Constraints are one of the extension mechanisms provided for UML. ArgoUML is equipped with a powerful constraint editor based on the Object Constraint Language (OCL) defined in the UML 1.4 standard.
![[Caution]](images/caution.png) | Caution |
|---|---|
The OCL editor implementation for ArgoUML V0.26 doesn't support OCL constraints for elements other than Classes and Features. This is something of a general restriction of OCL. Although the UML specification claims that there may be a constraint for every model element, the OCL specification only defines classes/interfaces and operations as allowable contexts. It is not before OCL 2.0 that a more general definition of allowable contexts is introduced. The key issue is that for each context definition you need to define what is the contextualClassifier, i.e., the classifier that will be associated with the self keyword. The creators of the OCL specification claim that this is not an issue for the OCL specification, but rather for UML or some integration task force. Conversely, it seems that the UML specification people seem to expect this to be defined in the OCL specification (which is why we did a first step in that direction in OCL 2.0). So, to cut a long story short, it appeared that the simplest solution for ArgoUML at the moment would be to enable the OCL property panel only for those model elements for which there actually exists a definition of the contextualClassifier in OCL 1.4. These are (s. above) Class/Interface and Feature. |
The standard pre-defines a small number of constraints
(for example the xor constraint over a set
of associations indicating that only one may be manifest for
any particular instance).
The standard also envisages a number of circumstances where general purpose constraints may be useful:
To specify invariants on classes and types in the class model;
To specify type invariants for stereotypes;
To describe pre-conditions and post-conditions on operations and methods;
To describe guards;
As a navigation language; and
To specify constraints on operations.
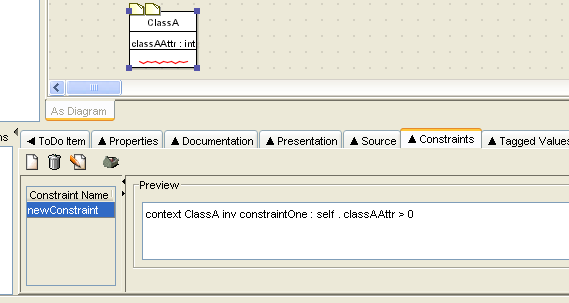
Figure 13.14, “
A typical Constraints tab on the
details pane
” shows a
typical constraint tab for a model element in ArgoUML (in this case
a class).
Along the top of the tab are a series of icons.

New Constraint. This creates a new constraint and launches the constraint editor in theConstraints tabfor that new constraint (see Section 13.7.1, “ The Constraint Editor ”). The new constraint is created with a context declaration for the currently selected model element.![[Warning]](images/warning.png)
Warning It seems logical, that when a new constraint is created, it needs to be edited. But ArgoUML V0.26 fails to start the OCL editor upon creation; you have to do this by primo selecting the new constraint first, secundo rename it, and tertio press the
Edit Constraintbutton. It is essental for successfully creating a constraint to follow these 4 steps accurately: create, select, rename, edit. The step to rename is necessary, because the validity check will refuse the constraint if its name differs from the name mentioned in the constraint text. For the same reason, renaming a constraint afterwards is impossible.
Delete Constraint. The constraint currently selected in theConstraint Namebox (see below) is deleted.![[Caution]](images/caution.png)
Caution In V0.26 of ArgoUML this button is not downlighted when it is not functional, i.e. when no constraint is selected.

Edit Constraint. This launches the constraint editor in theConstraintstab (see Section 13.7.1, “ The Constraint Editor ”). The editor is invoked on the constraint currently selected in theConstraint Namebox.![[Caution]](images/caution.png)
Caution In V0.26 of ArgoUML this button is not downlighted when it is not functional, i.e. when no constraint is selected.

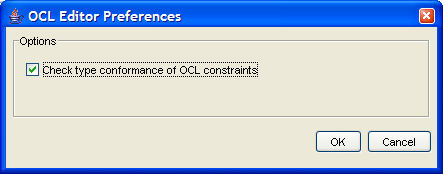
Configure Constraint Editor. This a dialog to configure options in the constraint editor (see Figure 13.15, “ Dialog box for configuring constraints ” ).The dialog box has a check box for the following option.
Check type conformance of OCL constraints. OCL is strictly typed. At the early stages of design it may be helpful to disable type checking, rather than follow through all the detailed specification needed to get type consistency.
At the bottom are two buttons, labeled
OK(to accept the option changes) andCancel(to discard the changes).
The main body of the constraints tab comprises two boxes, a smaller to the left and a larger one to the right. The two are separated by two small arrow buttons which control the size of the boxes.
Shrink Left. Button 1 click on this icon shrinks the box on the left. Its effect may be reversed by use of theShrink Rightbutton (see below).
Shrink Right. Button 1 click on this icon shrinks the box on the right. Its effect may be reversed by use of theShrink Leftbutton (see above).
Finer control can be achieved by using button 1 motion to drag the dividing bar to left and right.
The box on the left is titled Constraint
Name and lists all the constraints (if any) so far
defined for the selected model element. A constraint may be selected
by button 1 click.
The box on the right is labeled
Preview and contains the text of the constraint. This
box only shows some contents if a constraint is selected. Where
a constraint is too large for the box, a scroll bar is provided
to the right.
This is invoked through the use of the
Edit Constraint button on the main
Constraints tab. The constraint editor takes up the
whole tab (see
Figure 13.16, “
Dialog box for configuring constraints
”).
Along the top of the tab are a series of icons.

Cancel Edit Constraint. This exits the constraint editor without saving any changes and returns to the mainConstraintstab.
Check OCL Syntax. This button invokes a full syntax check of the OCL written in the editor. If the syntax is valid, the constraint is saved, and control returns to the mainConstraintstab. If the syntax is not valid, a dialog box explains the problem.![[Warning]](images/warning.png)
Warning Whether type checking is included should be configurable with the
Configure Constraint Editorbutton (see below). But ArgoUML V0.20 does always check, and refuses to accept any constraint with the slightest error.
Configure Constraint Editor. This a dialog to configure options in the constraint editor. It is also available in the mainConstraintstab and is discussed in detail there (see Section 13.7, “ Constraints Tab ” ).
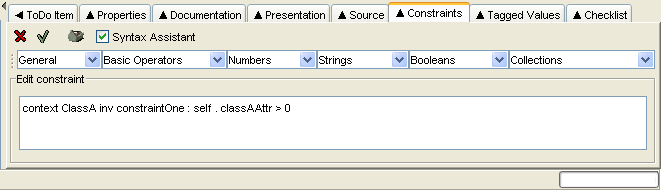
To the right of the toolbar is a check box labeled
Syntax Assistant (unchecked by default),
which will enable the syntax assistant in the constraint
editor.
If the syntax assistant is enabled, six drop down menus are provided in a row immediately below the toolbar. These provide standard templates for OCL that, when selected, will be inserted into the constraint being edited.
The syntax assistant can be made floating in a separate window by button 1 motion on the small divider area to the left of the row of drop-down menus.
General. General OCL constructors. Entries:inv(inserts an invariant);pre(inserts a pre-condition);post(inserts a post-condition);self(inserts a self-reference);@pre(inserts a reference to a value at the start of an operation); andresult(inserts a reference to a previous result).Basic Operators. Relational operators and parentheses. Entries:=;<>;<;>;<=;>=; and().Numbers. Arithmetic operators and functions. Entries:+;-;*;/;mod;div;abs;max;min;round; andfloor.Strings. String functions. Entries:concat;size;toLower;toUpper; andsubstring.Booleans. Logical functions. Entries:or;and;xor;not;implies; andif then else.Collections. Operators and functions on collections -bags, sets and sequences. The large number of functions are organized into sub-groups.General. Functions that apply to all types of collection. Entries:Collection {}(insert a new collection);Set {}(insert a a new set);Bag {}(insert a new bag);Sequence {}(insert a new sequence);size;count;isEmpty;notEmpty;includes;includesAll;iterate;exists;forAll;collect;select;reject;union;intersection;including;excluding; andsum.Sets. Operators and functions that apply only to sets. Entries:-(set difference); andsymmetricDifference.Sequences. Functions that apply to sequences. Entries:first;last;at;append;prepend; andsubSequence.
The remainder of the tab comprises a writable text area containing the text to be edited. The mouse buttons have their standard behavior within an editable text area (see Section 8.2, “ General Mouse Behavior in ArgoUML ”).
In addition, cut, copy and paste operations may be
invoked through the keyboard shortcuts
Ctrl-X, Ctrl-C and
Ctrl-V respectively.