XDCR basic topologies
XDCR can be configured to support a variety of different topologies; the most common are unidirectional and bidirectional.
Unidirectional Replication is one-way replication, where active data gets replicated from the source cluster to the destination cluster. You may use unidirectional replication when you want to create an active offsite backup, replicating data from one cluster to a backup cluster.
Bidirectional Replication enables two clusters to replicate data with each other. Setting up bidirectional replication in Couchbase Server involves setting up two unidirectional replication links from one cluster to the other. This is useful when you want to load balance your workload across two clusters where each cluster bidirectionally replicates data to the other cluster.
In both topologies, data changes on the source cluster are replicated to the destination cluster only after they are persisted to disk. You can also have more than two datacenters and replicate data between all of them.
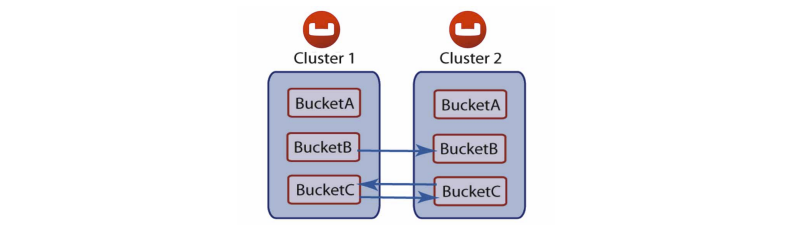
XDCR can be setup on a per bucket basis. A bucket is a logical container for documents in Couchbase Server. Depending on your application requirements, you might want to replicate only a subset of the data in Couchbase Server between two clusters. With XDCR you can selectively pick which buckets to replicate between two clusters in a unidirectional or bidirectional fashion. As shown in Figure 3, there is no XDCR between Bucket A (Cluster 1) and Bucket A (Cluster 2). Unidirectional XDCR is setup between Bucket B (Cluster 1) and Bucket B (Cluster 2). There is bidirectional XDCR between Bucket C (Cluster 1) and Bucket C (Cluster 2):
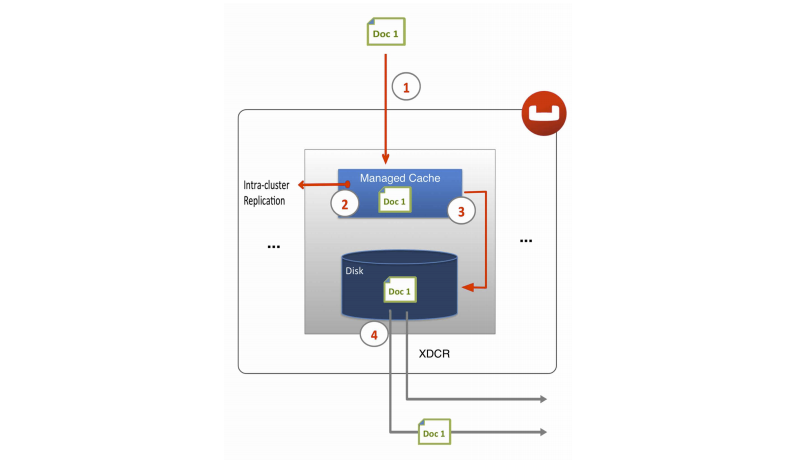
Cross datacenter replication in Couchbase Server involves replicating active data to multiple, geographically diverse datacenters either for disaster recovery or to bring data closer to its users for faster data access, as shown in below:
As shown above, after the document is stored in Couchbase Server and before XDCR replicates a document to other datacenters, a couple of things happen within each Couchbase Server node.
- Each server in a Couchbase cluster has a managed cache. When an application stores a document in Couchbase Server it is written into the managed cache.
- The document is added into the intra-cluster replication queue to be replicated to other servers within the cluster.
- The document is added into the disk write queue to be asynchronously persisted to disk. The document is persisted to disk after the disk-write queue is flushed.
- After the documents are persisted to disk, XDCR pushes the replica documents to other
clusters. On the destination cluster, replica documents received will be stored in cache.
This means that replica data on the destination cluster can undergo low latency read/write
operations: