Groupware service¶
Introduction to the groupware service¶
Zentyal integrates Zarafa [1] as a complete solution for groupware environment with the aim of offering an alternative to Microsoft Exchange.
| [1] | http://www.zarafa.com/ |
Configuration of a groupware server (Zarafa) with Zentyal¶
In order to start running Zarafa, you must start with a mail server configured as explained in Electronic Mail Service (SMTP/POP3-IMAP4). In this scenario, you select one of the existing virtual domains in the groupware module and, from that moment, the mail whose target is any email account located in that domain will be stored in Zarafa and not in the server you were using until that moment. The mail whose destinations are other virtual domains will continue being stored in the same way.
This groupware module integrates with the existing mail module so that an user must consider his/her associated quota plus enabled Zarafa account.
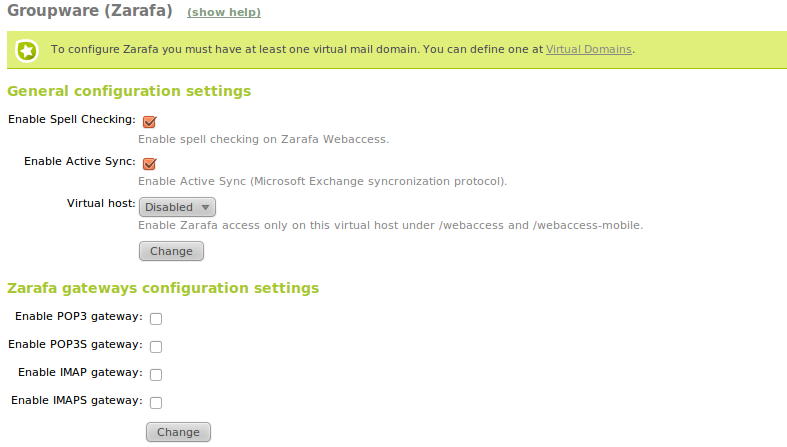
You can access the configuration in Groupware where you can configure the following parameters:
- Virtual domain:
- Domain associated to Zarafa. You should create at least one virtual domain Mail -> Virtual Domain previously.
- Enable correction:
- Enable the option to check spelling while you type an e-mail through the Zentyal web interface.
- Enable ActiveSnyc:
- Enable the support for ActiveSync mobile devices for synchronizing email, contacts, calendars and tasks. For more information, see the list of supported devices [3] .
- Virtual host:
- In the default installation, you can access Zarafa web interface at http://ip_address/webaccess (and http://ip_address/webaccess-mobile for mobile devices) from all IP addresses and domains associated with the server, but you make this web interface available only through a virtual host configured on the HTTP server, for example, http://mail.home.lan/webaccess.
To give the users access through POP3, POP3 on SSL, IMAP or IMAP on SSL to their mailboxes, select the corresponding Zarafa Gateways. Keep in mind that if any of these services are enabled in the mail module, it can’t be enabled here and these Zarafa Gateways can only authenticate users with Zarafa account and not all users with an email account.
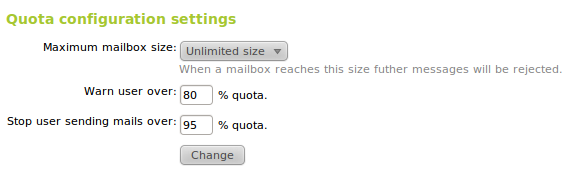
Finally, you can define the email quota, i.e., the maximum mailbox size each user can have. The user will receive a notification email when the specified percentage in the first instance is exceeded and if the second instance is exceeded, the user won’t be allowed to continue sending emails until he/she has freed up space. When an user reaches the maximum quota the emails sent to this user are rejected.
As mentioned earlier, besides an email account each user should have a Zarafa account. Furthermore, the quota defined in the mail module for each user will be applied to Zarafa and it can be unlimited, globally defined or specifically set for this user.
While until now the mail users were authenticated by the name of their email account, for example bob@home.lan, in the Zarafa web interface or its gateways they will be identified by their username, bob in the previous example, but the configuration for delivery through SMTP doesn’t change.
For more information about Zarafa, see the User Manual [4] and the administrators that need a deeper understanding of the application, reading of the Administration Manual [5] is recommended.
| [4] | http://www.zarafa.com/wiki/index.php/Z-Push_Mobile_Compatibility_List |
| [5] | http://doc.zarafa.com/trunk/User_Manual/en-US/html/index.html |
| [6] | http://doc.zarafa.com/trunk/Administrator_Manual/en-US/html/index.html |