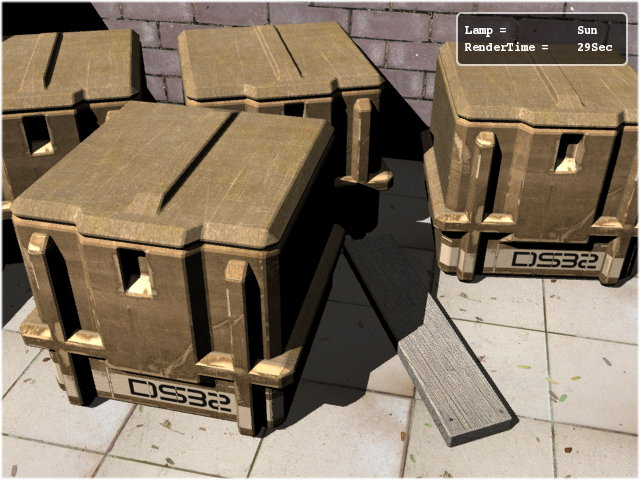
This is also a directional light source. It tries to emulate sunlight by shooting light of the same intensity everywhere in the scene without attenuation (Figure 28.17, “The Sun light at value 2. No wonder why this lamp is called Sun.”). This results in the environment being lit up with constant ambience. Its value must be kept lower. The sample scene uses a light intensity value of .100. It is obviously good for out door lights, especially for a sun.
In outdoor scenes, if you do not want sharper shadows you can disable shadow casting for Sun, and use other lamps for shadow generation. But make sure they have sufficient light intensity to cast a shadow.
Hemi - Yafray does not support Blender's implementation of Hemi light internally; right now it just uses Yafray's implementation of Sun light instead.
Photon - Last of all, the Photon light
source or photons lamp button is not to be
confused with any light source. It does not cast any shadow or
light, it is only used in Caustics* calculations and requires being
placed or directed where you need the caustic calculation. Photon
lamp shoots photons in an area, the photons are used by Yafray as
the specialized ray elements only to calculate the caustics on
passing through the objects like glass or mirrors, which have
the property of bending light when passed through them, known as
total internal reflection. Basically the
placement of Photon lamp is to allow the user to optimize the
rendering. Caustics is one of the most computation intensive jobs in
Ray tracing.
Note
This photon lamp and photons are not to be confused with the photon option in the GI method, which is explained in the the section called “Part 3”.