JSONWriter
Not available in Community Designer

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| JSONWriter Attributes |
| Details |
| Best Practices |
| See also |
Short Description
JSONWriter writes data in the JSON format.
| Component | Data output | Input ports | Output ports | Each to all outputs | Different to different outputs | Transformation | Transf. req. | Java | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSONWriter | JSON file | 1-n | 0-1 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Icon

Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0-N | At least one | Input records to be joined and mapped into the JSON structure. | Any (each port can have different metadata) |
| Output | 0 |  | Optional. For port writing. |
Only one field (byte or cbyte or
string) is used.
The field name is used in File URL
to govern how the output records are processed - see
Writing to Output Port
|
Metadata
JSONWriter does not propagate metadata.
JSONWriter has no metadata template.
JSONWriter Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| File URL | yes | The target file for the output JSON. See Supported File URL Formats for Writers. | |
| Charset |
The encoding of an output file generated by JSONWriter. The default encoding depends on DEFAULT_SOURCE_CODE_CHARSET in defaultProperties. | UTF-8 | <other encodings> | |
| Mapping | [1] | Defines how input data is mapped onto an output JSON. See Details. | |
| Mapping URL | [1] | External text file containing the mapping definition. | |
| Advanced | |||
| Create directories | By default, non-existing directories are not created.
If set to true, they are created.
| false (default) | true | |
| Omit new lines wherever possible |
By default, each element is written to a separate line.
If set to true, new lines are omitted when
writing data to the output JSON structure. Thus, all JSON
elements are on one line only.
| false (default) | true | |
| Cache size | A size of of the database used when caching data from ports to elements (the data is first processed then written). The larger your data is, the larger cache is needed to maintain fast processing. | auto (default) | e.g. 300MB, 1GB etc. | |
| Cache in Memory | Cache data records in memory instead of JDBM's disk cache (default). Note that while it is possible to set maximal size of the cache for the disk cache, this setting is ignored in case in-memory-cache si used. As a result, an OutOfMemoryError may occur when caching too many data records. | false (default) | true | |
| Sorted input | Tells JSONWriter whether the input data is sorted. Setting the attribute to true declares you want to use the sort order defined in Sort keys, see below. | false (default) | true | |
| Sort keys | Tells JSONWriter how the input data is sorted, thus enabling streaming. The sort order of fields can be given for each port in a separate tab. Working with Sort keys has been described in Sort Key. | ||
| Records per file | Maximum number of records that are written to a single file. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files | 1-N | |
| Max number of records | Maximum number of records written to all output files. See Selecting Output Records. | 0-N | |
| Partition key | A key whose values control the distribution of records among multiple output files. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | ||
| Partition lookup table | The ID of a lookup table. The table serves for selecting records which should be written to the output file(s). See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | ||
| Partition file tag | By default, output files are numbered. If this attribute is set to
Key file tag, output files are named
according to the values of Partition key
or Partition output fields. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more
information. | Number file tag (default) | Key file tag | |
| Partition output fields | Fields of Partition lookup table whose values serve for naming output file(s). See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | ||
| Partition unassigned file name | The name of a file that the unassigned records should be written into (if there are any). If it is not given, the data records whose key values are not contained in Partition lookup table are discarded. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | ||
| Create empty files | If set to false,
prevents the component from creating empty output file
when there are no input records. | true (default) | false | |
[1] One of these has to be specified. If both are specified, Mapping URL has a higher priority. | |||
Details
JSONWriter receives data from all connected input ports and converts records to JSON objects based on the mapping you define. Finally, the component writes the resulting tree structure of elements to the output: a JSON file, port or dictionary. JSONWriter can write lists.
Every JSON object can contain other nested JSON objects. Thus, the JSON format resembles XML and similar tree formats.
As a consequence, you map the input records to the output file in a manner which is very close to what you already know from XMLWriter. Mapping editors in both components have similar logic. The very basics of mapping are:
Connect input edges to JSONWriter and edit the component's Mapping attribute. This will open the visual mapping editor:
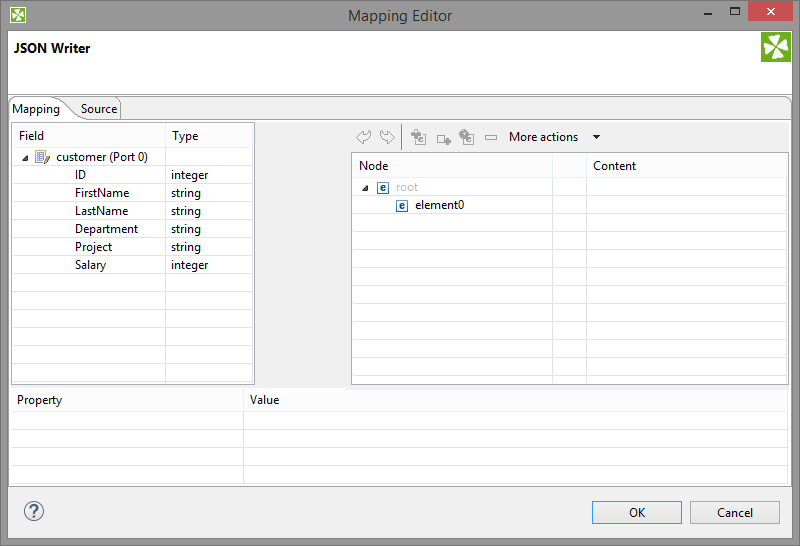
Figure 49.14. Mapping editor in JSONWriter after first open. Metadata on the input edge(s) are displayed on the left hand side. The right hand pane is where you design the desired JSON tree. Mapping is then performed by dragging metadata from left to right (and performing additional tasks described below).
In the right hand pane, design your JSON tree consisting of
![[Important]](figures/important.png)
Important Unlike XMLWriter, you do not map metadata to any 'attributes'.
Arrays - arrays are ordered sets of values in JSON enclosed between the [ and ] brackets. To learn how to map them in JSONWriter, see Example 49.6, “Writing arrays”.
Wildcard elements - another option to mapping elements explicitly. You use the Include and Exclude patterns to generate element names from respective metadata.
Connect input records to output (wildcard) elements to create Binding.
Example 49.5. Creating Binding
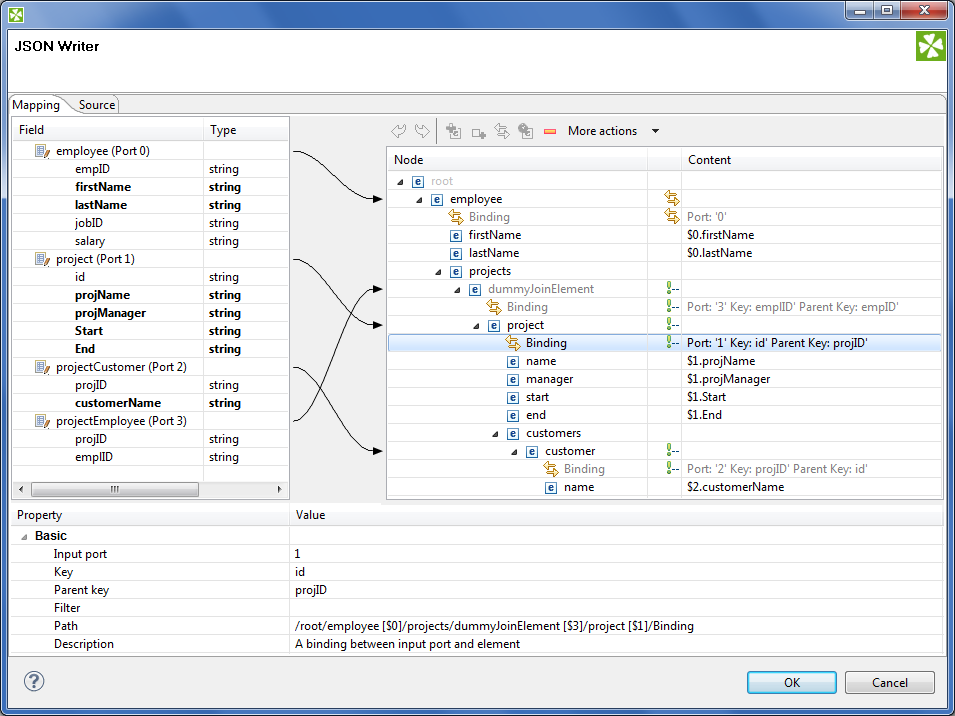
Figure 49.15. Example mapping in JSONWriter - employees are joined with projects they work on. Fields in bold (their content) will be printed to the output file - see below.
Excerpt from the output file related to the figure above (example of one employee written as JSON):
"employee" : { "firstName" : "Jane", "lastName" : "Simson", "projects" : { "project" : { "name" : "JSP", "manager" : "John Smith", "start" : "06062006", "end" : "in progress", "customers" : { "customer" : { "name" : "Sunny" }, "customer" : { "name" : "Weblea" } } }, "project" : { "name" : "OLAP", "manager" : "Raymond Brown", "start" : "11052004", "end" : "31012006", "customers" : { "customer" : { "name" : "Sunny" } } } } },Example 49.6. Writing arrays
Let us have the following mapping of the input file which contains information about actors. For explanatory reasons, we will part actors' personal data from their countries of origin. The summary of all countries will then be written into an array
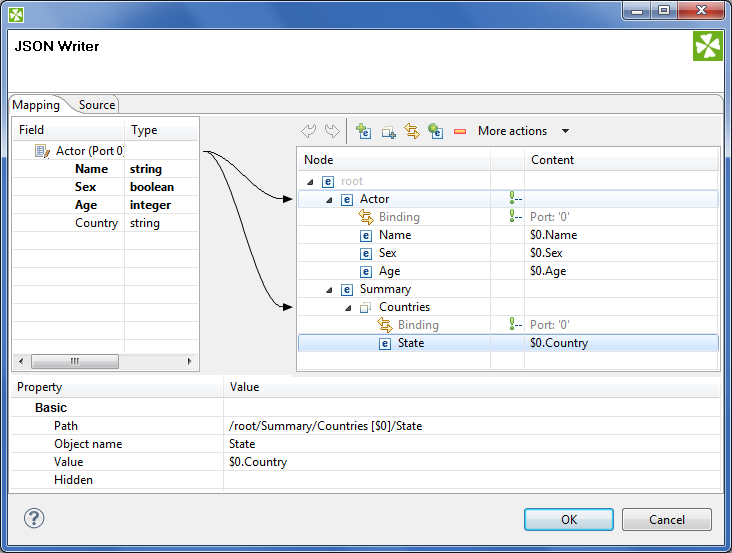
Figure 49.16. Mapping arrays in JSONWriter - notice the array contains a dummy element 'State' which you bind the input field to.
The output JSON:
{ "Actor" : { "Name" : "John Malkovich", "Sex" : true, "Age" : 50 }, "Actor" : { "Name" : "Liz Hurley", "Sex" : false, "Age" : 42 }, "Actor" : { "Name" : "Antonio Banderas", "Sex" : true, "Age" : 33 }, "Summary" : { "Countries" : [ "USA", "ENG", "ESP" ] } }At any time, you can switch to the Source tab and write/check the mapping yourself in code.
If the basic instructions found here were not satisfying, please consult XMLWriter's Details where the whole mapping process is described profusely.
Best Practices
We recommend users to explicitly specify Charset.