Loop
Not available in Community Designer

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| Loop Attributes |
| Details |
| Examples |
| Compatibility |
| See also |
Short Description
The Loop component allows repeated execution of a group of components or repeated processing of records.
| Component | Same input metadata | Sorted inputs | Inputs | Outputs | Each to all outputs | Java | CTL | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loop |  |  | 2 | 2 |  |  |  |  |
![[Important]](figures/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
It is highly important to manage token flow correctly. For example each token sent to loop body must be navigated back to Loop component. The token cannot be duplicated or cannot disappear. If these strictly rules are not kept, your jobflow processing can easily stuck in a deadlock situation. |
Icon

Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0 |  | Entry point for loop processing. | Any |
| 1 |  | Tokens from loop body must be returned back to Loop component via this port. | Any | |
| Output | 0 |  | Tokens which do not satisfy 'While condition' are sent to this port to end up the looping. | Any |
| 1 |  | Tokens which satisfy 'While condition' are sent to this port to start loop body. | Any |
Metadata
All input and output ports have arbitrary but identical metadata.
Loop Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| While condition | yes |
While this condition is satisfied the iterating token is repeatedly sent to loop body (second output port), otherwise token is sent out of loop (first output port). While condition is CTL2 expression, which is evaluated against two records. First record ($in.0) is the token incoming from one of the input ports (either an loop initialising token or token incoming from loop body).
The second record ($in.1) is artificial input for condition evaluator with just single
field $in.1.iterationNumber, which is automatically populated by number of iteration of current token.
So for example, if the loop should be executed exactly five times,
the condition could look like | CTL expression |
| Advanced | |||
| Logging level | no | Decides on which level token processing information should be logged. | INFO (default) | DEBUG | TRACE | OFF |
Details
The Loop component processes records (or tokens) one by one.
The record enters the Loop component.
Record is checked to fulfil the loop condition. If the condition is not fulfilled, the record is send out to the first output port and the processing continues from step 1 using the next record. If the condition is met, the record is send out to the second output port.
The record is processed by components in "loop body".
The record enters the Loop component through the second input port.
Processing continues from the step 2.
Edge Types
All edges in loop are automatically converted to fast-propagate version. See Types of Edges.
Examples
Repeating Actions in Jobflow - Login
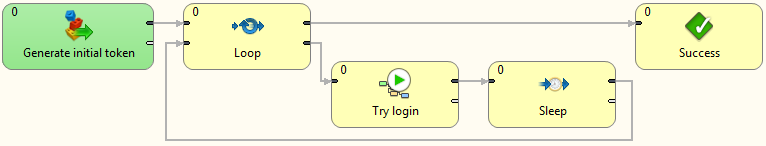
Figure 57.3. Example of Loop component usage
This jobflow simply generate an initial token by DataGenerator component. The loop component applies 'While condition' on this initial token. If the condition is not satisfied, token is sent out of the loop. On the other hand, if the condition is satisfied, token is sent to loop body, where the token is processed by some components. The token must be routed back to the Loop component, where the 'While condition' is evaluated again. The token looping is performed until the condition is not satisfied. Once the token is sent out of loop another initial token is read from first input port.
Compatibility
4.0.0
Since CloverETL 4.0.0 is Loop available also as an ordinary Commercial Component. Up to CloverETL 4-0-0-M2 Loop was available as a Jobflow Component only.