 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
General-purpose arrays with easy API for coefficient-wise operations.
The Array class is very similar to the Matrix class. It provides general-purpose one- and two-dimensional arrays. The difference between the Array and the Matrix class is primarily in the API: the API for the Array class provides easy access to coefficient-wise operations, while the API for the Matrix class provides easy access to linear-algebra operations.
This class can be extended with the help of the plugin mechanism described on the page Customizing/Extending Eigen by defining the preprocessor symbol EIGEN_ARRAY_PLUGIN.
 Inheritance diagram for Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >:
Inheritance diagram for Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >:Public Types | |
| enum | { RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime, SizeAtCompileTime, MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime, MaxSizeAtCompileTime, IsVectorAtCompileTime, Flags, IsRowMajor , CoeffReadCost } |
Public Member Functions | |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_abs_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | abs () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_abs2_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | abs2 () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_acos_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | acos () const |
| bool | all (void) const |
| bool | allFinite () const |
| bool | any (void) const |
| Array () | |
| Array (Index dim) | |
| Array (Index rows, Index cols) | |
| Array (const Scalar &val0, const Scalar &val1) | |
| Array (const Scalar &val0, const Scalar &val1, const Scalar &val2) | |
| Array (const Scalar &val0, const Scalar &val1, const Scalar &val2, const Scalar &val3) | |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| Array (const ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) | |
| Array (const Array &other) | |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| Array (const ReturnByValue< OtherDerived > &other) | |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| Array (const EigenBase< OtherDerived > &other) | |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_asin_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | asin () const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < CustomBinaryOp, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | binaryExpr (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other, const CustomBinaryOp &func=CustomBinaryOp()) const |
| Block< Derived > | block (Index startRow, Index startCol, Index blockRows, Index blockCols) |
| const Block< const Derived > | block (Index startRow, Index startCol, Index blockRows, Index blockCols) const |
| template<int BlockRows, int BlockCols> | |
| Block< Derived, BlockRows, BlockCols > | block (Index startRow, Index startCol) |
| template<int BlockRows, int BlockCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, BlockRows, BlockCols > | block (Index startRow, Index startCol) const |
| template<int BlockRows, int BlockCols> | |
| Block< Derived, BlockRows, BlockCols > | block (Index startRow, Index startCol, Index blockRows, Index blockCols) |
| template<int BlockRows, int BlockCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, BlockRows, BlockCols > | block (Index startRow, Index startCol, Index blockRows, Index blockCols) const |
| Block< Derived > | bottomLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| const Block< const Derived > | bottomLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomLeftCorner () |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomLeftCorner () const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| Block< Derived > | bottomRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| const Block< const Derived > | bottomRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomRightCorner () |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomRightCorner () const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | bottomRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| RowsBlockXpr | bottomRows (Index n) |
| ConstRowsBlockXpr | bottomRows (Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| NRowsBlockXpr< N >::Type | bottomRows (Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstNRowsBlockXpr< N >::Type | bottomRows (Index n=N) const |
| internal::cast_return_type < Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_cast_op < typename internal::traits < Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > >::Scalar, NewType >, const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > >::type | cast () const |
| ColXpr | col (Index i) |
| ConstColXpr | col (Index i) const |
| ConstColwiseReturnType | colwise () const |
| ColwiseReturnType | colwise () |
| ConjugateReturnType | conjugate () const |
| void | conservativeResize (Index nbRows, Index nbCols) |
| void | conservativeResize (Index nbRows, NoChange_t) |
| void | conservativeResize (NoChange_t, Index nbCols) |
| void | conservativeResize (Index size) |
| void | conservativeResizeLike (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_cos_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | cos () const |
| Index | count () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_cube_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | cube () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_abs_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | cwiseAbs () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_abs2_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | cwiseAbs2 () const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < std::equal_to< Scalar > , const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >, const OtherDerived > | cwiseEqual (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseScalarEqualReturnType | cwiseEqual (const Scalar &s) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_inverse_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | cwiseInverse () const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_max_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | cwiseMax (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_max_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const ConstantReturnType > | cwiseMax (const Scalar &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_min_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | cwiseMin (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_min_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const ConstantReturnType > | cwiseMin (const Scalar &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < std::not_equal_to< Scalar > , const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >, const OtherDerived > | cwiseNotEqual (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_product_op < typename Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >::Scalar, typename OtherDerived::Scalar > , const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >, const OtherDerived > | cwiseProduct (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_quotient_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | cwiseQuotient (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_sqrt_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | cwiseSqrt () const |
| const Scalar * | data () const |
| Scalar * | data () |
| EvalReturnType | eval () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_exp_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | exp () const |
| void | fill (const Scalar &value) |
| template<unsigned int Added, unsigned int Removed> | |
| const Flagged< Derived, Added, Removed > | flagged () const |
| const WithFormat< Derived > | format (const IOFormat &fmt) const |
| bool | hasNaN () const |
| SegmentReturnType | head (Index n) |
| ConstSegmentReturnType | head (Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| FixedSegmentReturnType< N >::Type | head (Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstFixedSegmentReturnType< N > ::Type | head (Index n=N) const |
| const ImagReturnType | imag () const |
| NonConstImagReturnType | imag () |
| Index | innerSize () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_inverse_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | inverse () const |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| bool | isApprox (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other, const RealScalar &prec=NumTraits< Scalar >::dummy_precision()) const |
| bool | isApproxToConstant (const Scalar &value, const RealScalar &prec=NumTraits< Scalar >::dummy_precision()) const |
| bool | isConstant (const Scalar &value, const RealScalar &prec=NumTraits< Scalar >::dummy_precision()) const |
| template<typename Derived > | |
| bool | isMuchSmallerThan (const typename NumTraits< Scalar >::Real &other, const RealScalar &prec) const |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| bool | isMuchSmallerThan (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other, const RealScalar &prec=NumTraits< Scalar >::dummy_precision()) const |
| bool | isOnes (const RealScalar &prec=NumTraits< Scalar >::dummy_precision()) const |
| bool | isZero (const RealScalar &prec=NumTraits< Scalar >::dummy_precision()) const |
| Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > & | lazyAssign (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
| ColsBlockXpr | leftCols (Index n) |
| ConstColsBlockXpr | leftCols (Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| NColsBlockXpr< N >::Type | leftCols (Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstNColsBlockXpr< N >::Type | leftCols (Index n=N) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_log_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | log () const |
| MatrixWrapper< Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | matrix () |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_max_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | max (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_max_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const CwiseNullaryOp < internal::scalar_constant_op < Scalar >, PlainObject > > | max (const Scalar &other) const |
| internal::traits< Derived >::Scalar | maxCoeff () const |
| template<typename IndexType > | |
| internal::traits< Derived >::Scalar | maxCoeff (IndexType *row, IndexType *col) const |
| template<typename IndexType > | |
| internal::traits< Derived >::Scalar | maxCoeff (IndexType *index) const |
| Scalar | mean () const |
| ColsBlockXpr | middleCols (Index startCol, Index numCols) |
| ConstColsBlockXpr | middleCols (Index startCol, Index numCols) const |
| template<int N> | |
| NColsBlockXpr< N >::Type | middleCols (Index startCol, Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstNColsBlockXpr< N >::Type | middleCols (Index startCol, Index n=N) const |
| RowsBlockXpr | middleRows (Index startRow, Index n) |
| ConstRowsBlockXpr | middleRows (Index startRow, Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| NRowsBlockXpr< N >::Type | middleRows (Index startRow, Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstNRowsBlockXpr< N >::Type | middleRows (Index startRow, Index n=N) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_min_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | min (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_min_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const CwiseNullaryOp < internal::scalar_constant_op < Scalar >, PlainObject > > | min (const Scalar &other) const |
| internal::traits< Derived >::Scalar | minCoeff () const |
| template<typename IndexType > | |
| internal::traits< Derived >::Scalar | minCoeff (IndexType *row, IndexType *col) const |
| template<typename IndexType > | |
| internal::traits< Derived >::Scalar | minCoeff (IndexType *index) const |
| const NestByValue< Derived > | nestByValue () const |
| Index | nonZeros () const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_boolean_and_op, const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >, const OtherDerived > | operator&& (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_product_op < typename Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >::Scalar, typename OtherDerived::Scalar > , const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >, const OtherDerived > | operator* (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const ScalarMultipleReturnType | operator* (const Scalar &scalar) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_multiple2_op < Scalar, std::complex< Scalar > >, const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | operator* (const std::complex< Scalar > &scalar) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_sum_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | operator+ (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_add_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | operator+ (const Scalar &scalar) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_difference_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | operator- (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_opposite_op < typename internal::traits < Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > >::Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | operator- () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_add_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | operator- (const Scalar &scalar) const |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_quotient_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > , const OtherDerived > | operator/ (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_quotient1_op < typename internal::traits < Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > >::Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | operator/ (const Scalar &scalar) const |
| CommaInitializer< Derived > | operator<< (const Scalar &s) |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| CommaInitializer< Derived > | operator<< (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| Array & | operator= (const EigenBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| Array & | operator= (const ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
| Array & | operator= (const Array &other) |
| const CwiseBinaryOp < internal::scalar_boolean_or_op, const Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >, const OtherDerived > | operator|| (const Eigen::ArrayBase< OtherDerived > &other) const |
| Index | outerSize () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_pow_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | pow (const Scalar &exponent) const |
| Scalar | prod () const |
| RealReturnType | real () const |
| NonConstRealReturnType | real () |
| template<typename Func > | |
| internal::result_of< Func(typename internal::traits< Derived > ::Scalar)>::type | redux (const Func &func) const |
| template<int RowFactor, int ColFactor> | |
| const Replicate< Derived, RowFactor, ColFactor > | replicate () const |
| const ReplicateReturnType | replicate (Index rowFacor, Index colFactor) const |
| void | resize (Index nbRows, Index nbCols) |
| void | resize (Index size) |
| void | resize (NoChange_t, Index nbCols) |
| void | resize (Index nbRows, NoChange_t) |
| void | resizeLike (const EigenBase< OtherDerived > &_other) |
| ReverseReturnType | reverse () |
| ConstReverseReturnType | reverse () const |
| void | reverseInPlace () |
| ColsBlockXpr | rightCols (Index n) |
| ConstColsBlockXpr | rightCols (Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| NColsBlockXpr< N >::Type | rightCols (Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstNColsBlockXpr< N >::Type | rightCols (Index n=N) const |
| RowXpr | row (Index i) |
| ConstRowXpr | row (Index i) const |
| ConstRowwiseReturnType | rowwise () const |
| RowwiseReturnType | rowwise () |
| SegmentReturnType | segment (Index start, Index n) |
| ConstSegmentReturnType | segment (Index start, Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| FixedSegmentReturnType< N >::Type | segment (Index start, Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstFixedSegmentReturnType< N > ::Type | segment (Index start, Index n=N) const |
| template<typename ThenDerived , typename ElseDerived > | |
| const Select< Derived, ThenDerived, ElseDerived > | select (const DenseBase< ThenDerived > &thenMatrix, const DenseBase< ElseDerived > &elseMatrix) const |
| template<typename ThenDerived > | |
| const Select< Derived, ThenDerived, typename ThenDerived::ConstantReturnType > | select (const DenseBase< ThenDerived > &thenMatrix, const typename ThenDerived::Scalar &elseScalar) const |
| template<typename ElseDerived > | |
| const Select< Derived, typename ElseDerived::ConstantReturnType, ElseDerived > | select (const typename ElseDerived::Scalar &thenScalar, const DenseBase< ElseDerived > &elseMatrix) const |
| Derived & | setConstant (const Scalar &value) |
| Derived & | setLinSpaced (Index size, const Scalar &low, const Scalar &high) |
| Sets a linearly space vector. More... | |
| Derived & | setLinSpaced (const Scalar &low, const Scalar &high) |
| Sets a linearly space vector. More... | |
| Derived & | setOnes () |
| Derived & | setRandom () |
| Derived & | setZero () |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_sin_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | sin () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_sqrt_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | sqrt () const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_square_op < Scalar >, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | square () const |
| Scalar | sum () const |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| void | swap (ArrayBase< OtherDerived > const &other) |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| void | swap (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other, int=OtherDerived::ThisConstantIsPrivateInPlainObjectBase) |
| template<typename OtherDerived > | |
| void | swap (PlainObjectBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
| SegmentReturnType | tail (Index n) |
| ConstSegmentReturnType | tail (Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| FixedSegmentReturnType< N >::Type | tail (Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstFixedSegmentReturnType< N > ::Type | tail (Index n=N) const |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < internal::scalar_tan_op < Scalar >, Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | tan () const |
| Block< Derived > | topLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| const Block< const Derived > | topLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | topLeftCorner () |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | topLeftCorner () const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | topLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | topLeftCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| Block< Derived > | topRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| const Block< const Derived > | topRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | topRightCorner () |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | topRightCorner () const |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| Block< Derived, CRows, CCols > | topRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) |
| template<int CRows, int CCols> | |
| const Block< const Derived, CRows, CCols > | topRightCorner (Index cRows, Index cCols) const |
| RowsBlockXpr | topRows (Index n) |
| ConstRowsBlockXpr | topRows (Index n) const |
| template<int N> | |
| NRowsBlockXpr< N >::Type | topRows (Index n=N) |
| template<int N> | |
| ConstNRowsBlockXpr< N >::Type | topRows (Index n=N) const |
| Eigen::Transpose< Derived > | transpose () |
| ConstTransposeReturnType | transpose () const |
| void | transposeInPlace () |
| const CwiseUnaryOp < CustomUnaryOp, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | unaryExpr (const CustomUnaryOp &func=CustomUnaryOp()) const |
| Apply a unary operator coefficient-wise. More... | |
| const CwiseUnaryView < CustomViewOp, const Array < _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > > | unaryViewExpr (const CustomViewOp &func=CustomViewOp()) const |
| CoeffReturnType | value () const |
| template<typename Visitor > | |
| void | visit (Visitor &func) const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Constant (Index rows, Index cols, const Scalar &value) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Constant (Index size, const Scalar &value) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Constant (const Scalar &value) |
| static const SequentialLinSpacedReturnType | LinSpaced (Sequential_t, Index size, const Scalar &low, const Scalar &high) |
| Sets a linearly space vector. More... | |
| static const RandomAccessLinSpacedReturnType | LinSpaced (Index size, const Scalar &low, const Scalar &high) |
| Sets a linearly space vector. More... | |
| static const SequentialLinSpacedReturnType | LinSpaced (Sequential_t, const Scalar &low, const Scalar &high) |
| Sets a linearly space vector. More... | |
| static const RandomAccessLinSpacedReturnType | LinSpaced (const Scalar &low, const Scalar &high) |
| Sets a linearly space vector. More... | |
| template<typename CustomNullaryOp > | |
| static const CwiseNullaryOp < CustomNullaryOp, Derived > | NullaryExpr (Index rows, Index cols, const CustomNullaryOp &func) |
| template<typename CustomNullaryOp > | |
| static const CwiseNullaryOp < CustomNullaryOp, Derived > | NullaryExpr (Index size, const CustomNullaryOp &func) |
| template<typename CustomNullaryOp > | |
| static const CwiseNullaryOp < CustomNullaryOp, Derived > | NullaryExpr (const CustomNullaryOp &func) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Ones (Index rows, Index cols) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Ones (Index size) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Ones () |
| static const CwiseNullaryOp < internal::scalar_random_op < Scalar >, Derived > | Random (Index rows, Index cols) |
| static const CwiseNullaryOp < internal::scalar_random_op < Scalar >, Derived > | Random (Index size) |
| static const CwiseNullaryOp < internal::scalar_random_op < Scalar >, Derived > | Random () |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Zero (Index rows, Index cols) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Zero (Index size) |
| static const ConstantReturnType | Zero () |
Map | |
| static ConstMapType | Map (const Scalar *data) |
| static MapType | Map (Scalar *data) |
| static ConstMapType | Map (const Scalar *data, Index size) |
| static MapType | Map (Scalar *data, Index size) |
| static ConstMapType | Map (const Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols) |
| static MapType | Map (Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols) |
|
static StridedConstMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | Map (const Scalar *data, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedMapType< Stride < Outer, Inner > >::type | Map (Scalar *data, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedConstMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | Map (const Scalar *data, Index size, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedMapType< Stride < Outer, Inner > >::type | Map (Scalar *data, Index size, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedConstMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | Map (const Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedMapType< Stride < Outer, Inner > >::type | Map (Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
| static ConstAlignedMapType | MapAligned (const Scalar *data) |
| static AlignedMapType | MapAligned (Scalar *data) |
| static ConstAlignedMapType | MapAligned (const Scalar *data, Index size) |
| static AlignedMapType | MapAligned (Scalar *data, Index size) |
| static ConstAlignedMapType | MapAligned (const Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols) |
| static AlignedMapType | MapAligned (Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols) |
|
static StridedConstAlignedMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | MapAligned (const Scalar *data, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedAlignedMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | MapAligned (Scalar *data, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedConstAlignedMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | MapAligned (const Scalar *data, Index size, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedAlignedMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | MapAligned (Scalar *data, Index size, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedConstAlignedMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | MapAligned (const Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
|
static StridedAlignedMapType < Stride< Outer, Inner > >::type | MapAligned (Scalar *data, Index rows, Index cols, const Stride< Outer, Inner > &stride) |
Protected Member Functions | |
| Array< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols > & | _set (const DenseBase< OtherDerived > &other) |
Copies the value of the expression other into *this with automatic resizing. More... | |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| template<typename Derived > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const DenseBase< Derived > &m) |
|
inherited |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RowsAtCompileTime |
The number of rows at compile-time. This is just a copy of the value provided by the Derived type. If a value is not known at compile-time, it is set to the Dynamic constant.
|
| ColsAtCompileTime |
The number of columns at compile-time. This is just a copy of the value provided by the Derived type. If a value is not known at compile-time, it is set to the Dynamic constant.
|
| SizeAtCompileTime |
This is equal to the number of coefficients, i.e. the number of rows times the number of columns, or to Dynamic if this is not known at compile-time.
|
| MaxRowsAtCompileTime |
This value is equal to the maximum possible number of rows that this expression might have. If this expression might have an arbitrarily high number of rows, this value is set to Dynamic. This value is useful to know when evaluating an expression, in order to determine whether it is possible to avoid doing a dynamic memory allocation. |
| MaxColsAtCompileTime |
This value is equal to the maximum possible number of columns that this expression might have. If this expression might have an arbitrarily high number of columns, this value is set to Dynamic. This value is useful to know when evaluating an expression, in order to determine whether it is possible to avoid doing a dynamic memory allocation. |
| MaxSizeAtCompileTime |
This value is equal to the maximum possible number of coefficients that this expression might have. If this expression might have an arbitrarily high number of coefficients, this value is set to Dynamic. This value is useful to know when evaluating an expression, in order to determine whether it is possible to avoid doing a dynamic memory allocation. |
| IsVectorAtCompileTime |
This is set to true if either the number of rows or the number of columns is known at compile-time to be equal to 1. Indeed, in that case, we are dealing with a column-vector (if there is only one column) or with a row-vector (if there is only one row). |
| Flags |
This stores expression Flags flags which may or may not be inherited by new expressions constructed from this one. See the list of flags. |
| IsRowMajor |
True if this expression has row-major storage order. |
| CoeffReadCost |
This is a rough measure of how expensive it is to read one coefficient from this expression. |
|
inline |
Default constructor.
For fixed-size matrices, does nothing.
For dynamic-size matrices, creates an empty matrix of size 0. Does not allocate any array. Such a matrix is called a null matrix. This constructor is the unique way to create null matrices: resizing a matrix to 0 is not supported.
Constructs a vector or row-vector with given dimension. This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
Note that this is only useful for dynamic-size vectors. For fixed-size vectors, it is redundant to pass the dimension here, so it makes more sense to use the default constructor Matrix() instead.
constructs an uninitialized matrix with rows rows and cols columns.
This is useful for dynamic-size matrices. For fixed-size matrices, it is redundant to pass these parameters, so one should use the default constructor Matrix() instead.
| Array | ( | const Scalar & | val0, |
| const Scalar & | val1 | ||
| ) |
constructs an initialized 2D vector with given coefficients
|
inline |
constructs an initialized 3D vector with given coefficients
|
inline |
constructs an initialized 4D vector with given coefficients
Constructor copying the value of the expression other
Copy constructor
|
inline |
Copy constructor with in-place evaluation
|
inlineprotectedinherited |
Copies the value of the expression other into *this with automatic resizing.
*this might be resized to match the dimensions of other. If *this was a null matrix (not already initialized), it will be initialized.
Note that copying a row-vector into a vector (and conversely) is allowed. The resizing, if any, is then done in the appropriate way so that row-vectors remain row-vectors and vectors remain vectors.
|
inlineinherited |
*this Example:
Output:
1 2 3
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Is ( 0.68 -0.211 0.566) inside the box: 0 Is (0.597 0.823 0.605) inside the box: 1
References Eigen::Dynamic.
|
inlineinherited |
*this contains only finite numbers, i.e., no NaN and no +/-INF values.
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameter CustomBinaryOp is the type of the functor of the custom operator (see class CwiseBinaryOp for an example)
Here is an example illustrating the use of custom functors:
Output:
(0.68,0.271) (0.823,-0.967) (-0.444,-0.687) (-0.27,0.998) (-0.211,0.435) (-0.605,-0.514) (0.108,-0.198) (0.0268,-0.563) (0.566,-0.717) (-0.33,-0.726) (-0.0452,-0.74) (0.904,0.0259) (0.597,0.214) (0.536,0.608) (0.258,-0.782) (0.832,0.678)
|
inlineinherited |
| startRow | the first row in the block |
| startCol | the first column in the block |
| blockRows | the number of rows in the block |
| blockCols | the number of columns in the block |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.block(1, 1, 2, 2): -6 1 -3 0 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 0 0 0 6 0 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of block(Index,Index,Index,Index).
The template parameters BlockRows and BlockCols are the number of rows and columns in the block.
| startRow | the first row in the block |
| startCol | the first column in the block |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.block<2,2>(1,1): -6 1 -3 0 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 0 0 0 6 0 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of block<>(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| BlockRows | number of rows in block as specified at compile-time |
| BlockCols | number of columns in block as specified at compile-time |
| startRow | the first row in the block |
| startCol | the first column in the block |
| blockRows | number of rows in block as specified at run-time |
| blockCols | number of columns in block as specified at run-time |
This function is mainly useful for blocks where the number of rows is specified at compile-time and the number of columns is specified at run-time, or vice versa. The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, blockRows should equal BlockRows unless BlockRows is Dynamic, and the same for the number of columns.
Example:
Output:
Matrix4i m = Matrix4i::Random(); cout << "Here is the matrix m:" << endl << m << endl; cout << "Here is the block:" << endl << m.block<2, Dynamic>(1, 1, 2, 3) << endl; m.block<2, Dynamic>(1, 1, 2, 3).setZero(); cout << "Now the matrix m is:" << endl << m << endl;
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of block<>(Index, Index, Index, Index).
| cRows | the number of rows in the corner |
| cCols | the number of columns in the corner |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.bottomLeftCorner(2, 2): 6 -3 6 6 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 3 9
This is the const version of bottomLeftCorner(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameters CRows and CCols are the number of rows and columns in the corner.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.bottomLeftCorner<2,2>(): 6 -3 6 6 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of bottomLeftCorner<int, int>().
| CRows | number of rows in corner as specified at compile-time |
| CCols | number of columns in corner as specified at compile-time |
| cRows | number of rows in corner as specified at run-time |
| cCols | number of columns in corner as specified at run-time |
This function is mainly useful for corners where the number of rows is specified at compile-time and the number of columns is specified at run-time, or vice versa. The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, cRows should equal CRows unless CRows is Dynamic, and the same for the number of columns.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.bottomLeftCorner<2,Dynamic>(2,2): 6 -3 6 6 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of bottomLeftCorner<int, int>(Index, Index).
| cRows | the number of rows in the corner |
| cCols | the number of columns in the corner |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.bottomRightCorner(2, 2): 0 9 3 9 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 0 6 6 0 0
This is the const version of bottomRightCorner(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameters CRows and CCols are the number of rows and columns in the corner.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.bottomRightCorner<2,2>(): 0 9 3 9 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 0 6 6 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of bottomRightCorner<int, int>().
| CRows | number of rows in corner as specified at compile-time |
| CCols | number of columns in corner as specified at compile-time |
| cRows | number of rows in corner as specified at run-time |
| cCols | number of columns in corner as specified at run-time |
This function is mainly useful for corners where the number of rows is specified at compile-time and the number of columns is specified at run-time, or vice versa. The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, cRows should equal CRows unless CRows is Dynamic, and the same for the number of columns.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.bottomRightCorner<2,Dynamic>(2,2): 0 9 3 9 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 0 6 6 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of bottomRightCorner<int, int>(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| n | the number of rows in the block |
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.bottomRows(2): 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Now the array a is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of bottomRows(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| N | the number of rows in the block as specified at compile-time |
| n | the number of rows in the block as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.bottomRows<2>(): 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Now the array a is: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of bottomRows<int>().
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameter NewScalar is the type we are casting the scalars to.
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
1 4 0 0 5 0 0 6 1
Referenced by VectorwiseOp< ExpressionType, Direction >::cross().
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 0.68 0.597 -0.33 -0.211 0.823 0.536 0.566 -0.605 -0.444 Here is the sum of each column: 1.04 0.815 -0.238 Here is the maximum absolute value of each column: 0.68 0.823 0.536
Referenced by Eigen::umeyama().
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
*this.Resizes the matrix to rows x cols while leaving old values untouched.
The method is intended for matrices of dynamic size. If you only want to change the number of rows and/or of columns, you can use conservativeResize(NoChange_t, Index) or conservativeResize(Index, NoChange_t).
Matrices are resized relative to the top-left element. In case values need to be appended to the matrix they will be uninitialized.
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes the matrix to rows x cols while leaving old values untouched.
As opposed to conservativeResize(Index rows, Index cols), this version leaves the number of columns unchanged.
In case the matrix is growing, new rows will be uninitialized.
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes the matrix to rows x cols while leaving old values untouched.
As opposed to conservativeResize(Index rows, Index cols), this version leaves the number of rows unchanged.
In case the matrix is growing, new columns will be uninitialized.
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes the vector to size while retaining old values.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.. This method does not work for partially dynamic matrices when the static dimension is anything other than 1. For example it will not work with Matrix<double, 2, Dynamic>.
When values are appended, they will be uninitialized.
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes the matrix to rows x cols of other, while leaving old values untouched.
The method is intended for matrices of dynamic size. If you only want to change the number of rows and/or of columns, you can use conservativeResize(NoChange_t, Index) or conservativeResize(Index, NoChange_t).
Matrices are resized relative to the top-left element. In case values need to be appended to the matrix they will copied from other.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameters nbRows and nbCols are the number of rows and of columns of the returned matrix. Must be compatible with this DenseBase type.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size matrix types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass nbRows and nbCols as arguments, so Zero() should be used instead.
The template parameter CustomNullaryOp is the type of the functor.
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameter size is the size of the returned vector. Must be compatible with this DenseBase type.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size vector types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass size as argument, so Zero() should be used instead.
The template parameter CustomNullaryOp is the type of the functor.
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
This variant is only for fixed-size DenseBase types. For dynamic-size types, you need to use the variants taking size arguments.
The template parameter CustomNullaryOp is the type of the functor.
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
*this Example:
Output:
2 4 6 5 1 0
|
inlineinherited |
*this Example:
Output:
4 16 36 25 1 0
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Comparing m with identity matrix: 1 1 0 1 Number of coefficients that are equal: 3
|
inlineinherited |
*this and a scalar s
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
0.5 2 1 0.333 4 1
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Comparing m with identity matrix: 0 0 1 0 Number of coefficients that are not equal: 1
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
a: 7 6 -3 -2 9 6 6 -6 -5 b: 1 -3 9 0 0 3 3 9 5 c: 7 -18 -27 0 0 18 18 -54 -25
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
0.5 1.5 1.33
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
1 1.41 2
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
Notice that in the case of a plain matrix or vector (not an expression) this function just returns a const reference, in order to avoid a useless copy.
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
Alias for setConstant(): sets all coefficients in this expression to val.
Referenced by PermutationBase< PermutationMatrix< SizeAtCompileTime, MaxSizeAtCompileTime, IndexType > >::determinant().
|
inlineinherited |
This is mostly for internal use.
|
inlineinherited |
See class IOFormat for some examples.
|
inlineinherited |
*this contains at least one Not A Number (NaN).
|
inlineinherited |
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
| n | the number of coefficients in the segment |
Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 6 Here is v.head(2): 7 -2 Now the vector v is: 0 0 6 6
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of head(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
| N | the number of coefficients in the segment as specified at compile-time |
| n | the number of coefficients in the segment as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 6 Here is v.head(2): 7 -2 Now the vector v is: 0 0 6 6
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of head<int>().
|
inlineinherited |
*this.
|
inlineinherited |
*this.
|
inlineinherited |
References DenseBase< Derived >::IsRowMajor, and DenseBase< Derived >::IsVectorAtCompileTime.
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
0.5 0.333 0.25
|
inherited |
true if *this is approximately equal to other, within the precision determined by prec.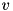 and
and 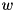 are considered to be approximately equal within precision
are considered to be approximately equal within precision 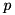 if
if
![\[ \Vert v - w \Vert \leqslant p\,\min(\Vert v\Vert, \Vert w\Vert). \]](form_16.png)
*this is approximately equal to the zero matrix or vector. Indeed, isApprox(zero) returns false unless *this itself is exactly the zero matrix or vector. If you want to test whether *this is zero, use internal::isMuchSmallerThan(const RealScalar&, RealScalar) instead.Referenced by Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::isApprox().
|
inherited |
|
inherited |
This is just an alias for isApproxToConstant().
|
inherited |
true if the norm of *this is much smaller than other, within the precision determined by prec.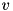 is considered to be much smaller than
is considered to be much smaller than 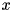 within precision
within precision 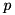 if
if
![\[ \Vert v \Vert \leqslant p\,\vert x\vert. \]](form_18.png)
For matrices, the comparison is done using the Hilbert-Schmidt norm. For this reason, the value of the reference scalar other should come from the Hilbert-Schmidt norm of a reference matrix of same dimensions.
|
inherited |
true if the norm of *this is much smaller than the norm of other, within the precision determined by prec.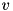 is considered to be much smaller than a vector
is considered to be much smaller than a vector 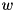 within precision
within precision 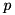 if
if
![\[ \Vert v \Vert \leqslant p\,\Vert w\Vert. \]](form_19.png)
|
inherited |
Example:
Output:
Here's the matrix m: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 m.isOnes() returns: 0 m.isOnes(1e-3) returns: 1
|
inherited |
Example:
Output:
Here's the matrix m:
0 0 0.0001
0 0 0
0 0 0
m.isZero() returns: 0
m.isZero(1e-3) returns: 1
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
| n | the number of columns in the block |
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.leftCols(2): 7 9 -2 -6 6 -3 6 6 Now the array a is: 0 0 -5 -3 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of leftCols(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| N | the number of columns in the block as specified at compile-time |
| n | the number of columns in the block as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.leftCols<2>(): 7 9 -2 -6 6 -3 6 6 Now the array a is: 0 0 -5 -3 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of leftCols<int>().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Sets a linearly space vector.
The function generates 'size' equally spaced values in the closed interval [low,high]. This particular version of LinSpaced() uses sequential access, i.e. vector access is assumed to be a(0), a(1), ..., a(size). This assumption allows for better vectorization and yields faster code than the random access version.
When size is set to 1, a vector of length 1 containing 'high' is returned.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
Example:
Output:
7 8 9 10 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Sets a linearly space vector.
The function generates 'size' equally spaced values in the closed interval [low,high]. When size is set to 1, a vector of length 1 containing 'high' is returned.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
Example:
Output:
7 8 9 10 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Sets a linearly space vector.
The function generates 'size' equally spaced values in the closed interval [low,high]. This particular version of LinSpaced() uses sequential access, i.e. vector access is assumed to be a(0), a(1), ..., a(size). This assumption allows for better vectorization and yields faster code than the random access version.
When size is set to 1, a vector of length 1 containing 'high' is returned.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
Example:
Output:
7 8 9 10 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Sets a linearly space vector.
The function generates 'size' equally spaced values in the closed interval [low,high]. When size is set to 1, a vector of length 1 containing 'high' is returned.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
Example:
Output:
7 8 9 10 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1
References DenseBase< Derived >::NullaryExpr().
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
0 0.693 1.1
|
inlineinherited |
|
inherited |
*this and other Example:
Output:
4 3 4
|
inlineinherited |
*this and scalar other
|
inlineinherited |
*this. *this contains NaN.
|
inherited |
*this contains NaN.
|
inherited |
*this contains NaN.
|
inlineinherited |
| startCol | the index of the first column in the block |
| numCols | the number of columns in the block |
Example:
Output:
A = 7 -6 0 9 -10 -2 -3 3 3 -5 6 6 -3 5 -8 6 -5 0 -8 6 9 1 9 2 -7 A(1..3,:) = -6 0 9 -3 3 3 6 -3 5 -5 0 -8 1 9 2
This is the const version of middleCols(Index,Index).
| N | the number of columns in the block as specified at compile-time |
| startCol | the index of the first column in the block |
| n | the number of columns in the block as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
A = 7 -6 0 9 -10 -2 -3 3 3 -5 6 6 -3 5 -8 6 -5 0 -8 6 9 1 9 2 -7 A(:,1..3) = -6 0 9 -3 3 3 6 -3 5 -5 0 -8 1 9 2
This is the const version of middleCols<int>().
| startRow | the index of the first row in the block |
| n | the number of rows in the block |
Example:
Output:
A = 7 -6 0 9 -10 -2 -3 3 3 -5 6 6 -3 5 -8 6 -5 0 -8 6 9 1 9 2 -7 A(2..3,:) = 6 6 -3 5 -8 6 -5 0 -8 6
This is the const version of middleRows(Index,Index).
| N | the number of rows in the block as specified at compile-time |
| startRow | the index of the first row in the block |
| n | the number of rows in the block as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
A = 7 -6 0 9 -10 -2 -3 3 3 -5 6 6 -3 5 -8 6 -5 0 -8 6 9 1 9 2 -7 A(1..3,:) = -2 -3 3 3 -5 6 6 -3 5 -8 6 -5 0 -8 6
This is the const version of middleRows<int>().
|
inherited |
*this and other Example:
Output:
2 2 3
|
inlineinherited |
*this and scalar other
|
inlineinherited |
*this. *this contains NaN.
|
inherited |
*this contains NaN.
|
inherited |
*this contains NaN.
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameters rows and cols are the number of rows and of columns of the returned matrix. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size matrix types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass rows and cols as arguments, so Zero() should be used instead.
The template parameter CustomNullaryOp is the type of the functor.
Referenced by DenseBase< Derived >::Constant(), MatrixBase< Derived >::Identity(), and DenseBase< Derived >::LinSpaced().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameter size is the size of the returned vector. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size vector types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass size as argument, so Zero() should be used instead.
The template parameter CustomNullaryOp is the type of the functor.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
This variant is only for fixed-size DenseBase types. For dynamic-size types, you need to use the variants taking size arguments.
The template parameter CustomNullaryOp is the type of the functor.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameters nbRows and nbCols are the number of rows and of columns of the returned matrix. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size matrix types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass rows and cols as arguments, so Ones() should be used instead.
Example:
Output:
1 1 1 1 1 1
The parameter newSize is the size of the returned vector. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size vector types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass size as argument, so Ones() should be used instead.
Example:
Output:
6 6 6 6 1 1
|
inlinestaticinherited |
This variant is only for fixed-size MatrixBase types. For dynamic-size types, you need to use the variants taking size arguments.
Example:
Output:
1 1 1 1 6 6 6 6
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
0 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
*this and other
|
inlineinherited |
*this scaled by the scalar factor scalar
|
inlineinherited |
Overloaded for efficient real matrix times complex scalar value
|
inherited |
*this and other
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
1 0 0
Example:
Output:
1 1 0
Example:
Output:
0 0 1
Example:
Output:
0 1 1
Example:
Output:
0 1 0
Example:
Output:
1 0 1
*this with each coeff incremented by the constant scalar Example:
Output:
6 7 8
|
inherited |
*this and other
|
inlineinherited |
*this
|
inlineinherited |
*this with each coeff decremented by the constant scalar Example:
Output:
-4 -3 -2
|
inlineinherited |
*this and other
|
inlineinherited |
*this divided by the scalar value scalar
|
inlineinherited |
Convenient operator to set the coefficients of a matrix.
The coefficients must be provided in a row major order and exactly match the size of the matrix. Otherwise an assertion is raised.
Example:
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0 12 13 0 0 0 1 14 15 16 14 5 6 15 8 9
|
inlineinherited |
The usage of using Base::operator=; fails on MSVC. Since the code below is working with GCC and MSVC, we skipped the usage of 'using'. This should be done only for operator=.
Copies the value of the expression other into *this with automatic resizing.
*this might be resized to match the dimensions of other. If *this was a null matrix (not already initialized), it will be initialized.
Note that copying a row-vector into a vector (and conversely) is allowed. The resizing, if any, is then done in the appropriate way so that row-vectors remain row-vectors and vectors remain vectors.
|
inline |
This is a special case of the templated operator=. Its purpose is to prevent a default operator= from hiding the templated operator=.
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
1 0 1
|
inlineinherited |
References DenseBase< Derived >::IsRowMajor, and DenseBase< Derived >::IsVectorAtCompileTime.
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 0.68 0.597 -0.33 -0.211 0.823 0.536 0.566 -0.605 -0.444 Here is the product of all the coefficients: 0.0019
References Eigen::Dynamic.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameters rows and cols are the number of rows and of columns of the returned matrix. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size matrix types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass rows and cols as arguments, so Random() should be used instead.
Example:
Output:
7 6 9 -2 6 -6
This expression has the "evaluate before nesting" flag so that it will be evaluated into a temporary matrix whenever it is nested in a larger expression. This prevents unexpected behavior with expressions involving random matrices.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameter size is the size of the returned vector. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size vector types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass size as argument, so Random() should be used instead.
Example:
Output:
7 -2
This expression has the "evaluate before nesting" flag so that it will be evaluated into a temporary vector whenever it is nested in a larger expression. This prevents unexpected behavior with expressions involving random matrices.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
This variant is only for fixed-size MatrixBase types. For dynamic-size types, you need to use the variants taking size arguments.
Example:
Output:
700 600 -200 600
This expression has the "evaluate before nesting" flag so that it will be evaluated into a temporary matrix whenever it is nested in a larger expression. This prevents unexpected behavior with expressions involving random matrices.
|
inlineinherited |
*this.
|
inlineinherited |
*this.
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameter BinaryOp is the type of the functor func which must be an associative operator. Both current STL and TR1 functor styles are handled.
|
inlineinherited |
*this Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 6 9 -2 6 -6 m.replicate<3,2>() = ... 7 6 9 7 6 9 -2 6 -6 -2 6 -6 7 6 9 7 6 9 -2 6 -6 -2 6 -6 7 6 9 7 6 9 -2 6 -6 -2 6 -6
|
inlineinherited |
*this Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 v.replicate(2,5) = ... 7 7 7 7 7 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 6 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 7 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 6 6 6 6 6
Resizes *this to a rows x cols matrix.
This method is intended for dynamic-size matrices, although it is legal to call it on any matrix as long as fixed dimensions are left unchanged. If you only want to change the number of rows and/or of columns, you can use resize(NoChange_t, Index), resize(Index, NoChange_t).
If the current number of coefficients of *this exactly matches the product rows * cols, then no memory allocation is performed and the current values are left unchanged. In all other cases, including shrinking, the data is reallocated and all previous values are lost.
Example:
Output:
here's the 2x3 matrix m: 1 2 3 4 5 6 let's resize m to 3x2. This is a conservative resizing because 2*3==3*2. here's the 3x2 matrix m: 1 5 4 3 2 6 now let's resize m to size 2x2. This is NOT a conservative resizing, so it becomes uninitialized: 6.91e-310 2.12e-314 4.94e-324 4.94e-323
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes *this to a vector of length size
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.. This method does not work for partially dynamic matrices when the static dimension is anything other than 1. For example it will not work with Matrix<double, 2, Dynamic>.
Example:
Output:
v: 3 rows, 1 cols w: 1 rows, 3 cols
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes the matrix, changing only the number of columns. For the parameter of type NoChange_t, just pass the special value NoChange as in the example below.
Example:
Output:
m: 3 rows, 5 cols
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes the matrix, changing only the number of rows. For the parameter of type NoChange_t, just pass the special value NoChange as in the example below.
Example:
Output:
m: 5 rows, 4 cols
|
inlineinherited |
Resizes *this to have the same dimensions as other. Takes care of doing all the checking that's needed.
Note that copying a row-vector into a vector (and conversely) is allowed. The resizing, if any, is then done in the appropriate way so that row-vectors remain row-vectors and vectors remain vectors.
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 6 -3 1 -2 9 6 0 6 -6 -5 3 Here is the reverse of m: 3 -5 -6 6 0 6 9 -2 1 -3 6 7 Here is the coefficient (1,0) in the reverse of m: 0 Let us overwrite this coefficient with the value 4. Now the matrix m is: 7 6 -3 1 -2 9 6 4 6 -6 -5 3
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of reverse().
|
inlineinherited |
This is the "in place" version of reverse: it reverses *this.
In most cases it is probably better to simply use the reversed expression of a matrix. However, when reversing the matrix data itself is really needed, then this "in-place" version is probably the right choice because it provides the following additional features:
|
inlineinherited |
| n | the number of columns in the block |
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.rightCols(2): -5 -3 1 0 0 9 3 9 Now the array a is: 7 9 0 0 -2 -6 0 0 6 -3 0 0 6 6 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of rightCols(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| N | the number of columns in the block as specified at compile-time |
| n | the number of columns in the block as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.rightCols<2>(): -5 -3 1 0 0 9 3 9 Now the array a is: 7 9 0 0 -2 -6 0 0 6 -3 0 0 6 6 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of rightCols<int>().
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
1 0 0 4 5 6 0 0 1
Referenced by VectorwiseOp< ExpressionType, Direction >::cross(), and Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::pretranslate().
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 0.68 0.597 -0.33 -0.211 0.823 0.536 0.566 -0.605 -0.444 Here is the sum of each row: 0.948 1.15 -0.483 Here is the maximum absolute value of each row: 0.68 0.823 0.605
Referenced by Eigen::umeyama().
|
inlineinherited |
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
| start | the first coefficient in the segment |
| n | the number of coefficients in the segment |
Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 6 Here is v.segment(1, 2): -2 6 Now the vector v is: 7 0 0 6
This is the const version of segment(Index,Index).
*this This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
| N | the number of coefficients in the segment as specified at compile-time |
| start | the index of the first element in the segment |
| n | the number of coefficients in the segment as specified at compile-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 6 Here is v.segment<2>(1): -2 6 Now the vector v is: 7 -2 0 0
This is the const version of segment<int>(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
Version of DenseBase::select(const DenseBase&, const DenseBase&) with the else expression being a scalar value.
|
inlineinherited |
Version of DenseBase::select(const DenseBase&, const DenseBase&) with the then expression being a scalar value.
|
inlineinherited |
Sets all coefficients in this expression to value.
|
inlineinherited |
Sets a linearly space vector.
The function generates 'size' equally spaced values in the closed interval [low,high]. When size is set to 1, a vector of length 1 containing 'high' is returned.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
Example:
Output:
0.5 0.75 1 1.25 1.5
|
inlineinherited |
Sets a linearly space vector.
The function fill *this with equally spaced values in the closed interval [low,high]. When size is set to 1, a vector of length 1 containing 'high' is returned.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
|
inlineinherited |
Sets all coefficients in this expression to one.
Example:
Output:
7 9 -5 -3 1 1 1 1 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
Sets all coefficients in this expression to random values.
Example:
Output:
0 7 0 0 0 -2 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 6 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
Sets all coefficients in this expression to zero.
Example:
Output:
7 9 -5 -3 0 0 0 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
4 9 16
|
inlineinherited |
References Eigen::Dynamic.
|
inline |
Override MatrixBase::swap() since for dynamic-sized matrices of same type it is enough to swap the data pointers.
|
inlineinherited |
swaps *this with the expression other.
|
inlineinherited |
swaps *this with the matrix or array other.
|
inlineinherited |
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
| n | the number of coefficients in the segment |
Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 6 Here is v.tail(2): 6 6 Now the vector v is: 7 -2 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of tail(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
| N | the number of coefficients in the segment as specified at compile-time |
| n | the number of coefficients in the segment as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the vector v: 7 -2 6 6 Here is v.tail(2): 6 6 Now the vector v is: 7 -2 0 0
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of tail<int>.
|
inlineinherited |
| cRows | the number of rows in the corner |
| cCols | the number of columns in the corner |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.topLeftCorner(2, 2): 7 9 -2 -6 Now the matrix m is: 0 0 -5 -3 0 0 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
This is the const version of topLeftCorner(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameters CRows and CCols are the number of rows and columns in the corner.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.topLeftCorner<2,2>(): 7 9 -2 -6 Now the matrix m is: 0 0 -5 -3 0 0 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of topLeftCorner<int, int>().
| CRows | number of rows in corner as specified at compile-time |
| CCols | number of columns in corner as specified at compile-time |
| cRows | number of rows in corner as specified at run-time |
| cCols | number of columns in corner as specified at run-time |
This function is mainly useful for corners where the number of rows is specified at compile-time and the number of columns is specified at run-time, or vice versa. The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, cRows should equal CRows unless CRows is Dynamic, and the same for the number of columns.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.topLeftCorner<2,Dynamic>(2,2): 7 9 -2 -6 Now the matrix m is: 0 0 -5 -3 0 0 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of topLeftCorner<int, int>(Index, Index).
| cRows | the number of rows in the corner |
| cCols | the number of columns in the corner |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.topRightCorner(2, 2): -5 -3 1 0 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 0 0 -2 -6 0 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
This is the const version of topRightCorner(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| CRows | the number of rows in the corner |
| CCols | the number of columns in the corner |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.topRightCorner<2,2>(): -5 -3 1 0 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 0 0 -2 -6 0 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of topRightCorner<int, int>().
| CRows | number of rows in corner as specified at compile-time |
| CCols | number of columns in corner as specified at compile-time |
| cRows | number of rows in corner as specified at run-time |
| cCols | number of columns in corner as specified at run-time |
This function is mainly useful for corners where the number of rows is specified at compile-time and the number of columns is specified at run-time, or vice versa. The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, cRows should equal CRows unless CRows is Dynamic, and the same for the number of columns.
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is m.topRightCorner<2,Dynamic>(2,2): -5 -3 1 0 Now the matrix m is: 7 9 0 0 -2 -6 0 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of topRightCorner<int, int>(Index, Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| n | the number of rows in the block |
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.topRows(2): 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 Now the array a is: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of topRows(Index).
|
inlineinherited |
| N | the number of rows in the block as specified at compile-time |
| n | the number of rows in the block as specified at run-time |
The compile-time and run-time information should not contradict. In other words, n should equal N unless N is Dynamic.
Example:
Output:
Here is the array a: 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9 Here is a.topRows<2>(): 7 9 -5 -3 -2 -6 1 0 Now the array a is: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 -3 0 9 6 6 3 9
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of topRows<int>().
|
inlineinherited |
Example:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 7 6 -2 6 Here is the transpose of m: 7 -2 6 6 Here is the coefficient (1,0) in the transpose of m: 6 Let us overwrite this coefficient with the value 0. Now the matrix m is: 7 0 -2 6
Referenced by Hyperplane< _Scalar, _AmbientDim, Options >::Through().
|
inlineinherited |
This is the const version of transpose().
Make sure you read the warning for transpose() !
|
inlineinherited |
This is the "in place" version of transpose(): it replaces *this by its own transpose. Thus, doing
has the same effect on m as doing
and is faster and also safer because in the latter line of code, forgetting the eval() results in a bug caused by aliasing.
Notice however that this method is only useful if you want to replace a matrix by its own transpose. If you just need the transpose of a matrix, use transpose().
*this must be a resizable matrix. This excludes (non-square) fixed-size matrices, block-expressions and maps.References Eigen::Dynamic.
|
inlineinherited |
Apply a unary operator coefficient-wise.
| [in] | func | Functor implementing the unary operator |
| CustomUnaryOp | Type of func |
The function ptr_fun() from the C++ standard library can be used to make functors out of normal functions.
Example:
Output:
0.68 0.823 -0.444 -0.27
-0.211 -0.605 0.108 0.0268
0.566 -0.33 -0.0452 0.904
0.597 0.536 0.258 0.832
becomes:
0.68 0.823 0 0
0 0 0.108 0.0268
0.566 0 0 0.904
0.597 0.536 0.258 0.832
Genuine functors allow for more possibilities, for instance it may contain a state.
Example:
Output:
0.68 0.823 -0.444 -0.27
-0.211 -0.605 0.108 0.0268
0.566 -0.33 -0.0452 0.904
0.597 0.536 0.258 0.832
becomes:
0.5 0.5 -0.444 -0.27
-0.211 -0.5 0.108 0.0268
0.5 -0.33 -0.0452 0.5
0.5 0.5 0.258 0.5
|
inlineinherited |
The template parameter CustomUnaryOp is the type of the functor of the custom unary operator.
Example:
Output:
0.68 0.823 -0.444 -0.27
-0.211 -0.605 0.108 0.0268
0.566 -0.33 -0.0452 0.904
0.597 0.536 0.258 0.832
becomes:
0.5 0.5 -0.444 -0.27
-0.211 -0.5 0.108 0.0268
0.5 -0.33 -0.0452 0.5
0.5 0.5 0.258 0.5
|
inlineinherited |
|
inherited |
Applies the visitor visitor to the whole coefficients of the matrix or vector.
The template parameter Visitor is the type of the visitor and provides the following interface:
References Eigen::Dynamic.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
The parameters rows and cols are the number of rows and of columns of the returned matrix. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size matrix types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass rows and cols as arguments, so Zero() should be used instead.
Example:
Output:
0 0 0 0 0 0
The parameter size is the size of the returned vector. Must be compatible with this MatrixBase type.
This is only for vectors (either row-vectors or column-vectors), i.e. matrices which are known at compile-time to have either one row or one column.
This variant is meant to be used for dynamic-size vector types. For fixed-size types, it is redundant to pass size as argument, so Zero() should be used instead.
Example:
Output:
0 0 0 0 0 0
|
inlinestaticinherited |
This variant is only for fixed-size MatrixBase types. For dynamic-size types, you need to use the variants taking size arguments.
Example:
Output:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
|
related |
Outputs the matrix, to the given stream.
If you wish to print the matrix with a format different than the default, use DenseBase::format().
It is also possible to change the default format by defining EIGEN_DEFAULT_IO_FORMAT before including Eigen headers. If not defined, this will automatically be defined to Eigen::IOFormat(), that is the Eigen::IOFormat with default parameters.