This section explains how to enable SSL/TLS security on the Camel CXF endpoint,
which acts as a proxy for the real Web service. Assuming that you already have the
X.509 certificates available, all that is required is to add a block of
configuration data to the Spring configuration file (where the configuration data is
contained in a httpj:engine-factory element). There is just one
slightly subtle aspect to this, however: you need to understand how the Camel CXF
endpoint gets associated with the SSL/TLS configuration details.
A WS endpoint can be configured by creating the endpoint in Spring and then
configuring SSL/TLS properties on its Jetty container. The configuration can be
somewhat confusing, however, for the following reason: the Jetty container (which is
configured by a httpj:engine-factory element in Spring) does
not explicitly reference the WS endpoints it contains and the WS
endpoints do not explicitly reference the Jetty container
either. The connection between the Jetty container and its contained endpoints is
established implicitly, in that they are both configured to use the same IP port, as
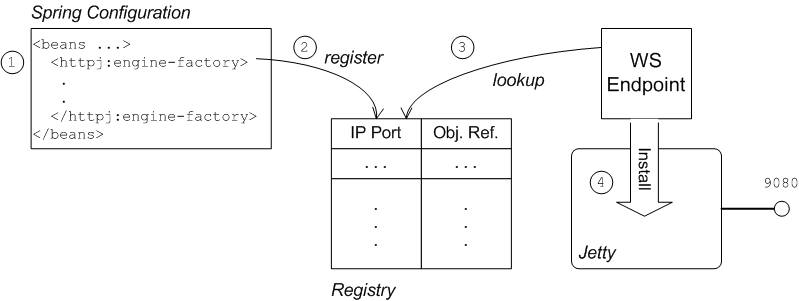
illustrated by Figure 7.2.
The connection between the Web service endpoint and the
httpj:engine-factory element is established as follows:
The Spring container loads and parses the file containing the
httpj:engine-factoryelement.When the
httpj:engine-factorybean is created, a corresponding entry is created in the registry, storing a reference to the bean. Thehttpj:engine-factorybean is also used to initialize a Jetty container that listens on the specified IP port.When the WS endpoint is created, it scans the registry to see if it can find a
httpj:engine-factorybean with the same IP port as the IP port in the endpoint's address URL.If one of the beans matches the endpoint's IP port, the WS endpoint installs itself into the corresponding Jetty container. If the Jetty container has SSL/TLS enabled, the WS endpoint shares those security settings.
To add SSL/TLS security to the Jetty container, thereby securing the WS proxy endpoint, perform the following steps:
The certificates used in this demonstration are taken from a sample in the
Fuse Service Framework 2.4.2-fuse-00-08 product. If you download and install the
standalone version of Fuse Service Framework, you will find the sample certificates in the
CXFInstallDir/samples/wsdl_first_https/certs
Copy the cherry.jks, wibble.jks, and
truststore.jks keystores from the
CXFInstallDir/samples/wsdl_first_https/certsCamelInstallDir/examples/camel-example-cxf-proxy/src/main/resources/certscerts sub-directory).
To configure the Jetty container that listens on IP port 9080 to use SSL/TLS
security, edit the camel-config.xml file in the
src/main/resources/META-INF/spring directory, adding the
httpj:engine-factory element as shown in Example 7.2.
In this example, the required attribute of the
sec:clientAuthentication element is set to false,
which means that a connecting client is not required to present
an X.509 certificate to the server during the SSL/TLS handshake (although it may do
so, if it has such a certificate).
Example 7.2. httpj:engine-factory Element with SSL/TLS Enabled
<beans ... >
...
<httpj:engine-factory bus="cxf">
<httpj:engine port="9080">
<httpj:tlsServerParameters>
<sec:keyManagers keyPassword="password">
<sec:keyStore type="JKS" password="password"
resource="certs/cherry.jks"/>
</sec:keyManagers>
<sec:trustManagers>
<sec:keyStore type="JKS" password="password"
resource="certs/truststore.jks"/>
</sec:trustManagers>
<sec:cipherSuitesFilter>
<sec:include>.*_WITH_3DES_.*</sec:include>
<sec:include>.*_WITH_DES_.*</sec:include>
<sec:exclude>.*_WITH_NULL_.*</sec:exclude>
<sec:exclude>.*_DH_anon_.*</sec:exclude>
</sec:cipherSuitesFilter>
<sec:clientAuthentication want="true" required="false"/>
</httpj:tlsServerParameters>
</httpj:engine>
</httpj:engine-factory>
</beans>Define the sec: and httpj: namespace prefixes, which
appear in the definition of the httpj:engine-factory element, by adding
the following highlighted lines to the beans element in the
camel-config.xml file:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:camel="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring"
xmlns:cxf="http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf"
xmlns:sec="http://cxf.apache.org/configuration/security"
xmlns:httpj="http://cxf.apache.org/transports/http-jetty/configuration"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring/camel-spring.xsd
http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf http://camel.apache.org/schema/cxf/camel-cxf.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/configuration/security http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/security.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/transports/http-jetty/configuration http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/configuration/http-jetty.xsd
">![[Note]](imagesdb/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
It is essential to specify the locations of the
|
The proxy endpoint at the start of the Apache Camel route is configured by the
cxf:cxfEndpoint element in the camel-config.xml file.
By default, this proxy endpoint is configured to use the HTTP protocol. You must
modify the address URL to use the secure HTTPS protocol instead, however. In the
camel-config.xml file, edit the address attribute of the
cxf:cxfEndpoint element, replacing the http: prefix by
the https: prefix, as shown in the following fragment:
<beans ...>
...
<cxf:cxfEndpoint id="reportIncident"
address="https://localhost:9080/camel-example-cxf-proxy/webservices/incident"
endpointName="s:ReportIncidentEndpoint"
serviceName="s:ReportIncidentEndpointService"
wsdlURL="etc/report_incident.wsdl"
xmlns:s="http://reportincident.example.camel.apache.org"/>
...
</beans>Notice also that the address URL is configured to use the IP port,
9080, which implicitly ensures that this endpoint is deployed into
the Jetty container configured by the http:engine-factory element. The
attributes of the cxf:cxfEndpoint specify the WSDL addressing details
as described in WSDL addressing details:
serviceNameSpecifies the WSDL service name.
endpointNameSpecifies the WSDL port name.
addressSpecifies the address URL of the proxy Web service.