 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
Computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of selfadjoint matrices.
This is defined in the Eigenvalues module.
| _MatrixType | the type of the matrix of which we are computing the eigendecomposition; this is expected to be an instantiation of the Matrix class template. |
A matrix 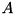 is selfadjoint if it equals its adjoint. For real matrices, this means that the matrix is symmetric: it equals its transpose. This class computes the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a selfadjoint matrix. These are the scalars
is selfadjoint if it equals its adjoint. For real matrices, this means that the matrix is symmetric: it equals its transpose. This class computes the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a selfadjoint matrix. These are the scalars 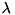 and vectors
and vectors 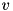 such that
such that 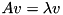 . The eigenvalues of a selfadjoint matrix are always real. If
. The eigenvalues of a selfadjoint matrix are always real. If 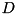 is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the diagonal, and
is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the diagonal, and 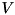 is a matrix with the eigenvectors as its columns, then
is a matrix with the eigenvectors as its columns, then 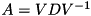 (for selfadjoint matrices, the matrix
(for selfadjoint matrices, the matrix 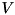 is always invertible). This is called the eigendecomposition.
is always invertible). This is called the eigendecomposition.
The algorithm exploits the fact that the matrix is selfadjoint, making it faster and more accurate than the general purpose eigenvalue algorithms implemented in EigenSolver and ComplexEigenSolver.
Only the lower triangular part of the input matrix is referenced.
Call the function compute() to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a given matrix. Alternatively, you can use the SelfAdjointEigenSolver(const MatrixType&, int) constructor which computes the eigenvalues and eigenvectors at construction time. Once the eigenvalue and eigenvectors are computed, they can be retrieved with the eigenvalues() and eigenvectors() functions.
The documentation for SelfAdjointEigenSolver(const MatrixType&, int) contains an example of the typical use of this class.
To solve the generalized eigenvalue problem 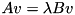 and the likes, see the class GeneralizedSelfAdjointEigenSolver.
and the likes, see the class GeneralizedSelfAdjointEigenSolver.
 Inheritance diagram for SelfAdjointEigenSolver< _MatrixType >:
Inheritance diagram for SelfAdjointEigenSolver< _MatrixType >:Public Types | |
| typedef NumTraits< Scalar >::Real | RealScalar |
Real scalar type for _MatrixType. More... | |
| typedef internal::plain_col_type < MatrixType, RealScalar > ::type | RealVectorType |
| Type for vector of eigenvalues as returned by eigenvalues(). More... | |
| typedef MatrixType::Scalar | Scalar |
Scalar type for matrices of type _MatrixType. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver & | compute (const MatrixType &matrix, int options=ComputeEigenvectors) |
| Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix. More... | |
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver & | computeDirect (const MatrixType &matrix, int options=ComputeEigenvectors) |
| Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix using a direct algorithm. More... | |
| const RealVectorType & | eigenvalues () const |
| Returns the eigenvalues of given matrix. More... | |
| const EigenvectorsType & | eigenvectors () const |
| Returns the eigenvectors of given matrix. More... | |
| ComputationInfo | info () const |
| Reports whether previous computation was successful. More... | |
| MatrixType | operatorInverseSqrt () const |
| Computes the inverse square root of the matrix. More... | |
| MatrixType | operatorSqrt () const |
| Computes the positive-definite square root of the matrix. More... | |
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver () | |
| Default constructor for fixed-size matrices. More... | |
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver (Index size) | |
| Constructor, pre-allocates memory for dynamic-size matrices. More... | |
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver (const MatrixType &matrix, int options=ComputeEigenvectors) | |
| Constructor; computes eigendecomposition of given matrix. More... | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static const int | m_maxIterations |
| Maximum number of iterations. More... | |
| typedef NumTraits<Scalar>::Real RealScalar |
| typedef internal::plain_col_type<MatrixType, RealScalar>::type RealVectorType |
Type for vector of eigenvalues as returned by eigenvalues().
This is a column vector with entries of type RealScalar. The length of the vector is the size of _MatrixType.
|
inline |
Default constructor for fixed-size matrices.
The default constructor is useful in cases in which the user intends to perform decompositions via compute(). This constructor can only be used if _MatrixType is a fixed-size matrix; use SelfAdjointEigenSolver(Index) for dynamic-size matrices.
Example:
Output:
The eigenvalues of A are: -1.58 -0.473 1.32 2.46 The eigenvalues of A+I are: -0.581 0.527 2.32 3.46
|
inline |
Constructor, pre-allocates memory for dynamic-size matrices.
| [in] | size | Positive integer, size of the matrix whose eigenvalues and eigenvectors will be computed. |
This constructor is useful for dynamic-size matrices, when the user intends to perform decompositions via compute(). The size parameter is only used as a hint. It is not an error to give a wrong size, but it may impair performance.
|
inline |
Constructor; computes eigendecomposition of given matrix.
| [in] | matrix | Selfadjoint matrix whose eigendecomposition is to be computed. Only the lower triangular part of the matrix is referenced. |
| [in] | options | Can be ComputeEigenvectors (default) or EigenvaluesOnly. |
This constructor calls compute(const MatrixType&, int) to compute the eigenvalues of the matrix matrix. The eigenvectors are computed if options equals ComputeEigenvectors.
Example:
Output:
Here is a random symmetric 5x5 matrix, A: 1.36 -0.816 0.521 1.43 -0.144 -0.816 -0.659 0.794 -0.173 -0.406 0.521 0.794 -0.541 0.461 0.179 1.43 -0.173 0.461 -1.43 0.822 -0.144 -0.406 0.179 0.822 -1.37 The eigenvalues of A are: -2.65 -1.77 -0.745 0.227 2.29 The matrix of eigenvectors, V, is: 0.326 -0.0984 -0.347 0.0109 0.874 0.207 -0.642 -0.228 -0.662 -0.232 -0.0495 0.629 0.164 -0.74 0.164 -0.721 -0.397 0.402 -0.115 0.385 0.573 -0.156 0.799 0.0256 0.0858 Consider the first eigenvalue, lambda = -2.65 If v is the corresponding eigenvector, then lambda * v = -0.865 -0.55 0.131 1.91 -1.52 ... and A * v = -0.865 -0.55 0.131 1.91 -1.52 Finally, V * D * V^(-1) = 1.36 -0.816 0.521 1.43 -0.144 -0.816 -0.659 0.794 -0.173 -0.406 0.521 0.794 -0.541 0.461 0.179 1.43 -0.173 0.461 -1.43 0.822 -0.144 -0.406 0.179 0.822 -1.37
References SelfAdjointEigenSolver< _MatrixType >::compute().
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver< MatrixType > & compute | ( | const MatrixType & | matrix, |
| int | options = ComputeEigenvectors |
||
| ) |
Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix.
| [in] | matrix | Selfadjoint matrix whose eigendecomposition is to be computed. Only the lower triangular part of the matrix is referenced. |
| [in] | options | Can be ComputeEigenvectors (default) or EigenvaluesOnly. |
*this This function computes the eigenvalues of matrix. The eigenvalues() function can be used to retrieve them. If options equals ComputeEigenvectors, then the eigenvectors are also computed and can be retrieved by calling eigenvectors().
This implementation uses a symmetric QR algorithm. The matrix is first reduced to tridiagonal form using the Tridiagonalization class. The tridiagonal matrix is then brought to diagonal form with implicit symmetric QR steps with Wilkinson shift. Details can be found in Section 8.3 of Golub & Van Loan, Matrix Computations.
The cost of the computation is about 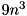 if the eigenvectors are required and
if the eigenvectors are required and 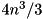 if they are not required.
if they are not required.
This method reuses the memory in the SelfAdjointEigenSolver object that was allocated when the object was constructed, if the size of the matrix does not change.
Example:
Output:
The eigenvalues of A are: -1.58 -0.473 1.32 2.46 The eigenvalues of A+I are: -0.581 0.527 2.32 3.46
References Eigen::ComputeEigenvectors, Eigen::NoConvergence, PlainObjectBase< Derived >::resize(), and Eigen::Success.
Referenced by SelfAdjointEigenSolver< _MatrixType >::SelfAdjointEigenSolver().
| SelfAdjointEigenSolver< MatrixType > & computeDirect | ( | const MatrixType & | matrix, |
| int | options = ComputeEigenvectors |
||
| ) |
Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix using a direct algorithm.
This is a variant of compute(const MatrixType&, int options) which directly solves the underlying polynomial equation.
Currently only 3x3 matrices for which the sizes are known at compile time are supported (e.g., Matrix3d).
This method is usually significantly faster than the QR algorithm but it might also be less accurate. It is also worth noting that for 3x3 matrices it involves trigonometric operations which are not necessarily available for all scalar types.
|
inline |
Returns the eigenvalues of given matrix.
The eigenvalues are repeated according to their algebraic multiplicity, so there are as many eigenvalues as rows in the matrix. The eigenvalues are sorted in increasing order.
Example:
Output:
The eigenvalues of the 3x3 matrix of ones are:
-3.09e-16
0
3
|
inline |
Returns the eigenvectors of given matrix.
Column 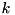 of the returned matrix is an eigenvector corresponding to eigenvalue number
of the returned matrix is an eigenvector corresponding to eigenvalue number 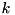 as returned by eigenvalues(). The eigenvectors are normalized to have (Euclidean) norm equal to one. If this object was used to solve the eigenproblem for the selfadjoint matrix
as returned by eigenvalues(). The eigenvectors are normalized to have (Euclidean) norm equal to one. If this object was used to solve the eigenproblem for the selfadjoint matrix 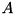 , then the matrix returned by this function is the matrix
, then the matrix returned by this function is the matrix 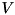 in the eigendecomposition
in the eigendecomposition 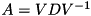 .
.
Example:
Output:
The first eigenvector of the 3x3 matrix of ones is:
0
-0.707
0.707
|
inline |
Reports whether previous computation was successful.
Success if computation was succesful, NoConvergence otherwise.
|
inline |
Computes the inverse square root of the matrix.
This function uses the eigendecomposition 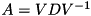 to compute the inverse square root as
to compute the inverse square root as 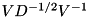 . This is cheaper than first computing the square root with operatorSqrt() and then its inverse with MatrixBase::inverse().
. This is cheaper than first computing the square root with operatorSqrt() and then its inverse with MatrixBase::inverse().
Example:
Output:
Here is a random positive-definite matrix, A: 1.41 -0.697 -0.111 0.508 -0.697 0.423 0.0991 -0.4 -0.111 0.0991 1.25 0.902 0.508 -0.4 0.902 1.4 The inverse square root of A is: 1.88 2.78 -0.546 0.605 2.78 8.61 -2.3 2.74 -0.546 -2.3 1.92 -1.36 0.605 2.74 -1.36 2.18 We can also compute it with operatorSqrt() and inverse(). That yields: 1.88 2.78 -0.546 0.605 2.78 8.61 -2.3 2.74 -0.546 -2.3 1.92 -1.36 0.605 2.74 -1.36 2.18
|
inline |
Computes the positive-definite square root of the matrix.
The square root of a positive-definite matrix  is the positive-definite matrix whose square equals
is the positive-definite matrix whose square equals  . This function uses the eigendecomposition
. This function uses the eigendecomposition 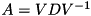 to compute the square root as
to compute the square root as 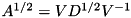 .
.
Example:
Output:
Here is a random positive-definite matrix, A:
1.41 -0.697 -0.111 0.508
-0.697 0.423 0.0991 -0.4
-0.111 0.0991 1.25 0.902
0.508 -0.4 0.902 1.4
The square root of A is:
1.09 -0.432 -0.0685 0.2
-0.432 0.379 0.141 -0.269
-0.0685 0.141 1 0.468
0.2 -0.269 0.468 1.04
If we square this, we get:
1.41 -0.697 -0.111 0.508
-0.697 0.423 0.0991 -0.4
-0.111 0.0991 1.25 0.902
0.508 -0.4 0.902 1.4
|
static |
Maximum number of iterations.
The algorithm terminates if it does not converge within m_maxIterations * n iterations, where n denotes the size of the matrix. This value is currently set to 30 (copied from LAPACK).