| Documentation |
|---|---|
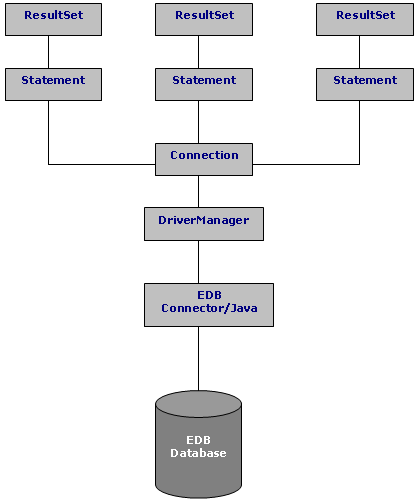
24.3. JDBC InterfaceThe following figure shows the core API interfaces in the JDBC specification and how they all tie up together. These interfaces are implemented in the java.sql package.
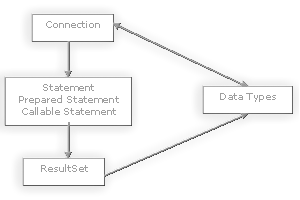
The core API is also composed of a set of classes apart from interfaces, and these classes and interfaces work together and are linked as shown in the diagram below:
All the statements in the JDBC interface eventually execute SQL to produce a ResultSet, and hence the Statement class is a parent to all the other Statement classes. And all the statements are executed using the underlying Connection to the database. A Statement object is used to send SQL statements to a database. There are actually three kinds of Statement objects, all of which act as containers for executing SQL statements on a given connection: Statement, PreparedStatement, which inherits from Statement, and CallableStatement, which inherits from PreparedStatement. They are specialized for sending particular types of SQL statements: A Statement object is used to execute a simple SQL statement with no parameters, a PreparedStatement object is used to execute a pre-compiled SQL statement with or without IN parameters, and a CallableStatement object is used to execute a call to a database stored procedure. We will start out by discussing the Statement object and then move onto the more advanced PreparedStatement and CallableStatement statement objects. The following diagram depicts the role of a class called DriverManager in a typical JDBC application. The DriverManager acts as the bridge between a Java application and the backend database. When the getConnection() method of this class is called, the DriverManager decides which JDBC driver to use for connecting to the relevant connection request.
|