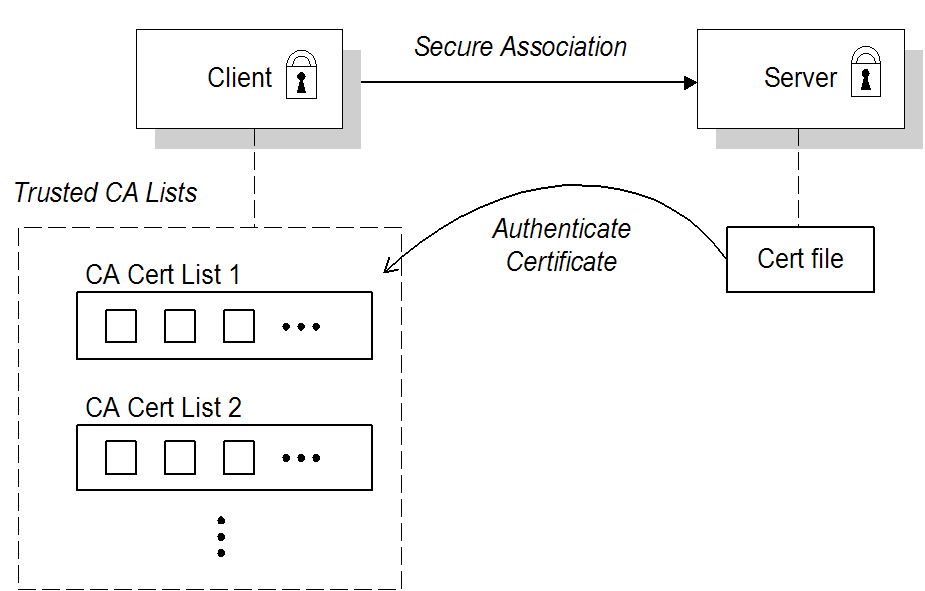
When an application is configured for target-only authentication, the target authenticates itself to the client but the client is not authentic to the target object, as shown in Figure 3.1.
Prior to running the application, the client and server should be set up as follows:
A certificate chain is associated with the server. The certificate chain is provided in the form of a Java keystore (ee Specifying an Application’s Own Certificate).
One or more lists of trusted certification authorities (CA) are made available to the client. (see Specifying Trusted CA Certificates).
During the security handshake, the server sends its certificate chain to the client (see Figure 3.1). The client then searches its trusted CA lists to find a CA certificate that matches one of the CA certificates in the server’s certificate chain.
On the client side, there are no policy settings required for target-only authentication. Simply configure your client without associating an X.509 certificate with the HTTPS port. You must provide the client with a list of trusted CA certificates, however (see Specifying Trusted CA Certificates).
On the server side, in the server’s XML configuration file, make sure that the sec:clientAuthentication element does not require client
authentication. This element can be omitted, in which case the default policy is to
not require client authentication. However, if the sec:clientAuthentication element is present, it should be
configured as follows:
<http:destination id="{Namespace}PortName.http-destination">
<http:tlsServerParameters>
...
<sec:clientAuthentication want="false" required="false"/>
</http:tlsServerParameters>
</http:destination>Where the want attribute is set to false (the default), specifying that the server does not request an X.509
certificate from the client during a TLS handshake. The required attribute is also set to false (the
default), specifying that the absence of a client certificate does not trigger an
exception during the TLS handshake.
![[Note]](imagesdb/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
The |
It is also necessary to associate an X.509 certificate with the server’s HTTPS port (see Specifying an Application’s Own Certificate ) and to provide the server with a list of trusted CA certificates (see Specifying Trusted CA Certificates ).
![[Note]](imagesdb/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
The choice of cipher suite can potentially affect whether or not target-only authentication is supported (see Configuring HTTPS Cipher Suites). |