The Enterprise Security Client includes basic diagnostic tools and a simple interface to log errors and common events, such as inserting and removing a smart card or changing the card's password. The diagnostic tools can identify and notify users about problems with the Enterprise Security Client, smart cards, and TPS connections.
To open the Diagnostics Information window:
Open the Enterprise Security Client.
Select the smart card to check from the list.
Click the Diagnostics button.
This opens the Diagnostic Information window for the selected smart card.
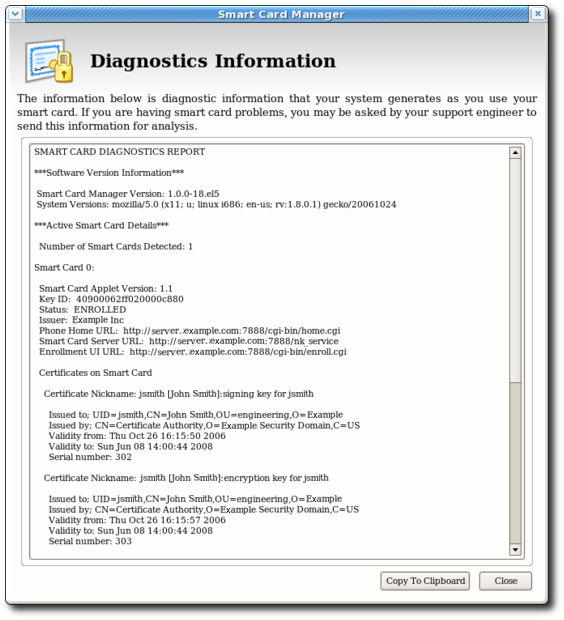
The Diagnostics Information screen displays the following information:
The Enterprise Security Client version number.
The version information for the Xulrunner framework upon which the client is running.
The number of cards detected by the Enterprise Security Client.
For each card detected, the following information is displayed:
The version of the applet running on the smart card.
The alpha-numeric ID of the smart card.
The card's status, which can be any of the three things:
NO_APPLET No key was detected.
UNINITIALIZED. The key was detected, but no certificates have been enrolled.
ENROLLED. The detected card has been enrolled with certificate and card information.
The card's Phone Home URL. This is the URL from which all Phone Home information is obtained.
The card issuer name, such as Example Corp.
The card's answer-to-reset (ATR) string. This is a unique value that can be used to identify different classes of smart cards. For example:
3BEC00FF8131FE45A0000000563333304A330600A1
The TPS Phone Home URL.
The TPS server URL. This is retrieved through Phone Home.
The TPS enrollment form URL. This is retrieved through Phone Home.
Detailed information about each certificate contained on the card.
A running log of the most recent Enterprise Security Client errors and common events.
The Enterprise Security Client records two types of diagnostic information. It records errors that are returned by the smart card, and it records events that have occurred through the Enterprise Security Client. It also returns basic information about the smart card configuration.
The Enterprise Security Client does not recognize a card.
Problems occur during a smart card operation, such as a certificate enrollment, password reset, or format operation.
The Enterprise Security Client loses the connection to the smart card. This can happen when problems occur communicating with the PCSC daemon.
The connection between the Enterprise Security Client and TPS is lost.
Smart cards can report certain error codes to the TPS; these are recorded in the TPS's tps-debug.log or tps-error.log files, depending on the cause for the message.
Table 5.1. Smart Card Error Codes
|
Return Code
|
Description
|
|---|
|
General Error Codes
|
|
6400
|
No specific diagnosis
|
|
6700
|
Wrong length in Lc
|
|
6982
|
Security status not satisfied
|
|
6985
|
Conditions of use not satisfied
|
|
6a86
|
Incorrect P1 P2
|
|
6d00
|
Invalid instruction
|
|
6e00
|
Invalid class
|
|
Install Load Errors
|
|
6581
|
Memory Failure
|
|
6a80
|
Incorrect parameters in data field
|
|
6a84
|
Not enough memory space
|
|
6a88
|
Referenced data not found
|
|
Delete Errors
|
|
6200
|
Application has been logically deleted
|
|
6581
|
Memory failure
|
|
6985
|
Referenced data cannot be deleted
|
|
6a88
|
Referenced data not found
|
|
6a82
|
Application not found
|
|
6a80
|
Incorrect values in command data
|
|
Get Data Errors
|
|
6a88
|
Referenced data not found
|
|
Get Status Errors
|
|
6310
|
More data available
|
|
6a88
|
Referenced data not found
|
|
6a80
|
Incorrect values in command data
|
|
Load Errors
|
|
6581
|
Memory failure
|
|
6a84
|
Not enough memory space
|
|
6a86
|
Incorrect P1/P2
|
|
6985
|
Conditions of use not satisfied
|
Simple events such as card insertions and removals, successfully completed operations, card operations that result in an error, and similar events.
Errors are reported from the TPS to the Enterprise Security Client.
The NSS crypto library is initialized.
Other low-level smart card events are detected.