Rack Awareness
The Rack Awareness feature permits logical groupings of servers on a cluster where each server group physically belongs to a rack or Availability Zone.
Rack Awareness provides the ability to specify that active and corresponding replica partitions be created on servers that are part of a separate rack or zone. To use and enable Rack Awareness, all servers in a cluster must be upgraded to Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition and minimally, version 2.5. By design, Couchbase Server evenly distributes data of active and replica vBuckets across the cluster for cluster performance and redundancy purposes. With Rack Awareness, server partitions are laid out so the replica partitions for servers in one server group are distributed in servers for a second group and vice versa. If one of the servers becomes unavailable or if an entire rack goes down, data is retained since the replicas are available on the second server group.
Replica vBuckets are evenly distributed from one server group to another server group to provide redundancy and data availability. The rebalance operation also evenly distributes the replica vBuckets from one server group to another server group across the cluster. If an imbalance occurs where there is an unequal number of servers in one server group, the rebalance operation performs a "best effort" of evenly distributing the replica vBuckets across the cluster.
Distribution of vBuckets and replica vBuckets
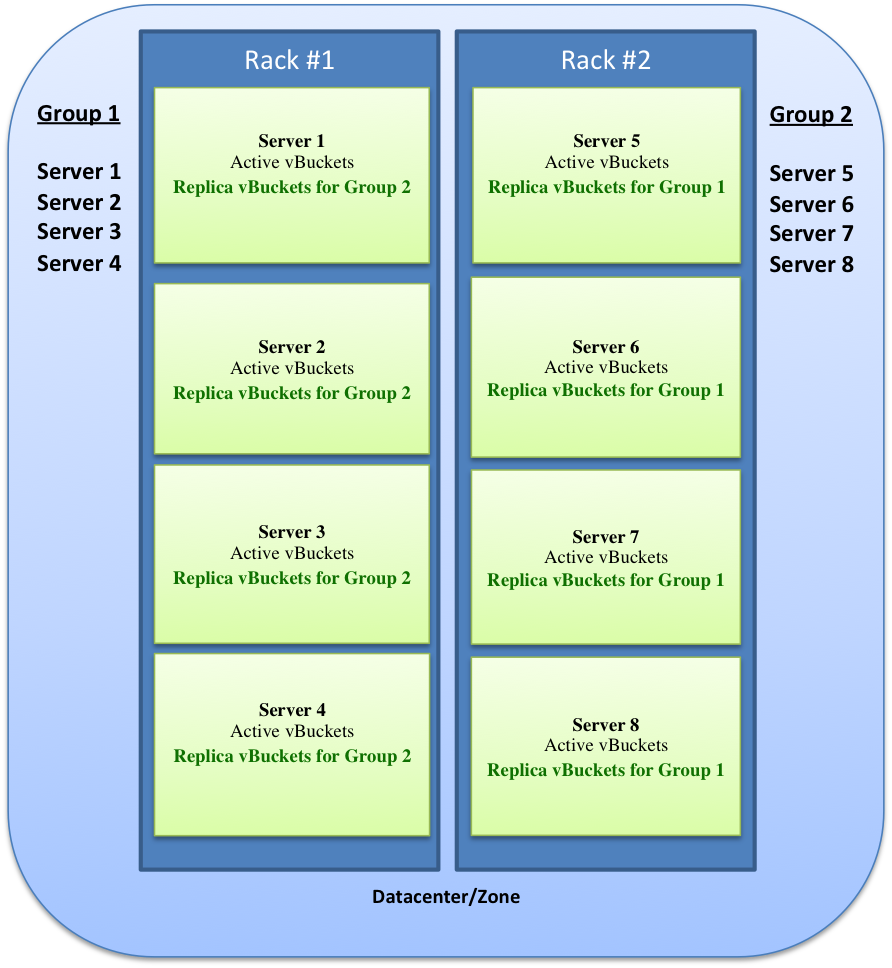
The following example shows how Rack Awareness functionality implements replica vBuckets to provide redundancy. In this example, there are two (2) server groups in the cluster and four (4) servers in each server group. Since there is equal number of servers in each server group, the cluster is balanced which guarantees that replica vBuckets for one server group are on a different server group.
The following diagram shows a cluster of servers on two racks, Rack #1 and Rack #2, where each rack has a group of four (4) servers.
- Group 1 has Servers 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- Group 1 servers have their active vBuckets and replica vBuckets from Group 2.
- Group 2 has Servers 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- Group 2 servers have their active vBuckets and replica vBuckets from Group 1.
Distribution with additional server
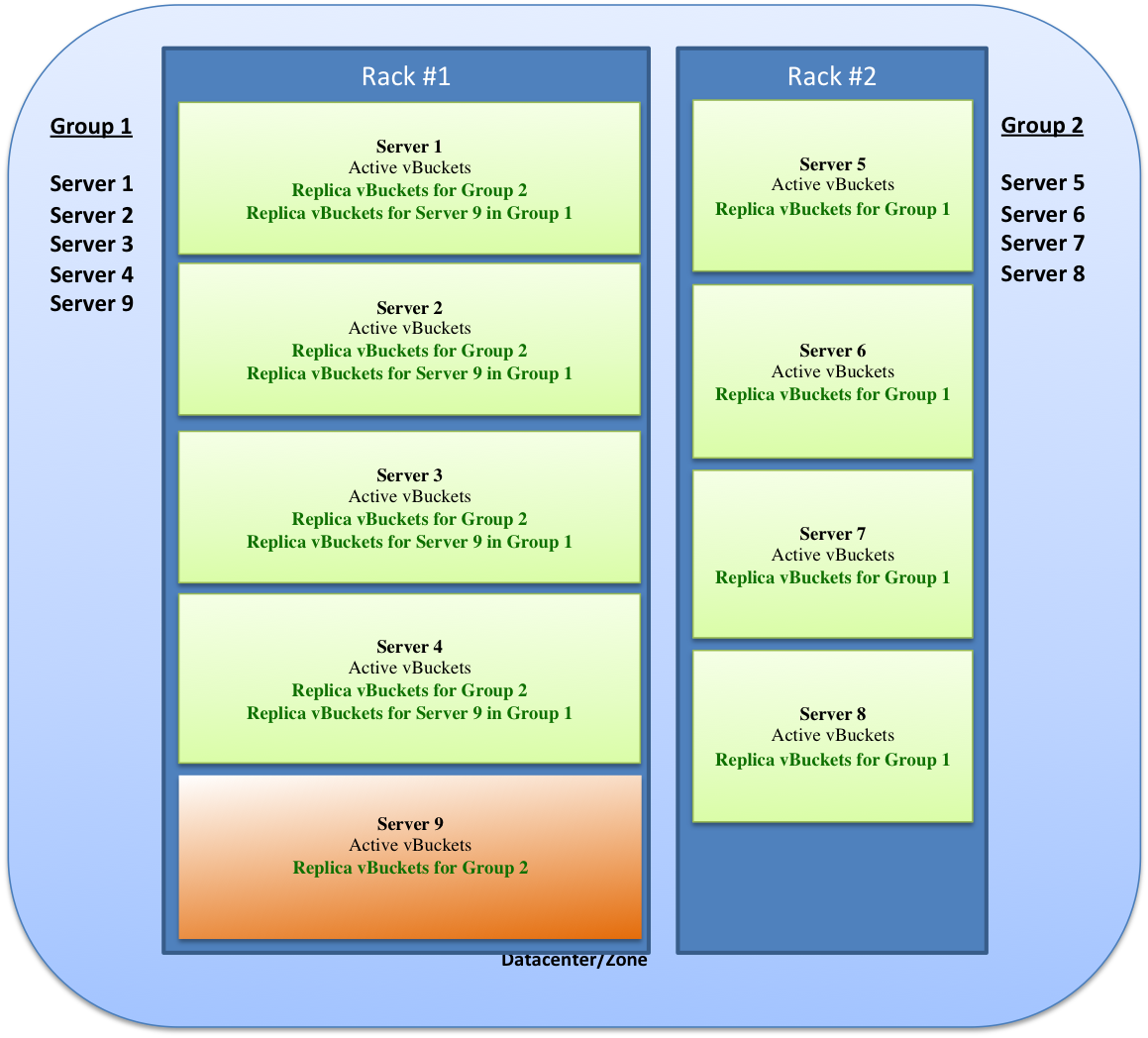
The following scenario shows how Rack Awareness functionality implements replica vBuckets when an imbalance is caused by an additional server being added to one server group. In this example, an additional server (Server 9) is added to a server group (Group 1). An imbalance occurs because one server group has more servers than the other server group. In this case, the rebalance operation performs a "best effort" of evenly distributing the replica vBuckets of the additional server across the nodes on all the racks in the cluster.
The following diagram shows a cluster of servers on two racks, Rack #1 and Rack #2, where one rack has a group of five (5) servers and the other rack has a group of four (4) servers.
- Group 1 has Servers 1, 2, 3, 4, and 9.
- Group 1 servers have their active vBuckets and replica vBuckets from Group 2.
- Group 1 Servers 1 - 4 also has replica vBuckets for Server 9.
- Group 2 has Servers 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- Group 2 servers have their active vBuckets and replica vBuckets from Group 1 including the replica vBuckets from Server 9 in Group 1.
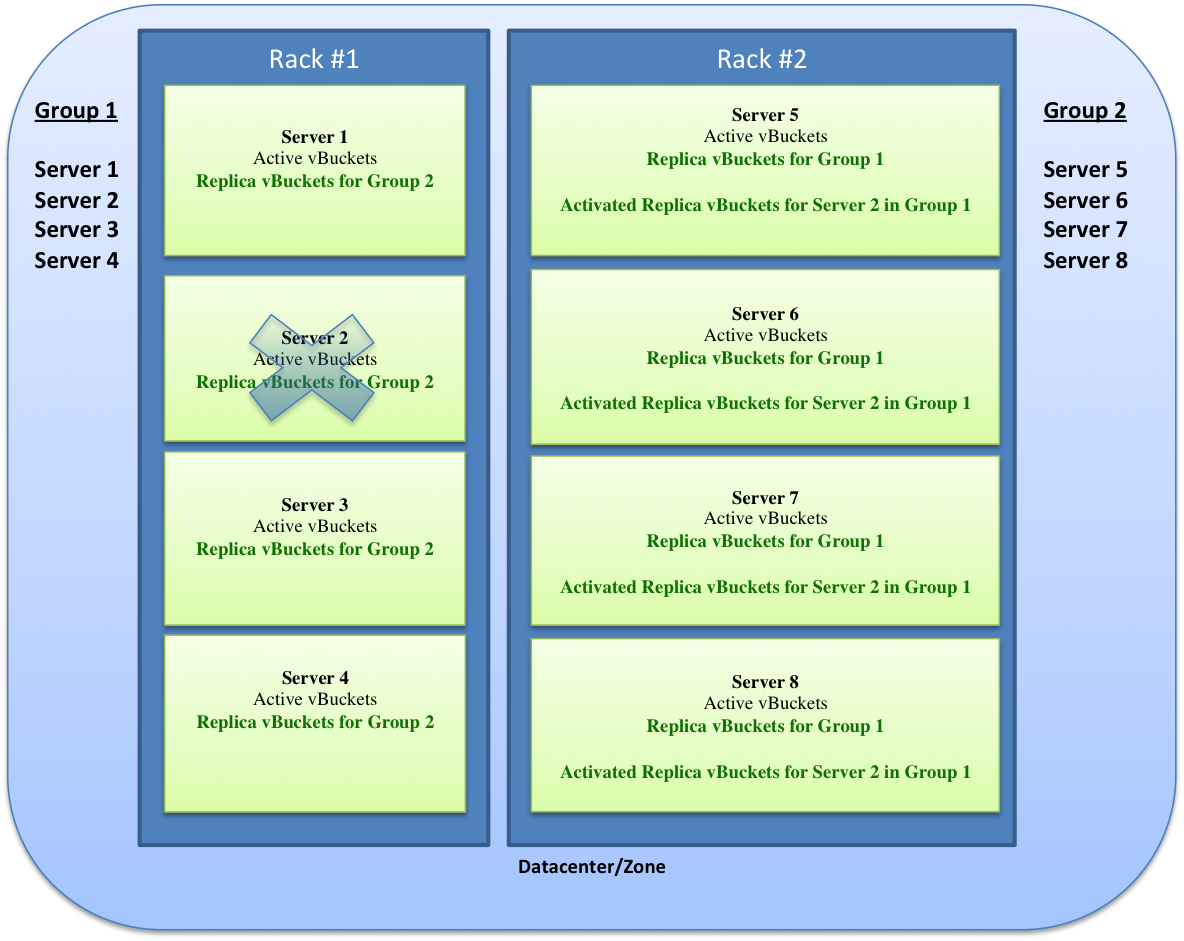
Distribution with unavailable server
The following scenario shows how Rack Awareness functionality implements replica vBuckets when an imbalance is caused by a server being removed or unavailable in a server group. In this example, a server (Server 2) is unavailable to a server group (Group 1). An imbalance occurs because one server group has fewer servers than the other server group. In this case, if the rebalance operation is performed, a "best effort" of evenly distributing the replica vBuckets across the cluster occurs.
The following diagram shows the loss of a server resulting in an imbalance. In this case, Server 2 (from Group 1, Rack #1) becomes unavailable. The replica vBuckets for Server 2 in Group 2, Rack #2 become enabled and rebalancing occurs.
- Group 1 has Servers 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- Group 1 servers have their active vBuckets and replica vBuckets from Group 2.
- Group 1 Server 2 becomes unavailable.
- Group 2 has Servers 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- Group 2 servers have their active vBuckets and replica vBuckets from Group 1.
- Group 2 server activates the replica vBuckets for Server 2 in Group 1.