AddressDoctor 5
Not available in Community Designer

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| AddressDoctor 5 Attributes |
| Details |
| Troubleshooting |
| See also |
Short Description
AddressDoctor 5 validates, corrects or completes the address format.
AddressDoctor 5 validates, corrects or completes specified address fields using AddressDoctor library and address database. The component filters records and records which are not known how to correct are sent to second (optional) output port.
| Component | Same input metadata | Sorted inputs | Inputs | Outputs | Java | CTL | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AddressDoctor 5 | - |  | 1 | 1-2 |  |  |  |
Icon
Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0 |  | For input data records | Any1 |
| Output | 0 |  | For transformed data records | Any2 |
| Output | 1 |  | For records that could not be transformed (error port) | Any2 |
AddressDoctor 5 Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| Config file | [1] | External file defining the configuration. | |
| Parameter file | [2] | External file defining parameters. | |
| Configuration | [1] | Specifies the address database and its location. | |
| Parameters | [2] | Controls how the transformation is performed. | |
| Input mapping | yes | Determines what will be processed. | |
| Output mapping | yes | Controls what will be mapped to the output. | |
| Element item delimiter | If the whole address is stored on a single line, this attribute specifies which special character separates the address fields. | delimiter is not used (default) | one of these: ; : # | \n \r\n clover_item_delimiter | |
| Advanced | |||
| Number of threads | The number of threads used for address processing. See Multithreading for more information. | 1 (default) | 1-N | |
[1] Either Config file or Configuration must be defined. [2] Define either Parameter file or Parameters. | |||
Details
| Error Port |
| Database Enrichments and File Types |
| Notes and Limitations |
AddressDoctor 5 serves as a GUI for setting parameters of third party AddressDoctor library. It passes the input data and configuration to the library. Then the library does the address validation. Afterwards, the component maps the outputs from the library back to CloverETL.
AddressDoctor 5 depends on external native libraries. These libraries are currently available only for MS windows and Linux. We are reselling the libraries.
If you ever get unsure about working with the component, a good place to look for help is the official AddressDoctor 5 documentation. It contains the necessary information for a detailed configuration of the AddressDoctor 5 component.
![[Note]](figures/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
A spin-off of working with the component is the so-called transliteration. That means you can e.g. input an address in the Cyrillic alphabet and have it converted to the Roman alphabet. No extra database is needed for this task. |
![[Note]](figures/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Address doctor is currently being tested against AddressDoctor5 library 5.2.8.16825. |
Error Port
Mapping of the fields sent to the error port is set up in Output mapping attribute: use the Error output mapping tab. There are two fields ERR_CODE (integer) and ERR_MESSAGE (string) describing the error.
Database Enrichments and File Types
Table 60.2. Database Enrichments and File Types
| File type | Description |
|---|---|
| Batch/Interactive | Most commonly used for basic address parsing and cleansing. |
| FastCompletion | Auto-completion style input which provides suggestions for partial input. |
| Certified | Provided for specific countries only. Implements special logic as dictated by the certification authority for given country. |
| GeoCoding | For geo coding lookups. Three types of geo files exist:
|
| Cameo | Provides additional demographic details in the databases. For example information about the income, number of children, cars, ... for the neighborhood. Available for small set of countries only. Information provided and its precision is very much dependent on the country. |
| Supplementary | Databases required for country-specific enrichments implemented in AD engine. Available for ~10 countries. |
Notes and Limitations
IBM Java
When running on IBM Java (e.g. in WebSphere), make sure to add the following JVM parameter to prevent AddressDoctor from crashing the JVM:
-Xmso2048k
See IBM WebSphere in CloverETL Server Manual.
Using AddressDoctor 5
Tell the graph where AddressDoctor libraries are placed - see AddressDoctor 5 Libraries
Obtain the address database - see AddressDoctor 5 Databases
Set up the component attributes - see AddressDoctor 5 Configuration
AddressDoctor 5 Libraries
To use AddressDoctor 5 component you need to set up external libraries.
The libraries provide address validation functionality.
Two types of libraries are needed: java library (.jar)
and native library (.dll or .so).
The native library performs address validation and the java library
enables to use the functionality of native library.
Download AddressDoctor 5 libraries from http://www.addressdoctor.com/en/support/enterprisedownloadv5.asp.
Unzip the libraries into directory chosen for AddressDoctor, e.g.
C:/AddressDoctoron MS Windows or/opt/AddressDoctoron unix-like systems.![[Note]](figures/note.png)
Note On Microsoft Windows 8 you need to enable Read & Execute access right to the file
lib/AddressDoctor5.dll. Otherwise graph execution fails with the error messageAddressDoctor5.dll: Access is denied.Add libraries to
classpathof CloverETL Runtime. Open → → → and add-Djava.library.path=C:\AddressDoctor\libto virtual machine parameters. Do not forget to restart CloverETL Runtime.
Configuring Libraries with CloverETL Server
When using AddressDoctor with CloverETL Server, paths to the libraries need to be configured
differently. The AddressDoctor5.jar java library needs to be placed on the
classpath of the application server. This is specific for each application server, for example with
Tomcat you need to place it into the lib directory of your Tomcat installation.
Path to the directory with the native library needs to be added to the
java library path via the java.library.path Java property.
This is also application server specific, in Tomcat you can create the bin/setenv.bat
(or bin/setenv.sh) file and add the following line
set "CATALINA_OPTS=%CATALINA_OPTS% -Djava.library.path=path/to/AddressDoctor/library/directory".
Continue with AddressDoctor 5 Configuration
AddressDoctor 5 Databases
Download address database from http://www.addressdoctor.com/en/support/countrydownloadv5.asp.
Unzip the address database into the same directory.
You will get an address database file - the file has suffix .MD.
The database can be configured either using graphical interface or in configuration file. In both cases you need Unlock Code to be able to use the data from databases.
Configuration Dialog (Configuration)
The Configuration dialog enables you to set up database location and Unlock Code using graphical user interface.
Open the attribute Configuration and set up a path to database file on DataBase tab.
Do not forget your database is supplied in one of the modes (e.g. BATCH_INTERACTIVE) and thus you have to set up a matching Type (applies to Enrichment databases set in Parameters, too).
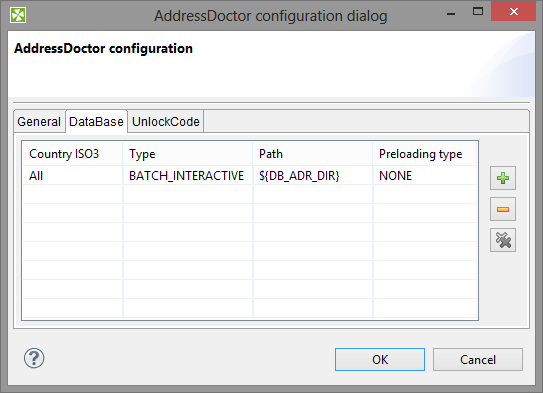
Figure 60.1. DataBase Configuration
To use the database you need to set up Unlock Code on tab UnlockCode.
![[Warning]](figures/warning.png) | Warning |
|---|---|
AddressDoctor engine is shared by all components running in the same JVM. That means that all AddressDoctor components in the same graph should have the same Configuration (or Configuration file). If the configurations differ, AddressDoctor engine will be initialized with the settings from one of the components, but the settings will be used by all of them.
Note that in CloverETL Server environment, the settings are shared between all running graphs.
Therefore it is recommended to set the configuration globally
using the
|
![[Tip]](figures/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
By default, AddressDoctor engine is initialized on demand when a graph with AddressDoctor component is executed and de-initialized when it is not needed. This lowers memory requirements, but introduces re-initialization overhead. Setting the
|
Database Configuration File (Config File)
Database Configuration File enables to set up address database location and Unlock Code.
Create a configuration file a set up Config file attribute to point to the configuration file.
The configuration file contains following lines:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <SetConfig> <General WriteXMLEncoding="UTF-16" WriteXMLBOM="NEVER" MaxMemoryUsageMB="1024" MaxAddressObjectCount="10" MaxThreadCount="1"/> <UnlockCode>Here place your code ...</UnlockCode> <DataBase CountryISO3="ALL" Type="BATCH_INTERACTIVE" Path="C:/AddressDoctor" PreloadingType="NONE"/> </SetConfig>
You should replace text Here place your code ... by your valid Unlock Code.
AddressDoctor 5 Configuration
The address validation process is configured by attributes:
Parameters
Parameters controls what transformation will be performed. Particular settings are highly specific and should be consulted with the official AddressDoctor 5 documentation.
For instance in the Process tab of the dialogue, you can configure various Enrichments. The enrichments allow you to add certificates of the address format. The certificates guarantee that a particular address format matches the official format of a national post office. Note that adding Enrichments usually slows the data processing and can optionally require an additional database.
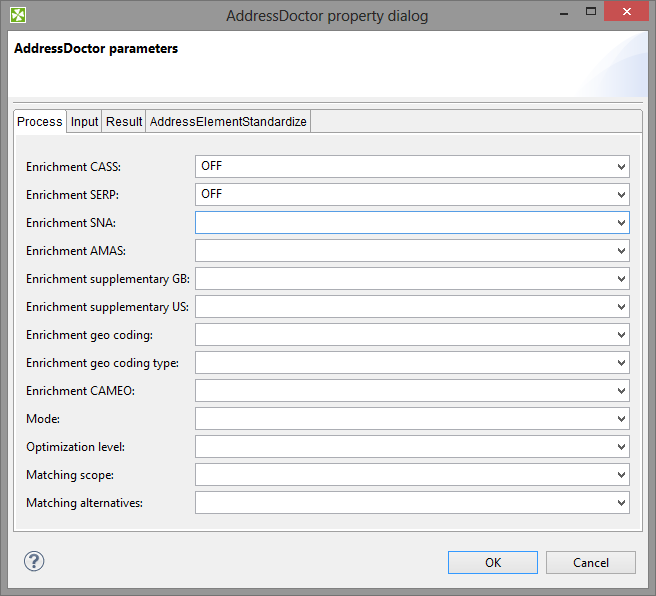 |
Figure 60.2. AddressDoctor Parameters
Input mapping
Input mapping determines what will be processed. You work with a wizard that lets you do the settings in two basic steps:
Select address properties form all AddressDoctor internal fields ("metadata") that are permitted on the input. Field names are accompanied by a number in parentheses informing you how many fields can form a property ("output metadata"). For instance "Street name (6)" tells you the street name can be written on up to 6 rows of the input file.
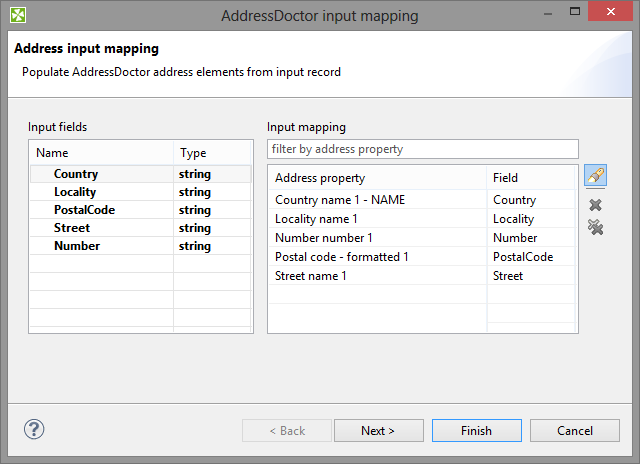
Figure 60.3. Input mapping wizard
Specify the internal mapping of AddressDoctor - drag input fields you have chosen in the previous step on the available fields of the Input mapping.
Examine the summary of the input mapping.
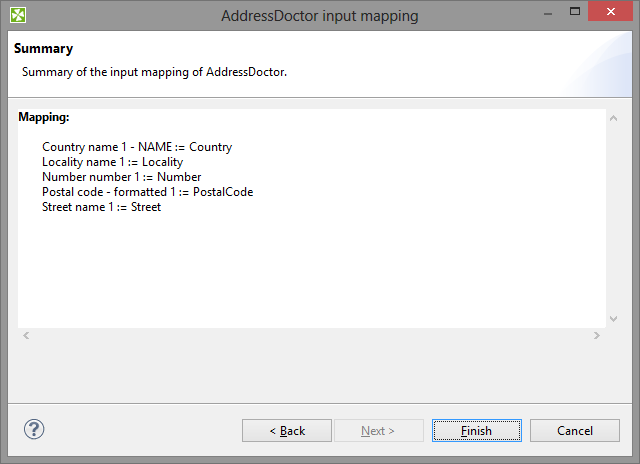
Figure 60.4. Input mapping wizard
Output mapping
Output mapping - here you decide what will be mapped to the output, i.e. the first output port. Optionally, you can map data to the second "error" port (if no such mapping is done, error codes and error messages are generated).
Similarly to Input mapping, you do the configuration by means of a clear wizard comprising these steps:
Select address properties for mapping.
Specify particular output mapping. That involves assigning the internal fields you have selected before to output fields. In the Error port tab, design a structure of the error output (its fields) that is sent to the second output port if the component cannot perform the address transformation.
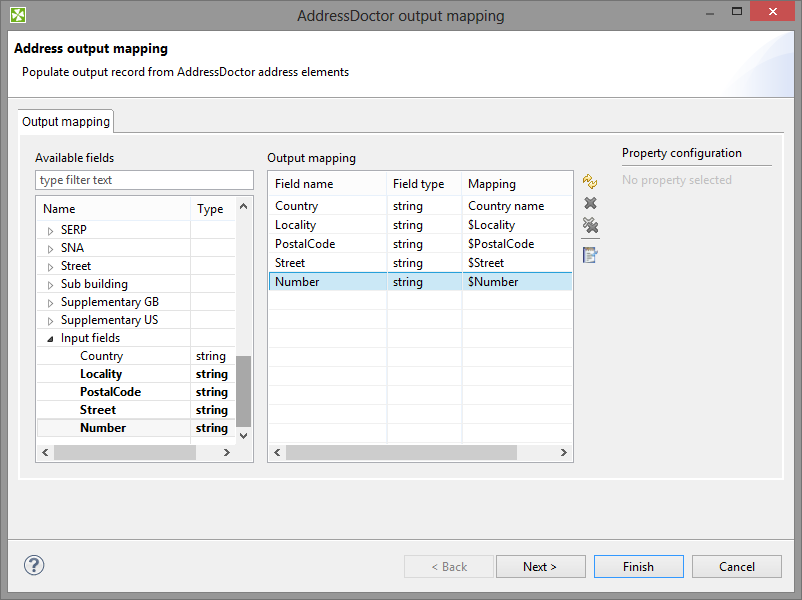
Figure 60.5. Output mapping
Examine the summary of the output mapping.
Multithreading
The Number of threads attribute can be used to increase the throughput of the component by using additional threads for address processing.
Multithreading is also influenced by the Configuration attribute. Max thread count is a total limit on the number of threads concurrently accessing the AddressDoctor library (e.g. from multiple AddressDoctor components). Typically it can be set to the same number as Number of threads attribute if using one AddressDoctor component. Additionally, for each thread requested by Number of threads two address objects will be used (see Max address object count in Configuration).
Multithreading preserves the order of output records.
![[Tip]](figures/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
It is recommended to use full database preloading to prevent the threads from blocking on file system calls. The Max memory usage option should be configured accordingly to accommodate all the used databases and address objects. |
Troubleshooting
If a graph fails with the message
Error: A database file has not been found.Check the path pointing to the database file to be correct.
Check the country of data being processed. You might not have a database for particular country.