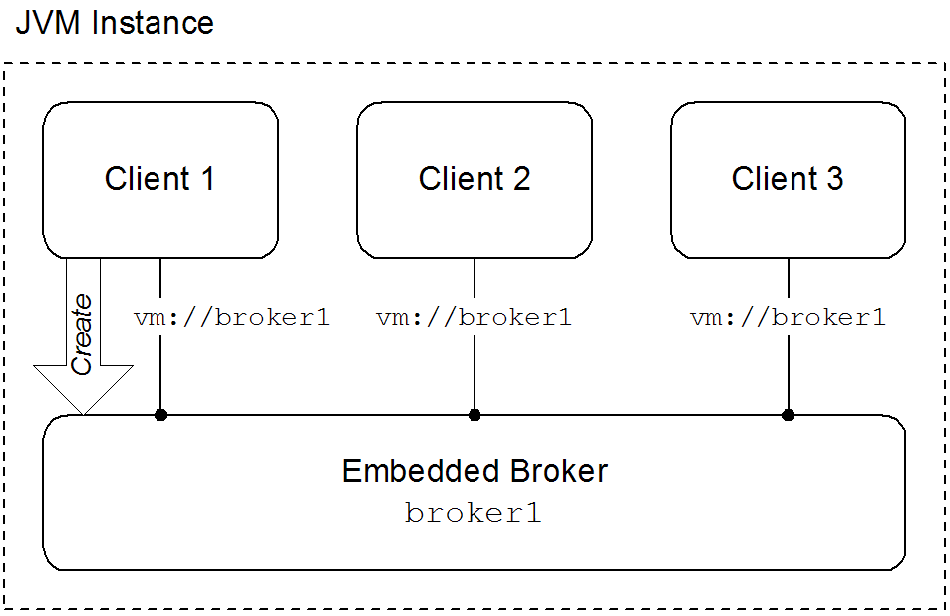
The VM transport enables Java clients running inside the same JVM to communicate with each other inside the JVM, without having to resort to a using a network connection. Because the clients require a broker to communicate, the VM transport can implicitly create an embedded broker the first time it is accessed. Figure 5.1 shows the basic architecture of the VM protocol.
The URI used to specify the VM transport comes in two flavors to provide maximum control over how the embedded broker is configured:
The VM transport uses a broker embedded in the same JVM as the clients to facilitate communication between the clients. The embedded broker can be created in several ways:
explicitly defining the broker in the application's configuration
explicitly creating the broker using the Java APIs
automatically when the first client attempts to connect to it using the VM transport
The VM transport uses the broker name specified in either the simple URI or in the configuration provided by the advanced URI's broker URI to determine if an embedded broker needs to be created. When a client uses the VM transport to connect to a broker, the transport checks to see if an embedded broker by that name already exists. If it does exist, the client is connected to the broker. If it does not exist, the broker is created and then the broker is connected to it.
When using explicitly created brokers there is a danger that your clients will
attempt to connect to the embedded broker before it is started. If this happens, the VM
transport will auto-create an instance of the broker for you. To avoid this conflict
you can set the waitForStart option or the create=false option
to manage how the VM transport determines when to create a new embedded broker.
The simple VM URI is used in most situations. It allows you to specify the name of the embedded broker to which the client will connect. It also allows for some basic broker configuration.
Example 5.1 shows the syntax for a simple VM URI.
BrokerNamespecifies the name of the embedded broker to which the client connects.TransportOptionsspecifies the configuration for the transport. They are specified in the form of a query list. Table 5.2 lists the available options.
In addition to the transport options listed in Table 5.2, the simple VM URI can use the options described in Table 5.1 to configure the embedded broker.
Table 5.1. VM Transport Broker Configuration Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
broker.*
| Properties prefixed by broker. configure the embedded
broker. You can specify any of the standard broker options described in
Table 5.3. |
brokerConfig
| Specifies an external broker configuration file. For example, to pick up the
broker configuration file, activemq.xml, you would set
brokerConfig as follows:
brokerConfig=xbean:activemq.xml. |
![[Important]](imagesdb/important.gif) | Important |
|---|---|
The broker configuration options specified on the VM URI are only meaningful if the client is responsible for instantiating the embedded broker. If the embedded broker is already started, the transport will ignore the broker configuration properties. |
Example 5.2 shows a basic VM URI that connects to
an embedded broker named broker1.
Example 5.3 creates and connects to an embedded broker that uses a non-persistent message store.
The advance VM URI provides you full control over how the embedded broker is configured. It uses a broker configuration URI similar to the one used by the administration tool to configure the embedded broker.
Example 5.4 shows the syntax for a simple VM URI.
BrokerConfigURIis a broker configuration URI. See Broker URI in Administering a Message Broker for information about broker configuration URIs.TransportOptionsspecifies the configuration for the transport. They are specified in the form of a query list. Table 5.2 lists the available options.
Example 5.5 creates and connects to an embedded broker configured using a broker configuration URI.
Table 5.2 shows options for configuring the VM transport.
Table 5.2. VM Transport Options
Table 5.3 shows the options used to configure the broker using the simple VM URI.
Table 5.3. Broker Options