| GTK+ 3 Reference Manual | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | Description | Object Hierarchy | Properties | Signals | ||||
#include <gtk/gtk.h> #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BACKGROUND_COLOR #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_COLOR #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_FONT #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_MARGIN #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_PADDING #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_WIDTH #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_RADIUS #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_STYLE #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_COLOR #define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BACKGROUND_IMAGE #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_BACKGROUND #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_BUTTON #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CALENDAR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CELL #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CHECK #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_DEFAULT #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ENTRY #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HEADER #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENU #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_RADIO #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_RUBBERBAND #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SCROLLBAR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SLIDER #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TOOLTIP #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TROUGH #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ACCELERATOR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_DOCK #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_GRIP #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENUBAR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENUITEM #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PROGRESSBAR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SPINNER #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TOOLBAR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PRIMARY_TOOLBAR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PANE_SEPARATOR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SEPARATOR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_DND #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ERROR #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_EXPANDER #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_FRAME #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HIGHLIGHT #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_INFO #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MARK #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_NOTEBOOK #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_QUESTION #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SCALE #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SPINBUTTON #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_VIEW #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_WARNING #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HORIZONTAL #define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_VERTICAL #define GTK_STYLE_REGION_COLUMN #define GTK_STYLE_REGION_COLUMN_HEADER #define GTK_STYLE_REGION_ROW #define GTK_STYLE_REGION_TAB struct GtkStyleContext; GtkStyleContext * gtk_style_context_new (void); void gtk_style_context_add_provider (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStyleProvider *provider,guint priority); void gtk_style_context_add_provider_for_screen (GdkScreen *screen,GtkStyleProvider *provider,guint priority); void gtk_style_context_get (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,...); GtkTextDirection gtk_style_context_get_direction (GtkStyleContext *context); GtkJunctionSides gtk_style_context_get_junction_sides (GtkStyleContext *context); const GtkWidgetPath * gtk_style_context_get_path (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_get_property (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *property,GtkStateFlags state,GValue *value); GdkScreen * gtk_style_context_get_screen (GtkStyleContext *context); GtkStateFlags gtk_style_context_get_state (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_get_style (GtkStyleContext *context,...); void gtk_style_context_get_style_property (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *property_name,GValue *value); void gtk_style_context_get_style_valist (GtkStyleContext *context,va_list args); void gtk_style_context_get_valist (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,va_list args); void gtk_style_context_get_color (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GdkRGBA *color); void gtk_style_context_get_background_color (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GdkRGBA *color); void gtk_style_context_get_border_color (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GdkRGBA *color); void gtk_style_context_get_border (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GtkBorder *border); void gtk_style_context_get_padding (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GtkBorder *padding); void gtk_style_context_get_margin (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GtkBorder *margin); const PangoFontDescription * gtk_style_context_get_font (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state); void gtk_style_context_invalidate (GtkStyleContext *context); gboolean gtk_style_context_state_is_running (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateType state,gdouble *progress); gboolean gtk_style_context_lookup_color (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *color_name,GdkRGBA *color); GtkIconSet * gtk_style_context_lookup_icon_set (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *stock_id); void gtk_style_context_notify_state_change (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkWindow *window,gpointer region_id,GtkStateType state,gboolean state_value); void gtk_style_context_pop_animatable_region (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region (GtkStyleContext *context,gpointer region_id); void gtk_style_context_cancel_animations (GtkStyleContext *context,gpointer region_id); void gtk_style_context_scroll_animations (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkWindow *window,gint dx,gint dy); void gtk_style_context_remove_provider (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStyleProvider *provider); void gtk_style_context_remove_provider_for_screen (GdkScreen *screen,GtkStyleProvider *provider); void gtk_style_context_reset_widgets (GdkScreen *screen); void gtk_style_context_set_background (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkWindow *window); void gtk_style_context_restore (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_save (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_set_direction (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkTextDirection direction); void gtk_style_context_set_junction_sides (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkJunctionSides sides); void gtk_style_context_set_path (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkWidgetPath *path); void gtk_style_context_add_class (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *class_name); void gtk_style_context_remove_class (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *class_name); gboolean gtk_style_context_has_class (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *class_name); GList * gtk_style_context_list_classes (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_add_region (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *region_name,GtkRegionFlags flags); void gtk_style_context_remove_region (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *region_name); gboolean gtk_style_context_has_region (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *region_name,GtkRegionFlags *flags_return); GList * gtk_style_context_list_regions (GtkStyleContext *context); void gtk_style_context_set_screen (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkScreen *screen); void gtk_style_context_set_state (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags flags); struct GtkBorder; GtkBorder * gtk_border_new (void); GtkBorder * gtk_border_copy (const GtkBorder *border_); void gtk_border_free (GtkBorder *border_); void gtk_render_arrow (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble angle,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble size); void gtk_render_background (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_check (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_expander (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_extension (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height,GtkPositionType gap_side); void gtk_render_focus (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_frame (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_frame_gap (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height,GtkPositionType gap_side,gdouble xy0_gap,gdouble xy1_gap); void gtk_render_handle (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_layout (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,PangoLayout *layout); void gtk_render_line (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x0,gdouble y0,gdouble x1,gdouble y1); void gtk_render_option (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); void gtk_render_slider (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height,GtkOrientation orientation); void gtk_render_activity (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height); GdkPixbuf * gtk_render_icon_pixbuf (GtkStyleContext *context,const GtkIconSource *source,GtkIconSize size);
GtkStyleContext is an object that stores styling information affecting a widget defined by GtkWidgetPath.
In order to construct the final style information, GtkStyleContext
queries information from all attached GtkStyleProviders. Style providers
can be either attached explicitly to the context through
gtk_style_context_add_provider(), or to the screen through
gtk_style_context_add_provider_for_screen(). The resulting style is a
combination of all providers' information in priority order.
For GTK+ widgets, any GtkStyleContext returned by
gtk_widget_get_style_context() will already have a GtkWidgetPath, a
GdkScreen and RTL/LTR information set. The style context will be also
updated automatically if any of these settings change on the widget.
If you are using the theming layer standalone, you will need to set a
widget path and a screen yourself to the created style context through
gtk_style_context_set_path() and gtk_style_context_set_screen(), as well
as updating the context yourself using gtk_style_context_invalidate()
whenever any of the conditions change, such as a change in the
"gtk-theme-name" setting or a hierarchy change in the rendered
widget.
GtkStyleContext has built-in support for state change transitions. Note that these animations respect the "gtk-enable-animations" setting.
For simple widgets where state changes affect the whole widget area,
calling gtk_style_context_notify_state_change() with a NULL region
is sufficient to trigger the transition animation. And GTK+ already
does that when gtk_widget_set_state() or gtk_widget_set_state_flags()
are called.
If a widget needs to declare several animatable regions (i.e. not
affecting the whole widget area), its "draw" signal handler
needs to wrap the render operations for the different regions with
calls to gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region() and
gtk_style_context_pop_animatable_region(). These functions take an
identifier for the region which must be unique within the style context.
For simple widgets with a fixed set of animatable regions, using an
enumeration works well:
Example 9. Using an enumeration to identify animatable regions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
enum { REGION_ENTRY, REGION_BUTTON_UP, REGION_BUTTON_DOWN }; ... gboolean spin_button_draw (GtkWidget *widget, cairo_t *cr) { GtkStyleContext *context; context = gtk_widget_get_style_context (widget); gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region (context, GUINT_TO_POINTER (REGION_ENTRY)); gtk_render_background (cr, 0, 0, 100, 30); gtk_render_frame (cr, 0, 0, 100, 30); gtk_style_context_pop_animatable_region (context); ... } |
For complex widgets with an arbitrary number of animatable regions, it is up to the implementation to come up with a way to uniquely identify each animatable region. Using pointers to internal structs is one way to achieve this:
Example 10. Using struct pointers to identify animatable regions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
void notebook_draw_tab (GtkWidget *widget, NotebookPage *page, cairo_t *cr) { gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region (context, page); gtk_render_extension (cr, page->x, page->y, page->width, page->height); gtk_style_context_pop_animatable_region (context); } |
The widget also needs to notify the style context about a state change for a given animatable region so the animation is triggered.
Example 11. Triggering a state change animation on a region
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
gboolean notebook_motion_notify (GtkWidget *widget, GdkEventMotion *event) { GtkStyleContext *context; NotebookPage *page; context = gtk_widget_get_style_context (widget); page = find_page_under_pointer (widget, event); gtk_style_context_notify_state_change (context, gtk_widget_get_window (widget), page, GTK_STATE_PRELIGHT, TRUE); ... } |
gtk_style_context_notify_state_change() accepts NULL region IDs as a
special value, in this case, the whole widget area will be updated
by the animation.
Widgets can add style classes to their context, which can be used to associate different styles by class (see the section called “Selectors”). Theme engines can also use style classes to vary their rendering. GTK+ has a number of predefined style classes:
| Style class | Macro | Used by |
|---|---|---|
| button | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_BUTTON | GtkButton, GtkToggleButton, GtkRadioButton, GtkCheckButton |
| default | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_DEFAULT | GtkButton |
| check | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CHECK | GtkCheckButton, GtkCheckMenuItem, GtkCellRendererToggle |
| radio | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_RADIO | GtkRadioButton, GtkRadioMenuItem, GtkCellRendererToggle |
| arrow | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ARROW | GtkArrow |
| calendar | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CALENDAR | GtkCalendar |
| entry | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ENTRY | GtkEntry |
| cell | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CELL | GtkCellRendererToggle |
| menu | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENU | GtkMenu, GtkMenuItem, GtkCheckMenuItem, GtkRadioMenuItem |
| expander | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_EXPANDER | GtkExpander |
| tooltip | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TOOLTIP | GtkTooltip |
| frame | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_FRAME | GtkFrame |
| scrolled-window | GtkScrolledWindow | |
| viewport | GtkViewport | |
| trough | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TROUGH | GtkScrollbar, GtkProgressBar, GtkScale |
| progressbar | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PROGRESSBAR | GtkProgressBar, GtkCellRendererProgress |
| slider | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SLIDER | GtkScrollbar, GtkScale |
| menuitem | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENUITEM | GtkMenuItem |
| popup | GtkMenu | |
| accelerator | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ACCELERATOR | GtkAccelLabel |
| menubar | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENUBAR | GtkMenuBar |
| toolbar | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TOOLBAR | GtkToolbar |
| dock | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_DOCK | GtkHandleBox |
| notebook | GtkNotebook | |
| background | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_BACKGROUND | GtkWindow |
| rubberband | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_RUBBERBAND | |
| header | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HEADER | |
| grip | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_GRIP | GtkWindow |
| spinner | GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SPINNER | GtkSpinner |
Widgets can also add regions with flags to their context. The regions used by GTK+ widgets are:
| Region | Flags | Macro | Used by |
|---|---|---|---|
| row | even, odd | GTK_STYLE_REGION_ROW | GtkTreeView |
| column | first, last, sorted | GTK_STYLE_REGION_COLUMN | GtkTreeView |
| column-header | GTK_STYLE_REGION_COLUMN_HEADER | ||
| tab | even, odd, first, last | GTK_STYLE_REGION_TAB | GtkNotebook |
If you are developing a library with custom GtkWidgets that
render differently than standard components, you may need to add a
GtkStyleProvider yourself with the GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_FALLBACK
priority, either a GtkCssProvider or a custom object implementing the
GtkStyleProvider interface. This way theming engines may still attempt
to style your UI elements in a different way if needed so.
If you are using custom styling on an applications, you probably want then
to make your style information prevail to the theme's, so you must use
a GtkStyleProvider with the GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_APPLICATION
priority, keep in mind that the user settings in
XDG_CONFIG_HOME/gtk-3.0/gtk.cssGTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_USER priority.
If a custom theming engine is needed, you probably want to implement a
GtkStyleProvider yourself so it points to your GtkThemingEngine
implementation, as GtkCssProvider uses gtk_theming_engine_load()
which loads the theming engine module from the standard paths.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BACKGROUND_COLOR "background-color"
A property holding the background color of rendered elements as a GdkRGBA.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_COLOR "color"
A property holding the foreground color of rendered elements as a GdkRGBA.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_FONT "font"
A property holding the font properties used when rendering text as a PangoFontDescription.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_MARGIN "margin"
A property holding the rendered element's margin as a GtkBorder. The margin is defined as the spacing between the border of the element and its surrounding elements. It is external to GtkWidgets's size allocations, and the most external spacing property of the padding/border/margin series.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_PADDING "padding"
A property holding the rendered element's padding as a GtkBorder. The padding is defined as the spacing between the inner part of the element border and its child. It's the innermost spacing property of the padding/border/margin series.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_WIDTH "border-width"
A property holding the rendered element's border width in pixels as a GtkBorder. The border is the intermediary spacing property of the padding/border/margin series.
gtk_render_frame() uses this property to find out the frame line width,
so GtkWidgets rendering frames may need to add up this padding when
requesting size
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_RADIUS "border-radius"
A property holding the rendered element's border radius in pixels as a gint.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_STYLE "border-style"
A property holding the element's border style as a GtkBorderStyle.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_COLOR "border-color"
A property holding the element's border color as a GdkRGBA.
#define GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BACKGROUND_IMAGE "background-image"
A property holding the element's background as a cairo_pattern_t.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_BACKGROUND "background"
A CSS class to match the window background.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CALENDAR "calendar"
A CSS class to match calendars.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_CELL "cell"
A CSS class to match content rendered in cell views.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_DEFAULT "default"
A CSS class to match the default widget.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HEADER "header"
A CSS class to match a header element.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_RUBBERBAND "rubberband"
A CSS class to match the rubberband selection rectangle.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SCROLLBAR "scrollbar"
A CSS class to match scrollbars.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TOOLTIP "tooltip"
A CSS class to match tooltip windows.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_TROUGH "trough"
A CSS class to match troughs, as in scrollbars and progressbars.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ACCELERATOR "accelerator"
A CSS class to match an accelerator.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MENUITEM "menuitem"
A CSS class to match menu items.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PROGRESSBAR "progressbar"
A widget class defining a resize grip
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PRIMARY_TOOLBAR "primary-toolbar"
A CSS class to match primary toolbars.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_PANE_SEPARATOR "pane-separator"
A CSS class for a pane separator, such as those in GtkPaned.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SEPARATOR "separator"
A CSS class for a separator.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_ERROR "error"
A widget class for an area displaying an error message, such as those in infobars
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_EXPANDER "expander"
A widget class defining an expander, such as those in treeviews
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_FRAME "frame"
A CSS class defining a frame delimiting content, such as GtkFrame or the scrolled window frame around the scrollable area.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HIGHLIGHT "highlight"
A CSS class defining a highlighted area, such as headings in assistants.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_INFO "info"
A widget class for an area displaying an informational message, such as those in infobars
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_MARK "mark"
A widget class defining marks in a widget, such as in scales
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_NOTEBOOK "notebook"
A widget class defining a notebook
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_QUESTION "question"
A widget class for an area displaying a question to the user, such as those in infobars
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_SPINBUTTON "spinbutton"
A widget class defining an spinbutton
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_VIEW "view"
A widget class defining a view, such as iconviews or treeviews
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_WARNING "warning"
A widget class for an area displaying a warning message, such as those in infobars
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_HORIZONTAL "horizontal"
A widget class for horizontally layered widgets.
#define GTK_STYLE_CLASS_VERTICAL "vertical"
A widget class for vertically layered widgets.
#define GTK_STYLE_REGION_COLUMN "column"
A widget region name to define a treeview column.
#define GTK_STYLE_REGION_COLUMN_HEADER "column-header"
A widget region name to define a treeview column header.
#define GTK_STYLE_REGION_ROW "row"
A widget region name to define a treeview row.
#define GTK_STYLE_REGION_TAB "tab"
A widget region name to define a notebook tab.
GtkStyleContext * gtk_style_context_new (void);
Creates a standalone GtkStyleContext, this style context
won't be attached to any widget, so you may want
to call gtk_style_context_set_path() yourself.
gtk_widget_get_style_context()
in order to get a style context ready to theme the widget.
Returns : |
A newly created GtkStyleContext. |
void gtk_style_context_add_provider (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStyleProvider *provider,guint priority);
Adds a style provider to context, to be used in style construction.
If both priorities are the same, A GtkStyleProvider
added through this function takes precedence over another added
through gtk_style_context_add_provider_for_screen().
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GtkStyleProvider |
|
the priority of the style provider. The lower
it is, the earlier it will be used in the style
construction. Typically this will be in the range
between GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_FALLBACK and
GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_USER
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_add_provider_for_screen (GdkScreen *screen,GtkStyleProvider *provider,guint priority);
Adds a global style provider to screen, which will be used
in style construction for all GtkStyleContexts under
screen.
GTK+ uses this to make styling information from GtkSettings available.
If both priorities are the same, A GtkStyleProvider
added through gtk_style_context_add_provider() takes precedence
over another added through this function.
|
a GdkScreen |
|
a GtkStyleProvider |
|
the priority of the style provider. The lower
it is, the earlier it will be used in the style
construction. Typically this will be in the range
between GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_FALLBACK and
GTK_STYLE_PROVIDER_PRIORITY_USER
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,...);
Retrieves several style property values from context for a
given state.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the property values for |
|
property name /return value pairs, followed by NULL
|
Since 3.0
GtkTextDirection gtk_style_context_get_direction (GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the widget direction used for rendering.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
the widget direction |
Since 3.0
GtkJunctionSides gtk_style_context_get_junction_sides
(GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the sides where rendered elements connect visually with others.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
the junction sides |
Since 3.0
const GtkWidgetPath * gtk_style_context_get_path (GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the widget path used for style matching.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
A GtkWidgetPath. [transfer none] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_property (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *property,GtkStateFlags state,GValue *value);
Gets a style property from context for the given state.
When value is no longer needed, g_value_unset() must be called
to free any allocated memory.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
style property name |
|
state to retrieve the property value for |
|
return location for the style property value. [out][transfer full] |
Since 3.0
GdkScreen * gtk_style_context_get_screen (GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the GdkScreen to which context is attached.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
a GdkScreen. [transfer none] |
GtkStateFlags gtk_style_context_get_state (GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the state used when rendering.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
the state flags |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_style (GtkStyleContext *context,...);
Retrieves several widget style properties from context according to the
current style.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
property name /return value pairs, followed by NULL
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_style_property (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *property_name,GValue *value);
Gets the value for a widget style property.
When value is no longer needed, g_value_unset() must be called
to free any allocated memory.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
the name of the widget style property |
|
Return location for the property value |
void gtk_style_context_get_style_valist (GtkStyleContext *context,va_list args);
Retrieves several widget style properties from context according to the
current style.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
va_list of property name/return location pairs, followed by NULL
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_valist (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,va_list args);
Retrieves several style property values from context for a given state.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the property values for |
|
va_list of property name/return location pairs, followed by NULL
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_color (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GdkRGBA *color);
Gets the foreground color for a given state.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the color for |
|
return value for the foreground color. [out] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_background_color (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GdkRGBA *color);
Gets the background color for a given state.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the color for |
|
return value for the background color. [out] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_border_color (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GdkRGBA *color);
Gets the border color for a given state.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the color for |
|
return value for the border color. [out] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_border (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GtkBorder *border);
Gets the border for a given state as a GtkBorder.
See GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_BORDER_WIDTH.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the border for |
|
return value for the border settings. [out] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_padding (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GtkBorder *padding);
Gets the padding for a given state as a GtkBorder.
See GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_PADDING.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the padding for |
|
return value for the padding settings. [out] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_get_margin (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state,GtkBorder *margin);
Gets the margin for a given state as a GtkBorder.
See GTK_STYLE_PROPERTY_MARGIN.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the border for |
|
return value for the margin settings. [out] |
Since 3.0
const PangoFontDescription * gtk_style_context_get_font (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags state);
Returns the font description for a given state. The returned object is const and will remain valid until the "changed" signal happens.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to retrieve the font for |
Returns : |
the PangoFontDescription for the given state. This object is owned by GTK+ and should not be freed. [transfer none] |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_invalidate (GtkStyleContext *context);
Invalidates context style information, so it will be reconstructed
again.
If you're using a GtkStyleContext returned from
gtk_widget_get_style_context(), you do not need to
call this yourself.
|
a GtkStyleContext. |
Since 3.0
gboolean gtk_style_context_state_is_running (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateType state,gdouble *progress);
Returns TRUE if there is a transition animation running for the
current region (see gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region()).
If progress is not NULL, the animation progress will be returned
there, 0.0 means the state is closest to being unset, while 1.0 means
it's closest to being set. This means transition animation will
run from 0 to 1 when state is being set and from 1 to 0 when
it's being unset.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a widget state |
|
return location for the transition progress. [out] |
Returns : |
TRUE if there is a running transition animation for state. |
Since 3.0
gboolean gtk_style_context_lookup_color (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *color_name,GdkRGBA *color);
Looks up and resolves a color name in the context color map.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
color name to lookup |
|
Return location for the looked up color. [out] |
Returns : |
TRUE if color_name was found and resolved, FALSE otherwise |
GtkIconSet * gtk_style_context_lookup_icon_set (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *stock_id);
Looks up stock_id in the icon factories associated to context and
the default icon factory, returning an icon set if found, otherwise
NULL.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
an icon name |
Returns : |
The looked up GtkIconSet, or NULL. [transfer none]
|
void gtk_style_context_notify_state_change (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkWindow *window,gpointer region_id,GtkStateType state,gboolean state_value);
Notifies a state change on context, so if the current style makes use
of transition animations, one will be started so all rendered elements
under region_id are animated for state state being set to value
state_value.
The window parameter is used in order to invalidate the rendered area
as the animation runs, so make sure it is the same window that is being
rendered on by the gtk_render_*() functions.
If region_id is NULL, all rendered elements using context will be
affected by this state transition.
As a practical example, a GtkButton notifying a state transition on the prelight state:
gtk_style_context_notify_state_change (context,
gtk_widget_get_window (widget),
NULL,
GTK_STATE_PRELIGHT,
button->in_button);
Can be handled in the CSS file like this:
GtkButton {
background-color: #f00
}
GtkButton:hover {
background-color: #fff;
transition: 200ms linear
}
This combination will animate the button background from red to white if a pointer enters the button, and back to red if the pointer leaves the button.
Note that state is used when finding the transition parameters, which
is why the style places the transition under the :hover pseudo-class.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GdkWindow |
|
animatable region to notify on, or NULL.
See gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region(). [allow-none]
|
|
state to trigger transition for |
|
TRUE if state is the state we are changing to,
FALSE if we are changing away from it |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_pop_animatable_region
(GtkStyleContext *context);
Pops an animatable region from context.
See gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region().
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region (GtkStyleContext *context,gpointer region_id);
Pushes an animatable region, so all further gtk_render_*() calls between
this call and the following gtk_style_context_pop_animatable_region()
will potentially show transition animations for this region if
gtk_style_context_notify_state_change() is called for a given state,
and the current theme/style defines transition animations for state
changes.
The region_id used must be unique in context so the theming engine
can uniquely identify rendered elements subject to a state transition.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
unique identifier for the animatable region |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_cancel_animations (GtkStyleContext *context,gpointer region_id);
Stops all running animations for region_id and all animatable
regions underneath.
A NULL region_id will stop all ongoing animations in context,
when dealing with a GtkStyleContext obtained through
gtk_widget_get_style_context(), this is normally done for you
in all circumstances you would expect all widget to be stopped,
so this should be only used in complex widgets with different
animatable regions.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
animatable region to stop, or NULL.
See gtk_style_context_push_animatable_region(). [allow-none]
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_scroll_animations (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkWindow *window,gint dx,gint dy);
This function is analogous to gdk_window_scroll(), and
should be called together with it so the invalidation
areas for any ongoing animation are scrolled together
with it.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GdkWindow used previously in
gtk_style_context_notify_state_change()
|
|
Amount to scroll in the X axis |
|
Amount to scroll in the Y axis |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_remove_provider (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStyleProvider *provider);
Removes provider from the style providers list in context.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GtkStyleProvider |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_remove_provider_for_screen (GdkScreen *screen,GtkStyleProvider *provider);
Removes provider from the global style providers list in screen.
|
a GdkScreen |
|
a GtkStyleProvider |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_reset_widgets (GdkScreen *screen);
This function recomputes the styles for all widgets under a particular GdkScreen. This is useful when some global parameter has changed that affects the appearance of all widgets, because when a widget gets a new style, it will both redraw and recompute any cached information about its appearance. As an example, it is used when the color scheme changes in the related GtkSettings object.
|
a GdkScreen |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_set_background (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkWindow *window);
Sets the background of window to the background pattern or
color specified in context for its current state.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GdkWindow |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_restore (GtkStyleContext *context);
Restores context state to a previous stage.
See gtk_style_context_save().
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_save (GtkStyleContext *context);
Saves the context state, so all modifications done through
gtk_style_context_add_class(), gtk_style_context_remove_class(),
gtk_style_context_add_region(), gtk_style_context_remove_region()
or gtk_style_context_set_junction_sides() can be reverted in one
go through gtk_style_context_restore().
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_set_direction (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkTextDirection direction);
Sets the reading direction for rendering purposes.
If you are using a GtkStyleContext returned from
gtk_widget_get_style_context(), you do not need to
call this yourself.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
the new direction. |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_set_junction_sides (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkJunctionSides sides);
Sets the sides where rendered elements (mostly through
gtk_render_frame()) will visually connect with other visual elements.
This is merely a hint that may or may not be honored by theming engines.
Container widgets are expected to set junction hints as appropriate for their children, so it should not normally be necessary to call this function manually.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
sides where rendered elements are visually connected to other elements |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_set_path (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkWidgetPath *path);
Sets the GtkWidgetPath used for style matching. As a consequence, the style will be regenerated to match the new given path.
If you are using a GtkStyleContext returned from
gtk_widget_get_style_context(), you do not need to call
this yourself.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GtkWidgetPath |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_add_class (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *class_name);
Adds a style class to context, so posterior calls to
gtk_style_context_get() or any of the gtk_render_*()
functions will make use of this new class for styling.
In the CSS file format, a GtkEntry defining an "entry" class, would be matched by:
GtkEntry.entry { ... }
While any widget defining an "entry" class would be matched by:
.entry { ... }
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
class name to use in styling |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_remove_class (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *class_name);
Removes class_name from context.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
class name to remove |
Since 3.0
gboolean gtk_style_context_has_class (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *class_name);
Returns TRUE if context currently has defined the
given class name
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a class name |
Returns : |
TRUE if context has class_name defined |
Since 3.0
GList * gtk_style_context_list_classes (GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the list of classes currently defined in context.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
a GList of
strings with the currently defined classes. The contents
of the list are owned by GTK+, but you must free the list
itself with g_list_free() when you are done with it. [transfer container][element-type utf8]
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_add_region (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *region_name,GtkRegionFlags flags);
Adds a region to context, so posterior calls to
gtk_style_context_get() or any of the gtk_render_*()
functions will make use of this new region for styling.
In the CSS file format, a GtkTreeView defining a "row" region, would be matched by:
GtkTreeView row { ... }
Pseudo-classes are used for matching flags, so the two
following rules:
GtkTreeView row:nth-child (even) { ... }
GtkTreeView row:nth-child (odd) { ... }
would apply to even and odd rows, respectively.
Region names must only contain lowercase letters and '-', starting always with a lowercase letter.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
region name to use in styling |
|
flags that apply to the region |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_remove_region (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *region_name);
Removes a region from context.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
region name to unset |
Since 3.0
gboolean gtk_style_context_has_region (GtkStyleContext *context,const gchar *region_name,GtkRegionFlags *flags_return);
Returns TRUE if context has the region defined.
If flags_return is not NULL, it is set to the flags
affecting the region.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a region name |
|
return location for region flags. [out][allow-none] |
Returns : |
TRUE if region is defined |
Since 3.0
GList * gtk_style_context_list_regions (GtkStyleContext *context);
Returns the list of regions currently defined in context.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
Returns : |
a GList of
strings with the currently defined regions. The contents
of the list are owned by GTK+, but you must free the list
itself with g_list_free() when you are done with it. [transfer container][element-type utf8]
|
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_set_screen (GtkStyleContext *context,GdkScreen *screen);
Attaches context to the given screen.
The screen is used to add style information from 'global' style providers, such as the screens GtkSettings instance.
If you are using a GtkStyleContext returned from
gtk_widget_get_style_context(), you do not need to
call this yourself.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a GdkScreen |
Since 3.0
void gtk_style_context_set_state (GtkStyleContext *context,GtkStateFlags flags);
Sets the state to be used when rendering with any of the gtk_render_*() functions.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
state to represent |
Since 3.0
struct GtkBorder;
A struct that specifies a border around a rectangular area that can be of different width on each side.
GtkBorder * gtk_border_new (void);
Allocates a new GtkBorder structure and initializes its elements to zero.
Returns : |
a newly allocated GtkBorder. Free with gtk_border_free()
|
Since 2.14
GtkBorder * gtk_border_copy (const GtkBorder *border_);
Copies a GtkBorder structure.
|
a GtkBorder |
Returns : |
a copy of border_. |
void gtk_border_free (GtkBorder *border_);
Frees a GtkBorder structure.
|
a GtkBorder |
void gtk_render_arrow (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble angle,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble size);
Renders an arrow pointing to angle.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
arrow angle from 0 to 2 * G_PI, being 0 the arrow pointing to the north |
|
Center X for the render area |
|
Center Y for the render area |
|
square side for render area |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_background (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders the background of an element.
Example 13. Typical background rendering, showing the effect of
background-image,
border-width and
border-radius

|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0.
void gtk_render_check (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders a checkmark (as in a GtkCheckButton).
The GTK_STATE_FLAG_ACTIVE state determines whether the check is
on or off, and GTK_STATE_FLAG_INCONSISTENT determines whether it
should be marked as undefined.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_expander (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders an expander (as used in GtkTreeView and GtkExpander) in the area
defined by x, y, width, height. The state GTK_STATE_FLAG_ACTIVE
determines whether the expander is collapsed or expanded.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_extension (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height,GtkPositionType gap_side);
Renders a extension (as in a GtkNotebook tab) in the rectangle
defined by x, y, width, height. The side where the extension
connects to is defined by gap_side.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
|
side where the gap is |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_focus (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders a focus indicator on the rectangle determined by x, y, width, height.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_frame (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders a frame around the rectangle defined by x, y, width, height.
Example 18. Examples of frame rendering, showing the effect of
border-image,
border-color,
border-width,
border-radius and
junctions
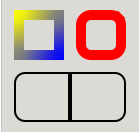
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_frame_gap (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height,GtkPositionType gap_side,gdouble xy0_gap,gdouble xy1_gap);
Renders a frame around the rectangle defined by (x, y, width, height),
leaving a gap on one side. xy0_gap and xy1_gap will mean X coordinates
for GTK_POS_TOP and GTK_POS_BOTTOM gap sides, and Y coordinates for
GTK_POS_LEFT and GTK_POS_RIGHT.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
|
side where the gap is |
|
initial coordinate (X or Y depending on gap_side) for the gap |
|
end coordinate (X or Y depending on gap_side) for the gap |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_handle (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders a handle (as in GtkHandleBox, GtkPaned and
GtkWindow's resize grip), in the rectangle
determined by x, y, width, height.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_layout (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,PangoLayout *layout);
Renders layout on the coordinates x, y
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin |
|
Y origin |
|
the PangoLayout to render |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_line (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x0,gdouble y0,gdouble x1,gdouble y1);
Renders a line from (x0, y0) to (x1, y1).
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X coordinate for the origin of the line |
|
Y coordinate for the origin of the line |
|
X coordinate for the end of the line |
|
Y coordinate for the end of the line |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_option (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders an option mark (as in a GtkRadioButton), the GTK_STATE_FLAG_ACTIVE
state will determine whether the option is on or off, and
GTK_STATE_FLAG_INCONSISTENT whether it should be marked as undefined.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_slider (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height,GtkOrientation orientation);
Renders a slider (as in GtkScale) in the rectangle defined by x, y,
width, height. orientation defines whether the slider is vertical
or horizontal.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
|
orientation of the slider |
Since 3.0
void gtk_render_activity (GtkStyleContext *context,cairo_t *cr,gdouble x,gdouble y,gdouble width,gdouble height);
Renders an activity area (Such as in GtkSpinner or the
fill line in GtkRange), the state GTK_STATE_FLAG_ACTIVE
determines whether there is activity going on.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
a cairo_t |
|
X origin of the rectangle |
|
Y origin of the rectangle |
|
rectangle width |
|
rectangle height |
Since 3.0
GdkPixbuf * gtk_render_icon_pixbuf (GtkStyleContext *context,const GtkIconSource *source,GtkIconSize size);
Renders the icon specified by source at the given size, returning the result
in a pixbuf.
|
a GtkStyleContext |
|
the GtkIconSource specifying the icon to render |
|
the size to render the icon at. A size of (GtkIconSize) -1 means render at the size of the source and don't scale. [type int] |
Returns : |
a newly-created GdkPixbuf containing the rendered icon. [transfer full] |
Since 3.0
"direction" property"direction" GtkTextDirection : Read / Write
Text direction.
Default value: GTK_TEXT_DIR_LTR
"changed" signalvoid user_function (GtkStyleContext *stylecontext,
gpointer user_data) : Run First
|
the object which received the signal. |
|
user data set when the signal handler was connected. |