StructuredDataWriter
Not available in Community Designer

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| StructuredDataWriter Attributes |
| Details |
| Examples |
| Best Practices |
| Troubleshooting |
| See also |
Short Description
StructuredDataWriter writes data to files (local or remote, delimited, fixed-length, or mixed) with user-defined structure. It can also compress output files and write to output port, or dictionary.
| Component | Data output | Input ports | Output ports | Transformation | Transf. required | Java | CTL | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StructuredDataWriter | structured flat file | 1-3 | 0-1 |  |  |  |  |  |
Icon

Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0 |  | Records for body | Any |
| 1 |  | Records for header | Any | |
| 2 |  | Records for footer | Any | |
| Output | 0 |  | For port writing. See Writing to Output Port. | One field (byte,
cbyte, string).
|
Metadata
StructuredDataWriter does not propagate metadata.
StructuredDataWriter has no metadata templates.
Metadata on output port has one field (byte, cbyte or string).
StructuredDataWriter Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| File URL | yes | Attribute specifying where received data will be written (flat file, output port, dictionary). See Supported File URL Formats for Writers. | |
| Charset | Encoding of records written to the output. | UTF-8 (default) | <other encodings> | |
| Append |
By default, new records overwrite the older ones.
If set to true, new records are appended to
the older records stored in the output file(s).
| false (default) | true | |
| Body mask | Mask used to write the body of the output file(s). It can be based on the records received through the first input port. See Masks and Output File Structure for more information about definition of Body mask and resulting output structure. | Default Body Structure (default) | user-defined | |
| Header mask | [1] | Mask used to write the header of the output file(s). It can be based on the records received through the second input port. See Masks and Output File Structure for more information about definition of Header mask and resulting output structure. | empty (default) | user-defined |
| Footer mask | [2] | Mask used to write the footer of the output file(s). It can be based on the records received through the third input port. See Masks and Output File Structure for more information about definition of Footer mask and resulting output structure. | empty (default) | user-defined |
| Advanced | |||
| Create directories | By default, non-existing directories are not created.
If set to true, they are created. | false (default) | true | |
| Records per file | Maximum number of records to be written to one output file. | 1-N | |
| Bytes per file | Maximum size of one output file in bytes. | 1-N | |
| Number of skipped records | Number of records to be skipped. See Selecting Output Records. | 0-N | |
| Max number of records | Maximum number of records to be written to all output files. See Selecting Output Records. | 0-N | |
| Partition key | Key whose values define the distribution of records among multiple output files. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | ||
| Partition lookup table | [1] | ID of lookup table serving for selecting records that should be written to output file(s). See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | |
| Partition file tag | By default, output files are numbered.
If it is set to Key file tag, output files are named
according to the values of Partition key
or Partition output fields.
See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files
for more information. | Number file tag (default) | Key file tag | |
| Partition output fields | [1] | Fields of Partition lookup table whose values serve to name output file(s). See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | |
| Partition unassigned file name | Name of the file into which the unassigned records should be written if there are any. If not specified, data records whose key values are not contained in Partition lookup table are discarded. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | ||
| Sorted input | In case of partitioning into multiple output files is turned on, all output files are open at once. Which could lead to undesirable memory footprint for many output files (thousands). Moreover, for example unix-based OS usually have very strict limitation of number of simultaneously open files (1024) per process. In case you run into one of these limitations, consider to sort the data according partition key using one of our standard sorting components and set this attribute to true. The partitioning algorithm does not need to keep open all output files, just the last one is open at one time. See Partitioning Output into Different Output Files for more information. | false (default) | true | |
| Create empty files | If set to false,
prevents the component from creating empty output file
when there are no input records.
| true (default) | false | |
[1] Must be specified if second input port is connected. However, does not need to be based on input data records. [2] Must be specified if third input port is connected. However, does not need to be based on input data records. | |||
Details
Masks and Output File Structure
Output File Structure
Output file consists of header, body, and footer, in this order.
Each of them is defined by specifying corresponding mask.
Having defined the mask, the mask content is written repeatedly, one mask is written for each incoming record.
If the Records per file attribute is defined, the output structure is distributed among various output files, but this attribute applies for Body mask only. Header and footer are the same for all output files.
Defining a Mask
Body mask, Header mask, and Footer mask can be defined in the Mask dialog. This dialog opens after clicking corresponding attribute row. In its window, you can see the Metadata and Mask panes.
You can define the mask either without field values or with field values.
Field values are referred using field names preceded by dollar sign.
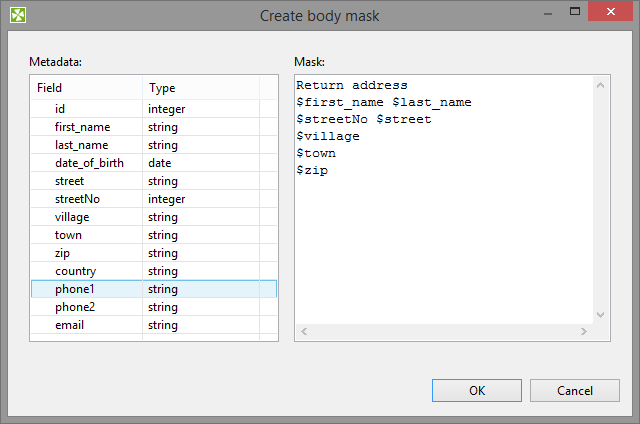 |
Figure 54.26. Create Mask Dialog
You do not have to map all input metadata fields.
Output can contain additional text not coming from input metadata.
E.g. Return address on figure above.
You can use StructuredDataWriter to generate XML files or to fill in the template.
Default Masks
Default Header mask is empty. But it must be defined if second input port is connected.
Default Footer mask is empty. But it must be defined if third input port is connected.
Default Body mask is empty. However, the resulting default body structure looks like the following:
<recordName> <field1name>field1value</field1name> <field2name>field2value</field2name> ... <fieldNname>fieldNvalue</fieldNname> </recordName>
This structure is written to the output file(s) for all records.
If Records per file is set, only the specified number of records are used for body in each output file at most.
Notes and Limitatinos
StructuredDataWriter cannot write lists and maps.
Examples
Writing Page with Header and Footer
Legacy application requires data in the following file structure: header, up to five data records and blank line. Convert data to format accepted by the legacy application:
F0512#4d6f6465726e20616e642070756e6368206361726420636f6d70617469626c65 Francis Smith 77 Jonathan Brown 5 Kate Wood 75 John Black 3 Elisabeth Doe 87
Solution
Connect an edge providing particular records to the first input port of StructuredDataWriter (metadata field body) and edge providing header to the second input port (metadata field header).
Edit the attributes:
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| File URL | ${DATOUT_DIR}/file_$$.txt |
| Body mask | $body |
| Header mask | $header |
| Footer mask | |
| Records per file | 5 |
Adjust line break in Body mask, Header mask and Footer mask attributes according to the input records.
If input records have line break, do not add line break after the string $body and $header.
If input records do not have line break, add line break after $body and $header;
fill in the line break to the attribute Footer mask too.
Best Practices
To write record with fixed-length metadata use FlatFileWriter to convert several fixed-length metadata fields into one field. Subsequently write the output from FlatFileWriter using StructuredDataWriter.
We recommend users to explicitly specify Charset.
Troubleshooting
If you partition data unsorted data into many output files, you may reach the limit of simultaneously opened files. This can you avoid by sorting the input and using attribute sorted input.