MongoDB Connections
MongoDB connection enables CloverETL to interact with the MongoDB™ NoSQL database [1].
Analogously to other connections in CloverETL, MongoDB connections can be created as both internal and external. See sections Creating Internal Database Connections and Creating External (Shared) Database Connections to learn how to create them. Definition process for MongoDB connections is very similar to other connections, just select Create MongoDB connection instead of Create DB connection.
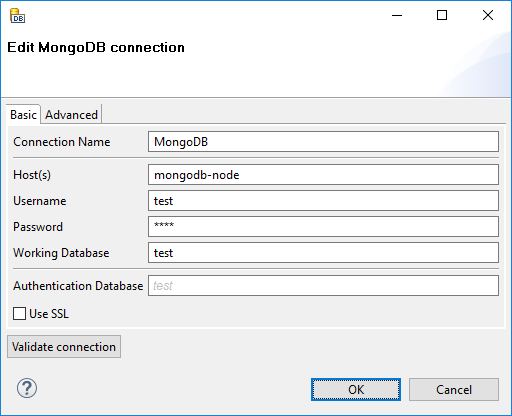
Figure 33.16. MongoDB Connection Dialog
Basic
From the connection properties, Connection Name, Host(s) and Database Instance are mandatory.
- Connection Name
In this field, type in a name you want for this connection. Note that if you are creating a new connection, the connection name you enter here will be used to generate an ID of the connection. Whereas the connection name is just an informational label, the connection ID is used to reference this connection from various graph components. Once the connection is created, the ID cannot be changed using this dialog to avoid accidental breaking of references (if you really want to change the ID of already created connection, you can do so in the Properties view).
- Host(s)
Enter the host name (or IP address) and port number in the form
host[:port]. If the port number is not specified, the default port 27017 will be used.If you need to connect to a replica set or a cluster, enter a comma-separated list of hosts.
- Username
The user name used for authentication.
- Password
The password used for authentication.
- Working Database
The name of the MongoDB database to connect to. The database is also used for authentication by default, this can be changed with the Authentication Database property (see below).
- Authentication Database
The database used for authentication. If not filled in, the working database is used as an authentication database.
- Use SSL
Enables SSL encryption
- Disable certificate validation
Disables the validations of certificates. Usefull with self-signed certificates.
Advanced
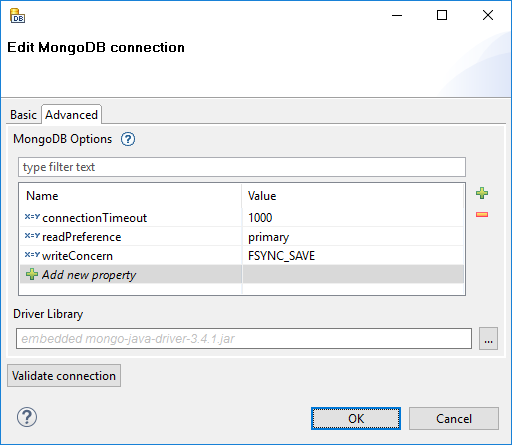
Figure 33.17. MongoDB Connection Dialog - Advanced Tab
- MongoDB Options
This table allows you to fine-tune some MongoDB parameters. Usually, leaving it empty is just fine.
The list of available options depends on the version of the driver library used.
See com.mongodb.MongoClientOptions.Builder if you use driver version 2.10.0 or newer. The options have the same names as the setter methods of the class.
For older driver versions, see com.mongodb.MongoOptions of the respective version. The options have the same names as the fields of the class.
![[Note]](figures/note.png)
Note Only the following types of options are supported:
- primitive data types, including
String -
ReadPreferencewith the valuesprimary,primaryPreferred,secondary,secondaryPreferredandnearest -
WriteConcernconstants, e.g. "writeConcern=JOURNAL_SAFE"
- primitive data types, including
- Driver Library
Optional. By default, an embedded driver will be used for the connection.
Usually, you don't need to provide a custom driver library, because the Java driver versions should be backwards compatible.
The paths to the driver library can be absolute or project relative. Graph parameters can be used as well.
Note that even though the connector tries to maximize backward compatibility, using an outdated version of the driver library may lead to
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundErrororjava.lang.NoSuchMethodErrorbeing thrown.The connection has primarily been tested with the embedded driver version 2.11.0, it should work with newer driver versions as well. It has also been successfully tested with prior driver versions up to 2.3, but the functionality may be limited.
![[Tip]](figures/tip.png)
Usage on the CloverETL Server If you do define the library paths, note that absolute paths are absolute paths on the application server. Relative paths are sandbox (project) relative and will work only if the library is located in a shared sandbox.
Once you've finished setting up your MongoDB connection, click the button to verify that the parameters you entered can be used to successfully establish a connection. Note that connection validation is unfortunately not available if the driver library is located in (remote) CloverETL Server sandbox.