| Home · All Classes · Modules |
The QProgressBar widget provides a horizontal or vertical progress bar. More...
Inherits QWidget.
The QProgressBar widget provides a horizontal or vertical progress bar.
A progress bar is used to give the user an indication of the progress of an operation and to reassure them that the application is still running.
The progress bar uses the concept of steps. You set it up by specifying the minimum and maximum possible step values, and it will display the percentage of steps that have been completed when you later give it the current step value. The percentage is calculated by dividing the progress (value() - minimum()) divided by maximum() - minimum().
You can specify the minimum and maximum number of steps with setMinimum() and setMaximum. The current number of steps is set with setValue(). The progress bar can be rewound to the beginning with reset().
If minimum and maximum both are set to 0, the bar shows a busy indicator instead of a percentage of steps. This is useful, for example, when using QFtp or QNetworkAccessManager to download items when they are unable to determine the size of the item being downloaded.
 |
A progress bar shown in the Macintosh widget style. |
 |
A progress bar shown in the Windows XP widget style. |
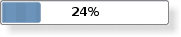 |
A progress bar shown in the Plastique widget style. |
Specifies the reading direction of the text for vertical progress bars.
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| QProgressBar.TopToBottom | 0 | The text is rotated 90 degrees clockwise. |
| QProgressBar.BottomToTop | 1 | The text is rotated 90 degrees counter-clockwise. |
Note that whether or not the text is drawn is dependent on the style. Currently CDE, CleanLooks, Motif, and Plastique draw the text. Mac, Windows and WindowsXP style do not.
This enum was introduced or modified in Qt 4.1.
See also textDirection.
The parent argument, if not None, causes self to be owned by Qt instead of PyQt.
Constructs a progress bar with the given parent.
By default, the minimum step value is set to 0, and the maximum to 100.
See also setRange().
Reimplemented from QObject.event().
Initialize option with the values from this QProgressBar. This method is useful for subclasses when they need a QStyleOptionProgressBar or QStyleOptionProgressBarV2, but don't want to fill in all the information themselves. This function will check the version of the QStyleOptionProgressBar and fill in the additional values for a QStyleOptionProgressBarV2.
See also QStyleOption.initFrom().
Reimplemented from QWidget.minimumSizeHint().
Reimplemented from QWidget.paintEvent().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void reset().
Reset the progress bar. The progress bar "rewinds" and shows no progress.
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setMaximum(int).
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setMinimum(int).
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setOrientation( ::Qt::Orientation).
Sets the progress bar's minimum and maximum values to minimum and maximum respectively.
If maximum is smaller than minimum, minimum becomes the only legal value.
If the current value falls outside the new range, the progress bar is reset with reset().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setValue(int).
Reimplemented from QWidget.sizeHint().
This is the default overload of this signal.
This signal is emitted when the value shown in the progress bar changes. value is the new value shown by the progress bar.
| PyQt 4.12.1 for X11 | Copyright © Riverbank Computing Ltd and The Qt Company 2015 | Qt 4.8.7 |