Locales are associated with users and define the format for date, time, and numbers. Locales are also used to search for translation files and to specify decimal precision and some of the colors that the user sees on the screen. This is a powerful feature that allows each user to interact with the application in their native language and formats.
Part of defining a Locale is setting the language and, optionally, the Country. It is the combination of language and Country that determines date and numeric formats and which translation file will be used. For example, a Locale that references English and the United States will display as follows:
- Date
M/D/YY
- Time
12 hour format
- Numbers
1,999.00
A Locale that refers to German and Germany will display like this:
- Date
DD.MM.YY
- Time
12 hour format
- Numbers
1.999,00
Translation information is stored in .qm files, which xTuple uses to
display the user interface in a different language. When a Language is
selected in a Locale and the Country is left as "Default," the xTuple client
expects to find the file xTuple.xx.qm (where
xx is the ISO two letter language code) located in the
directory where the xTuple client is located. The U.S. Library of Congress
is the ISO registration authority for language codes and makes the list of
languages available on its language codes
website. Please contact xTuple for more information about the
availability of .qm files for various languages.
When both a Language and a Country are selected, the xTuple client
looks for the file xTuple.xx_yy.qm located in the
directory where the xTuple client is installed. The xx
is the ISO two letter language code and yy is the two
letter country code. You can find country codes in xTuple by navigating to
System > Master Information > Countries and observing the abbreviation
column. If the xTuple client does not find a file that matches both Language
and Country (xTuple.xx_yy.qm) it next looks for a file
that contains the Language only (e.g.,
xTuple.xx.qm).
If no .qm translation file is found, the xTuple client will report the error and continue the logon. The user will be presented the screens in the default language, which is English. The conventions established for the Locale that define date, time, decimal precision, and color will be presented based on the Locale associated with the User. If you don't want to see this error message again, go to the Preferences window and check the Ignore Missing Translations check box.
Numbers are generally formatted by the application in accordance with the conventions associated with the selected language and Country. These conventions mostly concern the character used to distinguish the fractional part of a number from the integer part, commonly called the "decimal point" or decimal separator, and the character used as the "group separator" or, at least in the U.S., the "thousands separator." In addition to the core numeric format, the xTuple application lets you choose the precision of numeric display and data entry for different kinds of number.
To access the master list of Locales, select the "Locales" option. The following screen will appear:
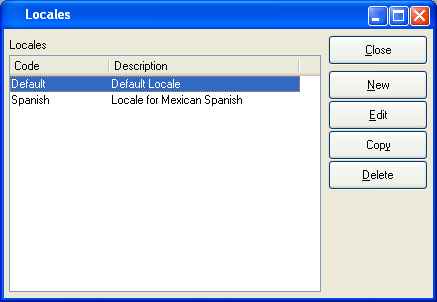
The "Locales" screen displays information on all existing Locales, including Locale name and Locale description.
To the far right of the screen, the following buttons are available:
- CLOSE
Closes the screen, returning you to the application desktop.
- NEW
Opens screen for creating a new Locale.
- EDIT
Enables you to edit highlighted Locale definitions. The edit screen is the same as that for creating a new Locale definition—except that when editing, the fields will contain Locale information. Double-clicking on a Locale master will also bring you to the editing screen.
- COPY
Highlight a Locale and then select this button to reach a screen for copying the Locale's definition.
- DELETE
Highlight a Locale definition and then select this button to remove the Locale from the list.
Locales are used to present information to users in the formats and language appropriate for their site. For example, the formatting of dates, times, and Currency are controlled by Locales. Translation of the application into a user's local language is also controlled by Locales.
Tip
Make the link between users and their Locales on the Maintain Users screen.
The xTuple Locale functionality is designed to coordinate with the settings in your local operating system. Because of this, it should only be necessary to specify the "Default" language and country value—and xTuple ERP will follow your operating system settings. For example, let's say you are located in China, running an operating system configured for China. In that scenario, using the default xTuple Locale values should result in xTuple ERP being formatted appropriately for China.
While in most cases using the default values will work, you may have the need to modify your Locale settings for specific cases. To create a new Locale, select the NEW button. The following screen will appear:
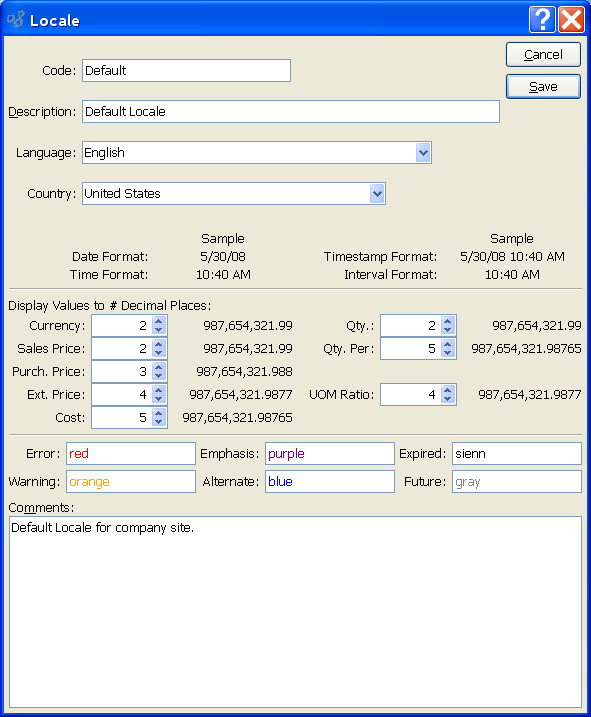
When creating a new Locale, you are presented with the following options:
- Code
-
Enter a code to uniquely identify the specified Locale setting. This code is referenced in the Maintain Users section, where Locales are associated with individual users.
Note
If you plan to use the Default Locale, then it may not be necessary to define any additional Locales. By using the Default Locale you allow your operating system settings to govern the presentation of xTuple ERP.
- Description
Enter a brief description to further define the specified Locale.
- Language
Select a language from the list of languages—or specify "Default" to indicate you want your operating system to define language option for you. The language selection impacts date and time formatting. It also tells the system which language translation file to load (if any). xTuple ERP supports multi-language translations of the product interface through the use of .qm files. If a .qm translation file is installed next to your xTuple ERP executable file, then the system will load the translation file at run time—automatically translating the application into your desired language. As long as your .qm file follows the standard ISO-derived naming convention (e.g.,
xTuple.cn.qm= Chinese andxTuple.es.qm= Spanish), then the system will successfully find it based on your Locale language selection.- Country
Select a country from the list of countries—or specify "Any" to indicate you want your operating system to define country option for you. The available countries will vary depending on the language selection. The country selection combined with the language selection impacts date and time formatting.
The following date and time formatting will be used, based on your language and country selections. If you are using the "Default" language and country selections, then the formatting will be inherited from your operating system.
- Time Format
Displays the format used for times within the application.
- Timestamp Format
Displays the timestamp format used to display any "timestamp" data within the application. Timestamps are typically used in transaction logs that record the specific date and time when an activity occurs within the system.
- Interval Format
Displays the format used for intervals within the application. The interval format is used to define how Work Order clock-in/clock-out times and effort are displayed.
While date and time formatting and the general format of numeric values are governed by the language and country selections, you do have the ability to manually determine the number of decimal places displayed for various types of numeric value. The following formatting options are available:
- Currency
The Currency format is used to display most monetary data within the application.
- Sales Price
The Sales Price format is used to display any Sales Price data within the application.
- Purch. Price
The Purchase Price format is used to display any Purchase Price data within the application.
- Ext. Price
The Extended Price format is used to display any Extended Price data within the application.
- Cost
The Cost format is used to display costing data within the application.
- Qty.
The Quantity format is used to display quantity data within the application.
- Qty. Per
The Quantity Per format is used to display quantity ratios within the application.
- UOM Ratio
The Unit of Measure Ratio format is used to display Unit of Measure Ratios within the application.
- Color Coding
Specify RGB values, or use any of the color names found in the
You have the ability to define the colors used by the application to
emphasize special cases in the data. When entering color choices, you can
either use standard RGB (Red, Green, Blue) values or any of the color names
found on the available colors
list. If you choose to enter RGB values then the format is either
#RGB, #RRGGBB, or
#RRRGGGBBB. Colors may be defined for any of the
following cases:
- Error
Specify the color-coding for errors.
- Warning
Specify the color-coding for warnings.
- Emphasis
Specify the color-coding for emphasis.
- Alternate
Specify the color-coding for alternate text.
- Expired
Specify the color-coding to indicate the expired condition.
- Future
Specify the color-coding to indicate the future condition.
To enter Comments related to the Locale, use the Comments field:
- Comments
This is a scrolling text field with word-wrapping for entering Comments related to the Locale.
To the far right of the screen, the following buttons are available:
- CANCEL
Closes the screen, returning you to the previous screen.
- SAVE
Creates the Locale setting and adds it to the master list of Locales.