The box model of XUL is used to divide a portion of the display into a series of boxes. Components inside of a box will orient themselves horizontally or vertically. By combining a series of boxes and separators, you can control the layout of the visual presentation.
A box can lay out its children in one of two orientations, either horizontally or vertically. A horizontal box lines up its components horizontally and a vertical box orients its components vertically. You can think of a box as one row or one column from an HTML table.
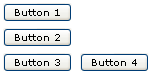
<zk>
<box orient="vertical">
<button label="Button 1"/>
<button label="Button 2"/>
</box>
<box orient="horizontal">
<button label="Button 3"/>
<button label="Button 4"/>
</box>
</zk>
|
Property |
Description |
Data Type |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Sets the widths/heights, which is a list of numbers separated by comma to denote the width/height of each cell in a box. |
|
|
|
|
Sets the orient. Values: |
|
|
|
|
Sets the spacing.(such as " |
|
|
|
|
Sets the vertical alignment of the adjacent cells of a box. Value: |
|
|
|
|
Sets the widths/heights, which is a list of numbers separated by comma to denote the width/height of each cell in a box. |
|
|
|
Name |
Description |
Return Data Type |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Returns the inner attributes used to wrap the children (never null). |
|
|
|
Returns the outer attributes used to wrap the children (never null). |
|
|
|
|