Tutorial - Selecting Your Input
From Audacity Manual
Now that you know you're getting sound into the computer and you've made your Audacity settings, it's time to set up your input device for recording.
Setting up the audio host and playback device
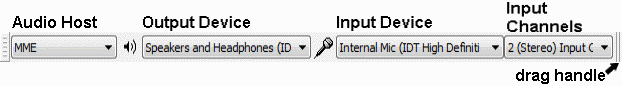
The Device toolbar is displayed by default in a new installation of Audacity. If the Device toolbar is not visible, click on .
You may want to expand the size of the Device toolbar by dragging right on the drag handle.
Choose your preferred audio host and output device from the drop-down menus.
- An audio host is an interface between Audacity and the sound card driver. In Windows the choices are: MME (the Audacity default, more compatible) or Windows DirectSound, the more modern replacement. In Linux there is often only one option: ALSA, other options could be OSS and/or Jack Audio Connection Kit (also known as "Jack" or "Jackd"). On Mac OS X the only choice is Core Audio.
- On Windows XP or earlier (given a recent computer), DirectSound's shorter path to the hardware should produce lower latency than MME.
- On Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8, DirectSound may have only slightly lower latency than MME because both interfaces are emulated. Selecting DirectSound and enabling both "Exclusive Mode" boxes in Windows "Sound" allows Audacity to request audio direct from the device without resampling. See the Wiki page for Windows 7 for more explanation.
- For output device, choose the named sound device your headphones or speakers are connected to (not a device like Microsoft Sound Mapper that uses the system default device). If you are using a USB-connected guitar, microphone or keyboard on Windows, you may also need to reset the default system playback device to your computer sound device in order to hear audio in other programs.
Click on , accept the default values in the dialog then click OK: a 30-second tone will be generated into a new track. Press Space to begin playback - you should hear a loud tone coming from your computer speakers. You can use the output slider on the Mixer Toolbar to control the volume at which you listen to your Audacity project.
Note that the playback meters in the Meter Toolbar do not change as you adjust the output slider: these meters always indicate the volume of the mix of your Audacity project.
Setting up the recording device
Now that you know that you can hear what Audacity is playing you can continue setting up for recording.
Choose your preferred input device from the Input Device drop-down menu in the Device Toolbar.
In the Input Channels drop-down menu choose whether you want to record in mono (1 channel) or stereo (2 channels). In general if you are recording a microphone or guitar you will want to record in mono. If you are recording a keyboard and the keyboard has stereo outputs you will want to record in stereo.
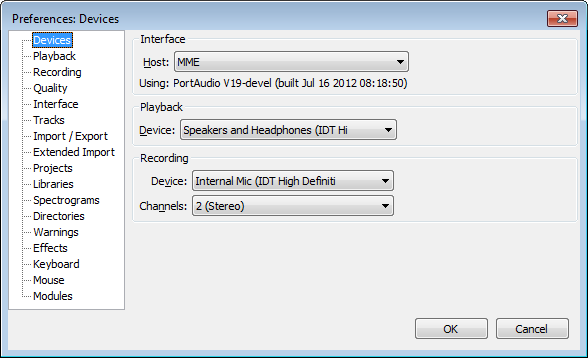
Audacity Preferences
If you prefer, you can make the above settings in the Audacity's Preferences. To access this, use Edit > Preferences
The image below shows the Devices section of Preferences:
There are many other settings that can be made in your Preferences do take some time to explore and understand these.
Links
> Forward to: Tutorial - Making a Test Recording