PCA Projection¶
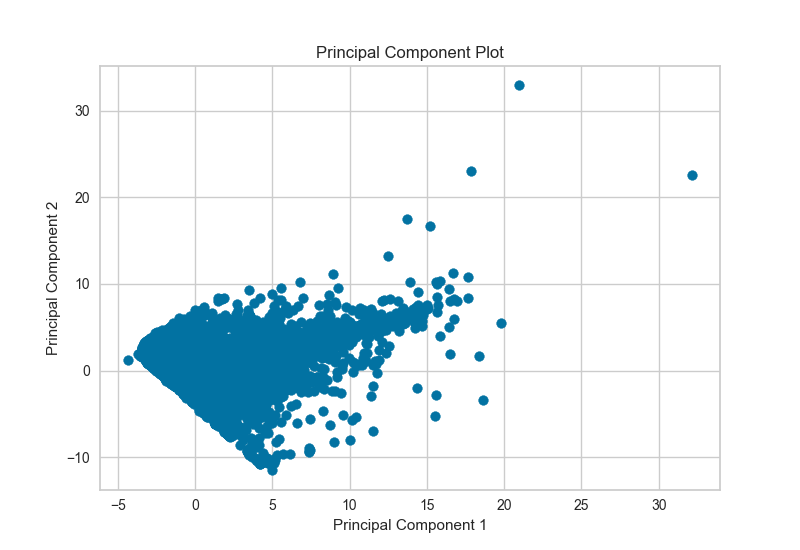
The PCA Decomposition visualizer utilizes principle component analysis to decompose high dimensional data into two or three dimensions so that each instance can be plotted in a scatter plot. The use of PCA means that the projected dataset can be analyzed along axes of principle variation and can be interpreted to determine if spherical distance metrics can be utilized.
# Load the classification data set
data = load_data('credit')
# Specify the features of interest
features = [
'limit', 'sex', 'edu', 'married', 'age', 'apr_delay', 'may_delay',
'jun_delay', 'jul_delay', 'aug_delay', 'sep_delay', 'apr_bill', 'may_bill',
'jun_bill', 'jul_bill', 'aug_bill', 'sep_bill', 'apr_pay', 'may_pay', 'jun_pay',
'jul_pay', 'aug_pay', 'sep_pay',
]
# Extract the numpy arrays from the data frame
X = data[features].as_matrix()
y = data.default.as_matrix()
visualizer = PCADecomposition(scale=True, center=False, col=y)
visualizer.fit_transform(X,y)
visualizer.poof()
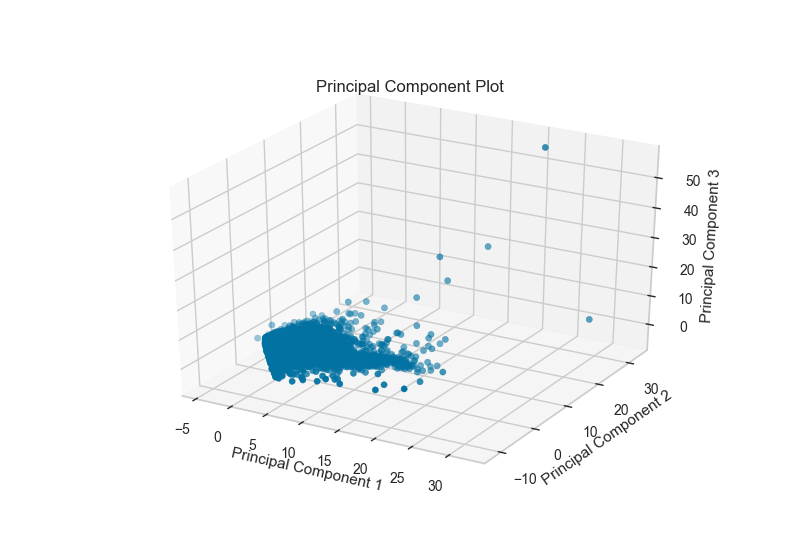
The PCA projection can also be plotted in three dimensions to attempt to visualize more princple components and get a better sense of the distribution in high dimensions.
visualizer = PCADecomposition(scale=True, center=False, col=y, proj_dim=3)
visualizer.fit_transform(X,y)
visualizer.poof()
API Reference¶
Decomposition based feature visualization with PCA.
-
class
yellowbrick.features.pca.PCADecomposition(X=None, y=None, ax=None, scale=True, color=None, proj_dim=2, colormap='RdBu', **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
yellowbrick.features.base.DataVisualizerProduce a two or three dimensional principal component plot of the data array
Xprojected onto it’s largest sequential principal components. It is common practice to scale the data arrayXbefore applying a PC decomposition. Variable scaling can be controlled using thescaleargument.Parameters: X : ndarray or DataFrame of shape n x m
A matrix of n instances with m features.
y : ndarray or Series of length n
An array or series of target or class values.
ax : matplotlib Axes, default: None
The axes to plot the figure on. If None is passed in the current axes. will be used (or generated if required).
scale : bool, default: True
Boolean that indicates if user wants to scale data.
proj_dim : int, default: 2
Dimension of the PCA visualizer.
color : list or tuple of colors, default: None
Specify the colors for each individual class.
colormap : string or cmap, default: None
Optional string or matplotlib cmap to colorize lines. Use either color to colorize the lines on a per class basis or colormap to color them on a continuous scale.
kwargs : dict
Keyword arguments that are passed to the base class and may influence the visualization as defined in other Visualizers.
Examples
>>> from sklearn import datasets >>> iris = datasets.load_iris() >>> X = iris.data >>> y = iris.target >>> params = {'scale': True, 'center': False, 'col': y} >>> visualizer = PCADecomposition(**params) >>> visualizer.fit(X) >>> visualizer.transform(X) >>> visualizer.poof()