Hardware Acceleration & Embedded Platforms.
Abstract
This document describes how to use hardware acceleration for fast rendering on embedded platforms supported by Qt. In short, it explains how the graphics pipeline works. Since there might be differences to how the APIs are being used on different embedded platforms, a table links to documentation dedicated to platform specific documentation for each supported hardware acceleration API.
Hardware Acceleration
When designing applications for embedded devices there is often a compromise between graphics effects and performance. On most devices, you cannot have both simply because the hardware needed for such operations just is not there. With a growing number of devices that use hardware dedicated to graphics operations there is less need to compromise.
In addition to enabling dynamic graphics effects, there are two other benefits to using graphics acceleration. One is that graphics acceleration hardware is more power efficient than using the CPU. The reason for this is that the CPU might require a clock speed that is up to 20 times higher than the GPU, achieving the same results. E.g. a typical hardware accelerated mobile graphics unit can rasterize one or two bilinear texture fetches in one cycle, while a software implementation takes easily more than 20 cycles. Typical System-on-a-chip (SoC) graphics hardware generally have a much lower clock speed and memory bandwidth, and different level of acceleration than desktop GPUs. One example is that many GPUs leave out transformation and lighting from the graphics pipeline and only implements rasterization.
Another reason to use a GPU is to offload the main CPU, either for power saving or to perform other operations in parallel. Often drawing speed with a GPU is not that much faster than a CPU but the clear benefit of using the GPU is to free up the CPU to perform other tasks which can be used to create a more responsive use experience.
The key to writing good applications for devices is therefore to limit the wow factor down to what the target hardware can handle, and to take advantage of any graphics dedicated hardware. Qt provides several ways to both render advanced effects on the screen and speed up your application using hardware accelerated graphics.
Qt for Embedded Graphics pipeline
Qt uses QPainter for all graphics operations. By using the same API regardless of platform, the code can be reused on different devices. QPainter use different paint engines implemented in the QPaintEngine API to do the actual painting.
The QPaintEngine API provides paint engines for each window system and painting framework supported by Qt. In regards to Qt for Embedded, this also includes implementations for OpenGL ES versions 1.1 and 2.0, as well as OpenVG and DirectFB(Embedded Linux only).
By using one of these paint engines, you will be able to improve the graphics performance of your Qt application. However, if the graphics operations used are not supported, this might as well be a trap, slowing down your application significantly. This all depends on what kind of graphics operations that are supported by the target devices hardware configuration.
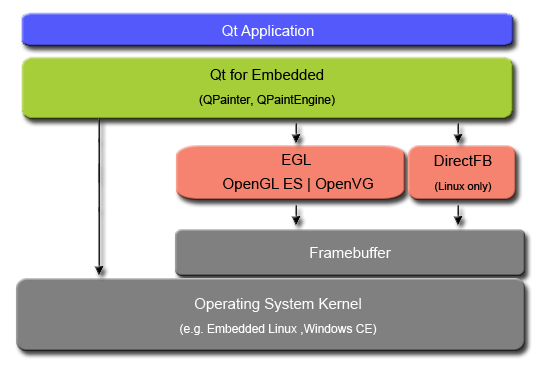
The paint engine will direct all graphics operations supported by the devices hardware to the GPU, and from there they are sent to the framebuffer. Unsupported graphics operations falls back to the QRasterPaintEngine and are handled by the CPU before sent to the framebuffer. In the end, the operating system sends the paint updates off to the screen/display. The fallback operation is quite expensive in regards to memory consumption, and should be avoided.
Hardware configuration requirements
Before implementing any application using hardware acceleration, it is wise to get an overview of what kind of hardware accelerated graphics operations that are available for the target device.
Note: On devices with no hardware acceleration, Qt will use QRasterPaintEngine, which handles the acceleration using software. On devices supporting OpenGL ES, OpenVG or DirectFB(not supported by Windows CE), Qt will use the respective paint engines to accelerate painting. However, hardware configurations that only support a limited set of hardware acceleration features, might slow the application graphics down rather than speeding it up when using unsupported operations that must fall back to the raster engine.
Different architectures
Based on the architecture used in a device we can make a recommendation on which hardware acceleration techniques to use. There are mainly two different architectures on embedded devices. These are devices with a Unified Memory Architecture (UMA), and devices with dedicated graphics memory. Generally, high-end devices will have dedicated graphics memory. Low-end devices will just use system memory, sometimes reserving a memory region and sometimes not.
In addition to this, we can categorize the devices into five types based on the different graphics operations supported by their hardware.
- No support for graphics acceleration.
- Support for blitter and alpha blending.
- Support for path based 2D vector graphics.
- Support for fixed function 3D graphics.
- Support for programmable 3D graphics.
Based on these characteristics the table below recommends which paint engines to use with the different types of hardware configurations.
Recommended use of hardware acceleration based on hardware
| Type | UMA | Non-UMA |
|---|---|---|
None | Qt Raster Engine | Qt Raster Engine |
Blitter | DirectFB | DirectFB |
2D Vector | OpenVG | OpenVG |
Fixed 3D | OpenGL (ES) 1.x | OpenGL (ES) 1.x |
Programmable 3D | OpenGL (ES) 2.x | OpenGL (ES) 2.x |
Note: Since the DirectFB API is quite primitive, the raster paint engine handles most of the operations.
Note: Blitter and Alpha blending is currently not supported on Windows CE.
Supported platforms
Since there might be differences to how the APIs are being used on the different embedded platforms, this table provides you with links to pages dedicated to platform specific documentation for each supported hardware acceleration API. Click the API link for the platform to go the correct documentation.
| Operating System | Hardware Acceleration Platform | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Windows CE | |||
Embedded Linux | |||
Symbian Platform | There are currently no support for hardware acceleration. | ||