 |  |  |  |  |
An exchange object is a wrapper that encapsulates a set of
related messages provide the primary means of accessing messages in FUSE Mediation Router and they
provide the primary means of accessing messages in FUSE Mediation Router. For example, you can access
In, Out, and Fault messages
using the getIn(), getOut(), and
getFault() accessors defined on Exchange
objects. An important feature of exchanges in FUSE Mediation Router is that they support lazy creation
of messages. This can provide a significant optimization in the case of routes that do not
require explicit access to messages.
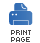
Figure 1.1 shows an exchange object passing through
a route. In the context of a route, an exchange object gets passed as the argument of the
Processor.process() method. This means that the exchange object
is directly accessible to the source endpoint, the target endpoint, and all of the
processors in between.
The org.apache.camel.Exchange interface defines methods
to access In, Out and Fault
messages, as shown in Example 1.1.
Example 1.1. Exchange Methods
Message getIn(); void setIn(Message in); Message getOut(); Message getOut(boolean lazyCreate); void setOut(Message out); Message getFault(); Message getFault(boolean lazyCreate); void setFault(Message fault);
For a complete description of the methods in the Exchange
interface, see The Exchange Interface.
FUSE Mediation Router supports lazy creation of In, Out,
and Fault messages. This means that message instances are not created
until you try to access them (for example, by calling getIn(),
getOut(), or getFault()). The lazy
message creation semantics are implemented by the
org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultExchange class.
If you call one of the no-argument accessors (getIn(),
getOut(), or getFault()), or if you call
an accessor with the boolean argument equal to true (that is,
getIn(true), getOut(true), or
getFault(true)), the default method implementation creates a new
message instance, if one does not already exist.
If you call an accessor with the boolean argument equal to false
(that is, getIn(false), getOut(false),
or getFault(false)), the default method implementation returns
the current message value.[1]