Compiling ArangoDB under Windows
Problem
I want to compile ArangoDB under Windows.
Note: For this recipe you need at least ArangoDB 2.4; it also works for 2.5 and above, up to 2.8. For ArangoDB version before 2.4 look at Compile on Windows (pre-2.4). For version 3.0 and above see Compile on Windows (3.x).
Solution
While compiling ArangoDB under Linux is straight forward - simply execute configure and make - compiling under Windows
is a bit more demanding.
Ingredients
For this recipe you need to install the following programs under Windows:
-
You need at least
makefrom cygwin. Cygwin also offers acmake. Do not install this version. The unit tests require the bash.You should also issue these commands to generate user informations for the cygwin commands:
mkpasswd > /etc/passwd mkgroup > /etc/groupTurning ACL off (noacl) for all mounts in cygwin fixes permissions troubles that may appear in the build:
# /etc/fstab # # This file is read once by the first process in a Cygwin process tree. # To pick up changes, restart all Cygwin processes. For a description # see https://cygwin.com/cygwin-ug-net/using.html#mount-table # noacl = Ignore Access Control List and let Windows handle permissions C:/cygwin64/bin /usr/bin ntfs binary,auto,noacl 0 0 C:/cygwin64/lib /usr/lib ntfs binary,auto,noacl 0 0 C:/cygwin64 / ntfs override,binary,auto,noacl 0 0 none /cygdrive cygdrive binary,posix=0,user,noacl 0 0 -
Either version 2.8.12, 3.0.2 or 3.1.2 should work. Attention - pitfall: the cygwin version doesn't work.
-
Either 2.x version should work - it's used to run V8s GYP. Make sure you add python.exe to your path environment variable; restarting your running shell may be necessary.
Visual Studio Express 2013 for Windows Desktop
More recent versions, such as Visual Studio Community 2015 don't work yet.
Please note that there are different versions of Visual Studio. The
Visual Studio for Windowswill not work. You need to installVisual Studio (Express) for Windows Desktop. You must configure your path in such a way that the compiler can be found. One way is to execute thevcvarsall.batscript from theVCfolder.
Ruby (for the unittests, if you intend to run them)
procdump (for the unittests; run once to accept the eula)
GitLink to adjust the pdb files to github
WinDbg (in the section "Standalone Debugging Tools for Windows (WinDbg)") to get automated backraces during unittest runs. Hint: Add its install path to the PATH environment.
Enable native symlinks for Cygwin and git
Cygwin will create proprietary files as placeholders by default instead of actually symlinking files. The placeholders later tell Cygwin where to resolve paths to. It does not intercept every access to the placeholders however, so that 3rd party scripts break. Windows Vista and above support real symlinks, and Cygwin can be configured to make use of it:
# use actual symlinks to prevent documentation build errors
# (requires elevated rights!)
export CYGWIN="winsymlinks:native"
Note that you must run Cygwin as administrator or change the Windows group
policies to allow user accounts to create symlinks (gpedit.msc if available).
BTW: You can create symlinks manually on Windows like:
mklink /H target/file.ext source/file.ext
mklink /D target/path source/path
mklink /J target/path source/path/for/junction
And in Cygwin:
ln -s source target
Use bundled Python and other executables
To use the bundled python 2.6, even if there's another python installation on your machine, use the following shell command in the Cygwin environment to extend the environment path (non-permanent):
export PATH=absolute/path/to/python_26:$PATH
Note that the build scripts aren't compatible with Python 3.x!
Add more paths if needed to make commands like ebook-convert available:
export PATH="/cygdrive/c/Program Files/Calibre2:absolute/path/to/python_26:$PATH"
Colons are used to separate individual paths (path1:path2). $PATH contains
the current environment paths, and must be used at the end of the export command
to not take precedence over the newly added paths.
Building the required libraries
First of all, start a bash from cygwin and clone the repository using the corresponding branch, e.g. for ArangoDB 2.6:
git clone -b 2.6 https://github.com/arangodb/arangodb-windows-libraries.git
and switch into the directory arangodb-windows-libraries. This repository contains the open-source libraries which
are needed by ArangoDB:
- etcd from CoreOS
- getopt
- libev
- linenoise
- openssl
- regex
- zlib
In order to build the corresponding 32bit and 64bit versions of these libraries, execute
make
make install
make 3rdParty
This will create a folder WindowsLibraries containing the headers and libraries.
Building ArangoDB itself
Clone the repository
https://github.com/arangodb/arangodb.git
and copy the previously created WindowsLibraries folder into this directory ArangoDB.
Next you need to build Google's V8 version, that is part of ArangoDB. This version contains V8 and ICU. Switch into the directory
ArangoDB/3rdParty
and execute
make -f Makefile.v8-windows
make -f Makefile.v8-windows install
Now switch back into the ArangoDB root folder and execute
make pack-win32
or
make pack-win64
in order to build the installer file for either 32 bit or 64 bit.
Development builds
For development builds which are able to run the unit tests run
make pack-win64-relative
Since most of the scripts assume they're running on a unix system, some directories are treated as mandatory and thus have to be created on the drive where you checked out your source:
mkdir -p /cygdrive/c/var/tmp/
You probably already downloaded and installed Ruby. Now we need to install the httparty and rspec gems. In order to use gem, you need to Install certificates. Once you did that you can run:
gem install httparty rspec
The bin/rspec.bat created by gem is not sufficient for being run by the unittesting facility; replace it with something like this:
@ECHO OFF
IF NOT "%~f0" == "~f0" GOTO :WinNT
@"C:\Program Files (x86)\Rub21-x64\bin\ruby.exe" "C:/Program Files (x86)/Ruby21-x64/bin/rspec" %1 %2 %3 %4 %5 %6 %7 %8 %9
GOTO :EOF
:WinNT
@"C:\Program Files (x86)\Ruby21-x64\bin\ruby.exe" "C:/Program Files (x86)/Ruby21-x64/bin/rspec" %*
You can then run the unittests like that:
bash ./scripts/unittest all --skipBoost true --skipGeo true
Executables only
If you do not need the installer file, you can use the cmake to build the executables. Instead of make pack-win32
use
mkdir Build32
cd Build32
cmake -G "Visual Studio 12" ..
This will create a solution file in the Build32 folder. You can now start Visual Studio and open this
solution file.
To build the 64 bit version, use
mkdir Build64
cd Build64
cmake -G "Visual Studio 12 Win64" ..
Alternatively use cmake to build the executables.
cmake --build . --config Release
In order to execute the binaries you need to copy the ICU datafile into the directory containing the executable
cp WindowsLibraries/64/icudtl.dat Build64/bin/Debug/icudt54l.dat
If you intend to use the machine for development purposes, it may be more practical to copy it somewhere else:
cp WindowsLibraries/64/icudtl.dat /cygdrive/c/Windows/icudt54l.dat
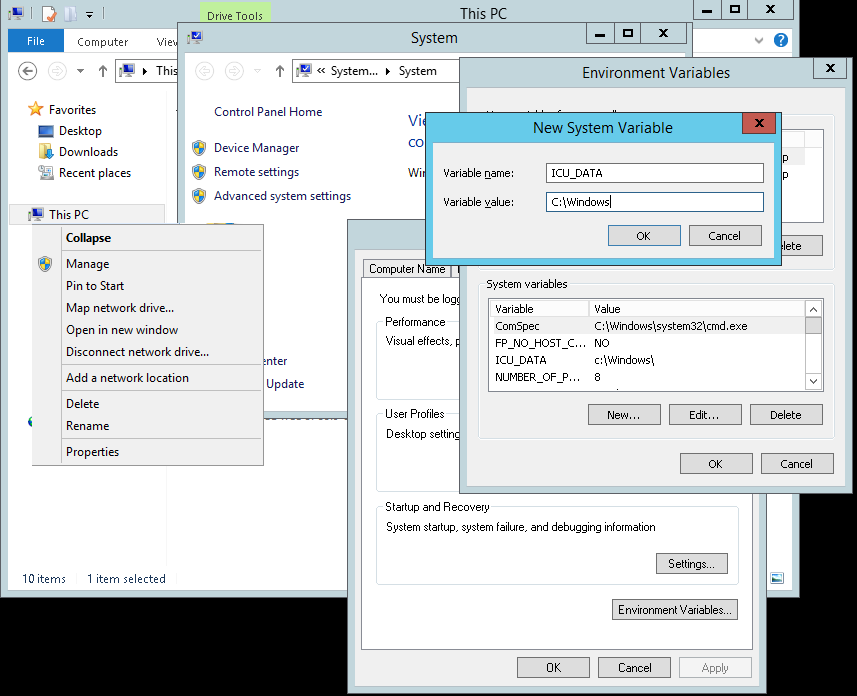
And configure your environment (yes this instruction remembers to the hitchhikers guide to the galaxy...) so that
ICU_DATA points to c:\\Windows. You do that by opening the explorer,
right click on This PC in the tree on the left, choose Properties in the opening window Advanced system settings,
in the Popup Environment Variables, another popup opens, in the System Variables part you click New,
And Key: :ICU_DATA to value: c:\\Windows
Authors: Frank Celler, Wilfried Goesgens and Simran Brucherseifer.
Tags: #windows #build