LookupJoin
Not available in Community Designer

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| LookupJoin Attributes |
| Details |
| CTL Interface |
| Java Interfaces |
| Examples |
| Best Practices |
| See also |
Short Description
LookupJoin is a general purpose joiner. It merges potentionally unsorted records from one data source incoming through the single input port with another data source from lookup table based on a common key.
| Component | Same input metadata | Sorted inputs | Slave inputs | Outputs | Output for drivers without slave | Output for slaves without driver | Joining based on equality | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LookupJoin |  |  | 1 (virtual) | 1-2 |  |  |  |  |
Icon
Ports
The joined data is then sent to the first output port.
The second output port can optionally be used to capture unmatched master records.
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0 |  | Master input port | Any |
| 1 (virtual) |  | Slave input port | Any | |
| Output | 0 |  | Output port for the joined data | Any |
| 1 |  | Optional output port for master data records without
slave matches. (Only if the Join type
attribute is set to Inner join.) This
applies only to LookupJoin and
DBJoin. | Input 0 |
Metadata
LookupJoin propagates metadata from first input port to second output port and from second output port to first input port. The propagation does not change priority of metadata.
LookupJoin has no metadata template.
Either data source (input port and lookup table) may potentially have different metadata structure.
LookupJoin Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| Join key | yes | Key according to which the incoming data flows are joined. See Join key. | |
| Left outer join | If set to true, also driver records
without corresponding slave are parsed. Otherwise,
inner join is performed. | false (default) | true | |
| Lookup table | yes |
ID of the lookup table to be used as the resource of slave records. Number of lookup key fields and their data types must be the same as those of Join key. These fields values are compared and matched records are joined. | |
| Transform | [1] | Transformation in CTL or Java defined in the graph. | |
| Transform URL | [1] | External file defining the transformation in CTL or Java. | |
| Transform class | [1] | External transformation class. | |
| Transform source charset |
Encoding of external file defining the transformation. The default encoding depends on DEFAULT_SOURCE_CODE_CHARSET in defaultProperties. | E.g. UTF-8 | |
| Advanced | |||
| Clear lookup table after finishing |
When set to Simple lookup table and Range lookup table will contain 0 entries after this operation. For the other lookup table types this will only erase cached data and therefore make more memory available, but the lookup table will still contain the same entries. | false (default) | true | |
| Deprecated | |||
| Error actions | Definition of the action that should be performed when the specified transformation returns some Error code. See Return Values of Transformations. | ||
| Error log | URL of the file to which error messages for specified Error actions should be written. If not set, they are written to Console. | ||
[1] One of these must be set. These transformation attributes
must be specified. Any of these transformation attributes must use a
common CTL template for Joiners or implement a
| |||
Details
LookupJoin is a general purpose joiner used in most common situations. It does not require that the input to be sorted and is very fast as it is processed in memory.
The data attached to the first input port is called the master, the second data source is called the slave. Its data is considered as if it were coming through the second (virtual) input port. Each master record is matched to the slave record on one or more fields known as the join key. The output is produced by applying a transformation which maps joined inputs to the output.
Slave data is pulled out from a lookup table, so depending on the lookup table the data can be stored in the memory. That also depends on the lookup table type - e.g. Database lookup stores only the values which have already been queried. Master data is not stored in the memory.
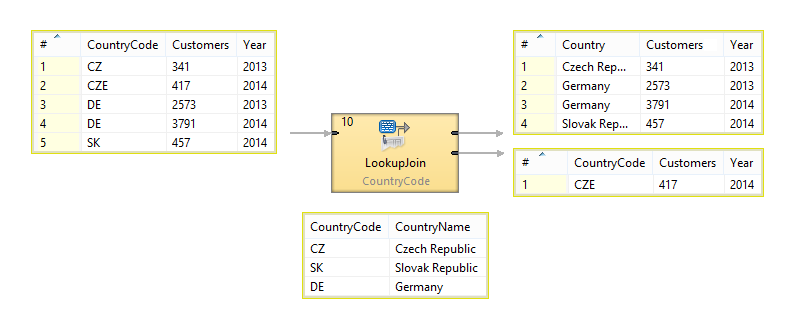 |
Figure 56.5. LookupJoin - how it works
Join key
Join key is a sequence of field names from the input metadata separated by semicolon, colon or pipe. You can define the key in the Edit key wizard.
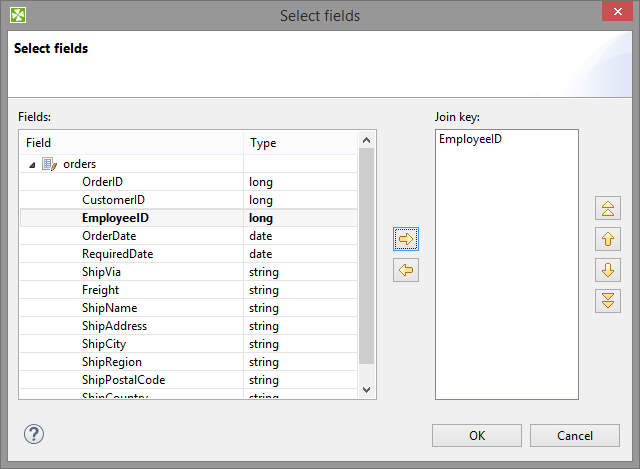 |
Figure 56.6. Edit Key Wizard
A counterpart of this Join key of the input metadata is the key of lookup table in lookup tables. It is specified in the lookup table itself.
Example 56.5. Join Key for LookupJoin
$first_name;$last_name
This is the master part of fields that should serve to join master records with slave records.
Lookup key should look like this:
$fname;$lname
Corresponding fields will be compared and matching values will serve to join master and slave records.
Key Duplicates in Lookup Table
If the lookup table allows key duplicates, more output records can be created from a single input record.
CTL Interface
All Joiners share the same transformation template which can be found in CTL Templates for Joiners.
Java Interfaces
If you define your transformation in Java, it must implement the following interface that is common for all Joiners:
See Public Clover API.
Examples
Enrichment of Records Using Data from Lookup Table
Given a list of number of customers for particular year per country with metadata fields CountryCode, Customers and Year.
CZ |341 |2013 CZE|417 |2014 DE |2573|2013 DE |3791|2014 SK |457 |2014 ...
Replace the country code by country name.
The list of country codes and corresponding country names is available
from lookup table CountryCodeLookup.
CZ |Czech Republic DE |Germany SK |Slovak Republic ...
Solution
Use attributes Join Key, Lookup Table, and Transform.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Join Key | CountryCode |
| Lookup Table | CountryCodeLookup |
| Transform | See the code below. |
function integer transform() {
$out.0.Customers = $in.0.Customers;
$out.0.Country = $in.1.CountryName;
$out.0.Year = $in.0.Year;
return ALL;
}Values found in lookup table are mapped in the same way as if they came from second input port.
The result records are
Czech Republic |341 |2013 Germany |2573|2013 Germany |3791|2014 Slovak Republic|457 |2014
The country code CZE has not been found in the lookup table,
so it has been sent unchanged to the second output port if an edge is connected.
Matching Ranges with Range Lookup Table
This example shows usage of Range Lookup Table table in LookupJoin.
Records on the first data stream contains groups of accounts. Each group of accounts is defined by lowest and highest account numbers, e.g. 12300 and 12399.
Data on the second data stream contains account numbers. Match accounts with groups.
Solution
Load records containing account ranges with LookupTableReaderWriter into Range Lookup Table.
In the next phase, use LookupJoin to match the records from the second data stream.
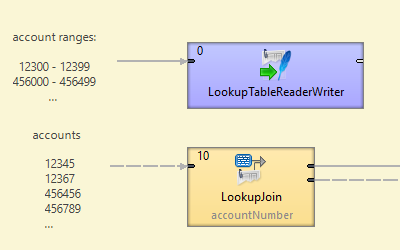 |
Figure 56.7. LookupJoin with Range Lookup Table
In LookupJoin set Join Key, Lookup Table, and Transform.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Join Key | accountNumber |
| Lookup Table | RangeLookupTable0 |
| Transform | Map the fields that are necessary. |
![[Note]](figures/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Matching account into the ranges depends on data type. If the account ranges and account number are specified as a whole number (integer/long), the records are compared as numbers. If the account ranges and account number are specified as a string, the records are compared as strings. If account numbers are integers (or longs) and the range is from 10 to 50, account 200 is out of the range. If account numbers are strings and the range is from 10 to 50, account 200 is within the range. |
Best Practices
If the transformation is specified in an external file (with Transform URL), we recommend users to explicitly specify Transform source charset.