 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
Computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of general complex matrices.
This is defined in the Eigenvalues module.
| _MatrixType | the type of the matrix of which we are computing the eigendecomposition; this is expected to be an instantiation of the Matrix class template. |
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix 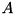 are scalars
are scalars 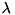 and vectors
and vectors 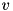 such that
such that 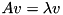 . If
. If 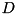 is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the diagonal, and
is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the diagonal, and 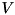 is a matrix with the eigenvectors as its columns, then
is a matrix with the eigenvectors as its columns, then 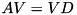 . The matrix
. The matrix 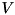 is almost always invertible, in which case we have
is almost always invertible, in which case we have 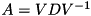 . This is called the eigendecomposition.
. This is called the eigendecomposition.
The main function in this class is compute(), which computes the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a given function. The documentation for that function contains an example showing the main features of the class.
Public Types | |
| typedef std::complex< RealScalar > | ComplexScalar |
| Complex scalar type for MatrixType. More... | |
| typedef Matrix< ComplexScalar, ColsAtCompileTime, 1, Options &(~RowMajor), MaxColsAtCompileTime, 1 > | EigenvalueType |
| Type for vector of eigenvalues as returned by eigenvalues(). More... | |
| typedef Matrix< ComplexScalar, RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime, Options, MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime > | EigenvectorType |
| Type for matrix of eigenvectors as returned by eigenvectors(). More... | |
| typedef _MatrixType | MatrixType |
Synonym for the template parameter _MatrixType. | |
| typedef MatrixType::Scalar | Scalar |
| Scalar type for matrices of type MatrixType. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| ComplexEigenSolver () | |
| Default constructor. More... | |
| ComplexEigenSolver (Index size) | |
| Default Constructor with memory preallocation. More... | |
| ComplexEigenSolver (const MatrixType &matrix, bool computeEigenvectors=true) | |
| Constructor; computes eigendecomposition of given matrix. More... | |
| ComplexEigenSolver & | compute (const MatrixType &matrix, bool computeEigenvectors=true) |
| Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix. More... | |
| const EigenvalueType & | eigenvalues () const |
| Returns the eigenvalues of given matrix. More... | |
| const EigenvectorType & | eigenvectors () const |
| Returns the eigenvectors of given matrix. More... | |
| Index | getMaxIterations () |
| Returns the maximum number of iterations. | |
| ComputationInfo | info () const |
| Reports whether previous computation was successful. More... | |
| ComplexEigenSolver & | setMaxIterations (Index maxIters) |
| Sets the maximum number of iterations allowed. | |
| typedef std::complex<RealScalar> ComplexScalar |
Complex scalar type for MatrixType.
This is std::complex<Scalar> if Scalar is real (e.g., float or double) and just Scalar if Scalar is complex.
| typedef Matrix<ComplexScalar, ColsAtCompileTime, 1, Options&(~RowMajor), MaxColsAtCompileTime, 1> EigenvalueType |
Type for vector of eigenvalues as returned by eigenvalues().
This is a column vector with entries of type ComplexScalar. The length of the vector is the size of MatrixType.
| typedef Matrix<ComplexScalar, RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime, Options, MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime> EigenvectorType |
Type for matrix of eigenvectors as returned by eigenvectors().
This is a square matrix with entries of type ComplexScalar. The size is the same as the size of MatrixType.
|
inline |
Default constructor.
The default constructor is useful in cases in which the user intends to perform decompositions via compute().
|
inline |
Default Constructor with memory preallocation.
Like the default constructor but with preallocation of the internal data according to the specified problem size.
|
inline |
Constructor; computes eigendecomposition of given matrix.
| [in] | matrix | Square matrix whose eigendecomposition is to be computed. |
| [in] | computeEigenvectors | If true, both the eigenvectors and the eigenvalues are computed; if false, only the eigenvalues are computed. |
This constructor calls compute() to compute the eigendecomposition.
References ComplexEigenSolver< _MatrixType >::compute().
| ComplexEigenSolver< MatrixType > & compute | ( | const MatrixType & | matrix, |
| bool | computeEigenvectors = true |
||
| ) |
Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix.
| [in] | matrix | Square matrix whose eigendecomposition is to be computed. |
| [in] | computeEigenvectors | If true, both the eigenvectors and the eigenvalues are computed; if false, only the eigenvalues are computed. |
*this This function computes the eigenvalues of the complex matrix matrix. The eigenvalues() function can be used to retrieve them. If computeEigenvectors is true, then the eigenvectors are also computed and can be retrieved by calling eigenvectors().
The matrix is first reduced to Schur form using the ComplexSchur class. The Schur decomposition is then used to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
The cost of the computation is dominated by the cost of the Schur decomposition, which is 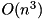 where
where 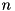 is the size of the matrix.
is the size of the matrix.
Example:
Output:
Here is a random 4x4 matrix, A:
(-0.211,0.68) (0.108,-0.444) (0.435,0.271) (-0.198,-0.687)
(0.597,0.566) (0.258,-0.0452) (0.214,-0.717) (-0.782,-0.74)
(-0.605,0.823) (0.0268,-0.27) (-0.514,-0.967) (-0.563,0.998)
(0.536,-0.33) (0.832,0.904) (0.608,-0.726) (0.678,0.0259)
The eigenvalues of A are:
(0.137,0.505)
(-0.758,1.22)
(1.52,-0.402)
(-0.691,-1.63)
The matrix of eigenvectors, V, is:
(-0.246,-0.106) (0.418,0.263) (0.0417,-0.296) (-0.122,0.271)
(-0.205,-0.629) (0.466,-0.457) (0.244,-0.456) (0.247,0.23)
(-0.432,-0.0359) (-0.0651,-0.0146) (-0.191,0.334) (0.859,-0.0877)
(-0.301,0.46) (-0.41,-0.397) (0.623,0.328) (-0.116,0.195)
Consider the first eigenvalue, lambda = (0.137,0.505)
If v is the corresponding eigenvector, then lambda * v =
(0.0197,-0.139)
(0.29,-0.19)
(-0.0412,-0.223)
(-0.274,-0.0891)
... and A * v =
(0.0197,-0.139)
(0.29,-0.19)
(-0.0412,-0.223)
(-0.274,-0.0891)
Finally, V * D * V^(-1) =
(-0.211,0.68) (0.108,-0.444) (0.435,0.271) (-0.198,-0.687)
(0.597,0.566) (0.258,-0.0452) (0.214,-0.717) (-0.782,-0.74)
(-0.605,0.823) (0.0268,-0.27) (-0.514,-0.967) (-0.563,0.998)
(0.536,-0.33) (0.832,0.904) (0.608,-0.726) (0.678,0.0259)
References Eigen::Success.
Referenced by ComplexEigenSolver< _MatrixType >::ComplexEigenSolver().
|
inline |
Returns the eigenvalues of given matrix.
This function returns a column vector containing the eigenvalues. Eigenvalues are repeated according to their algebraic multiplicity, so there are as many eigenvalues as rows in the matrix. The eigenvalues are not sorted in any particular order.
Example:
Output:
The eigenvalues of the 3x3 matrix of ones are: (0,-0) (0,0) (3,0)
|
inline |
Returns the eigenvectors of given matrix.
computeEigenvectors was set to true (the default).This function returns a matrix whose columns are the eigenvectors. Column 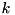 is an eigenvector corresponding to eigenvalue number
is an eigenvector corresponding to eigenvalue number 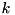 as returned by eigenvalues(). The eigenvectors are normalized to have (Euclidean) norm equal to one. The matrix returned by this function is the matrix
as returned by eigenvalues(). The eigenvectors are normalized to have (Euclidean) norm equal to one. The matrix returned by this function is the matrix 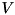 in the eigendecomposition
in the eigendecomposition 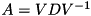 , if it exists.
, if it exists.
Example:
Output:
The first eigenvector of the 3x3 matrix of ones is: (0.154,0) (-0.772,0) (0.617,0)
|
inline |
Reports whether previous computation was successful.
Success if computation was succesful, NoConvergence otherwise. References ComplexSchur< _MatrixType >::info().