In the basic Camel CXF proxy demonstration, the Web services client is actually
implemented as a JUnit test under the src/test directory. This means
that the client can easily be run using the Maven command, mvn test. To
enable SSL/TLS security on the client, the Java implementation of the test client is
completely replaced and a Spring file, containing the SSL/TLS configuration, is
added to the src/test/resources/META-INF/spring directory. Before
describing the steps you need to perform to set up the client, this section explains
some details of the client's Java code and Spring configuration.
Apart from changing the URL scheme on the endpoint address to https:,
most of the configuration to enable SSL/TLS security on a client proxy is contained
in a http:conduit element in Spring configuration. The way in which
this configuration is applied to the client proxy, however, is potentially
confusing, for the following reason: the http:conduit element
does not explicitly reference the client proxy and the
client proxy does not explicitly reference the http:conduit
element. The connection between the http:conduit element
and the client proxy is established implicitly, in that they both reference the same
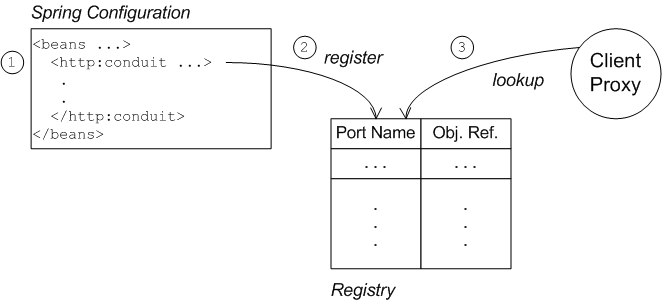
WSDL port, as illustrated by Figure 7.3.
The connection between the client proxy and the http:conduit element
is established as follows:
The client loads and parses the Spring configuration file containing the
http:conduitelement.When the
http:conduitbean is created, a corresponding entry is created in the registry, which stores a reference to the bean under the specified WSDL port name (where the name is stored in QName format).When the JAX-WS client proxy is created, it scans the registry to see if it can find a
http:conduitbean associated with the proxy's WSDL port name. If it finds such a bean, it automatically injects the configuration details into the proxy.
The client is configured with the following keystores from the
src/main/resources/certs directory:
wibble.jksA Java keystore containing the client's own X.509 certificate and private key. In fact, this certificate is not strictly necessary to run the current example, because the server does not require the client to send a certificate during the TLS handshake (see Example 7.2).
truststore.jksA Java keystore containing the CA certificate that issued both the server certificate,
cherry.jks, and the client certificate,wibble.jks.
The example client is not deployed directly into a Spring container, but it
requires some Spring definitions in order to define a secure HTTP conduit. So how
can you create the Spring definitions without a Spring container? It turns out that
it is easy to read Spring definitions into a Java-based client using the
org.apache.cxf.bus.spring.SpringBusFactory class.
The following code shows how to read Spring definitions from the file,
META-INF/spring/cxf-client.xml, and create an Fuse Service Framework Bus
object that incorporates those definitions:
// Java
import org.apache.cxf.bus.spring.SpringBusFactory;
...
protected void startCxfBus() throws Exception {
bf = new SpringBusFactory();
Bus bus = bf.createBus("META-INF/spring/cxf-client.xml");
bf.setDefaultBus(bus);
}In principle, there are several different ways of creating a WSDL proxy: you could
use the JAX-WS API to create a proxy based on the contents of a WSDL file; you could
use the JAX-WS API to create a proxy without a WSDL file; or
you could use the Fuse Service Framework-specific class, JaxWsProxyFactoryBean, to
create a proxy.
For this SSL/TLS client, the most convenient approach is to use the JAX-WS API to create a proxy without using a WSDL file, as shown in the following Java sample:
// Java
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentEndpoint;
...
// create the webservice client and send the request
Service s = Service.create(SERVICE_NAME);
s.addPort(
PORT_NAME,
"http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/",
ADDRESS_URL
);
ReportIncidentEndpoint client =
s.getPort(PORT_NAME, ReportIncidentEndpoint.class);![[Note]](imagesdb/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
In this example, you cannot use the
|
The SERVICE_NAME and PORT_NAME constants are the QNames
of the WSDL service and the WSDL port respectively, as defined in Example 7.1. The ADDRESS_URL string has
the same value as the proxy Web service address and is defined as follows:
private static final String ADDRESS_URL = "https://localhost:9080/camel-example-cxf-proxy/webservices/incident";
In particular, note that the address must be defined with the
URL scheme, https, which selects HTTP over SSL/TLS.
To define a JAX-WS client with SSL/TLS security enabled, perform the following steps:
Example 7.3 shows the complete code for a
Java client that is implemented as a JUnit test case. This client replaces the
existing test, ReportIncidentRoutesTest.java, in the
src/test/java/org/apache/camel/example/reportincident sub-directory
of the examples/camel-example-cxf-proxy demonstration.
To add the client to the
CamelInstallDir/examples/camel-example-cxf-proxysrc/test/java/org/apache/camel/example/reportincident
sub-directory, move the existing ReportIncidentRoutesTest.java file to
a backup location, then create a new ReportIncidentRoutesTest.java file
and paste the code from Example 7.3 into
this file.
Example 7.3. ReportIncidentRoutesTest Java client
// Java
package org.apache.camel.example.reportincident;
import org.apache.camel.spring.Main;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import org.apache.cxf.Bus;
import org.apache.cxf.bus.spring.SpringBusFactory;
import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentEndpoint;
import org.apache.camel.example.reportincident.ReportIncidentEndpointService;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
/**
* Unit test of our routes
*/
public class ReportIncidentRoutesTest {
private static final QName SERVICE_NAME
= new QName("http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org", "ReportIncidentEndpointService");
private static final QName PORT_NAME =
new QName("http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org", "ReportIncidentEndpoint");
private static final String WSDL_URL = "file:src/main/resources/etc/report_incident.wsdl";
// should be the same address as we have in our route
private static final String ADDRESS_URL = "https://localhost:9080/camel-example-cxf-proxy/webservices/incident";
protected SpringBusFactory bf;
protected void startCxfBus() throws Exception {
bf = new SpringBusFactory();
Bus bus = bf.createBus("META-INF/spring/cxf-client.xml");
bf.setDefaultBus(bus);
}
@Test
public void testRendportIncident() throws Exception {
startCxfBus();
runTest();
}
protected void runTest() throws Exception {
// create input parameter
InputReportIncident input = new InputReportIncident();
input.setIncidentId("123");
input.setIncidentDate("2008-08-18");
input.setGivenName("Claus");
input.setFamilyName("Ibsen");
input.setSummary("Bla");
input.setDetails("Bla bla");
input.setEmail("[email protected]");
input.setPhone("0045 2962 7576");
// create the webservice client and send the request
Service s = Service.create(SERVICE_NAME);
s.addPort(PORT_NAME, "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/", ADDRESS_URL);
ReportIncidentEndpoint client = s.getPort(PORT_NAME, ReportIncidentEndpoint.class);
OutputReportIncident out = client.reportIncident(input);
// assert we got a OK back
assertEquals("OK;456", out.getCode());
}
}Example 7.4 shows the Spring
configuration that defines a http:conduit element for the
ReportIncidentEndpoint WSDL port. The http:conduit
element is configured to enable SSL/TLS security for any client proxies that use the
specified WSDL port.
To add the Spring configuration to the client test case, go to the
src/test/resources/META-INF/spring sub-directory, use your favorite
text editor to create the file, cxf-client.xml, and paste the contents
of Example 7.4 into the file.
Example 7.4. http:conduit Element with SSL/TLS Enabled
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:cxf="http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf"
xmlns:sec="http://cxf.apache.org/configuration/security"
xmlns:http="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/http/configuration"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf/camel-cxf.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/configuration/security http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/security.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/transports/http/configuration http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/http-conf.xsd
">
<http:conduit name="{http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org}ReportIncidentEndpoint.http-conduit">
<http:tlsClientParameters disableCNCheck="true">
<sec:trustManagers>
<sec:keyStore type="JKS" password="password"
resource="certs/truststore.jks"/>
</sec:trustManagers>
<sec:keyManagers keyPassword="password">
<sec:keyStore type="JKS" password="password"
resource="certs/wibble.jks"/>
</sec:keyManagers>
<sec:cipherSuitesFilter>
<sec:include>.*_WITH_3DES_.*</sec:include>
<sec:include>.*_WITH_DES_.*</sec:include>
<sec:exclude>.*_WITH_NULL_.*</sec:exclude>
<sec:exclude>.*_DH_anon_.*</sec:exclude>
</sec:cipherSuitesFilter>
</http:tlsClientParameters>
</http:conduit>
</beans>Please note the following points about the preceding configuration:
The
http:andsec:namespace prefixes are needed to define thehttp:conduitelement. In thexsi:schemaLocationelement, it is also essential to specify the locations of the correspondinghttp://cxf.apache.org/configuration/securityandhttp://cxf.apache.org/transports/http/configurationnamespaces.The
disableCNCheckattribute of thehttp:tlsClientParameterselement is set totrue. This means that the client does not check whether the Common Name in the server's X.509 certificate matches the server hostname. For more details, see Special Requirements on HTTPS Certificates in Web Services Security Guide.![[Important]](imagesdb/important.gif)
Important Disabling the CN check is not recommended in a production deployment.
In the
sec:keystoreelements, the certificate locations are specified using theresourceattribute, which finds the certificates on the classpath. When Maven runs the test, it automatically makes the contents ofsrc/main/resourcesavailable on the classpath, so that the certificates can be read from thesrc/main/resources/certsdirectory.![[Note]](imagesdb/note.gif)
Note You also have the option of specifying a certificate location using the
fileattribute, which looks in the filesystem. But theresourceattribute is more suitable for use with applications packaged in bundles.The
sec:cipherSuitesFilterelement is configured to exclude cipher suites matching.*_WITH_NULL_.*and.*_DH_anon_.*. These cipher suites are effectively incomplete and are not intended for normal use.![[Important]](imagesdb/important.gif)
Important It is recommended that you always exclude the ciphers matching
.*_WITH_NULL_.*and.*_DH_anon_.*.
Because the client is defined as a test case, you can run the client using the
standard Maven test goal. To run the client, open a new command window, change
directory to
CamelInstallDir/examples/camel-example-cxf-proxy
mvn test
If the test runs successfully, you should see the following output in the OSGi console window:
Incident was 123, changed to 456 Invoked real web service: id=456 by Claus Ibsen