QML BorderImage Element
The BorderImage element provides an image that can be used as a border. More...
Inherits Item
Properties
- border.bottom : int
- border.left : int
- border.right : int
- border.top : int
- horizontalTileMode : enumeration
- progress : real
- smooth : bool
- source : url
- status : enumeration
- verticalTileMode : enumeration
Detailed Description
The BorderImage element is used to create borders out of images by scaling or tiling parts of each image.
A BorderImage element breaks a source image, specified using the url property, into 9 regions, as shown below:
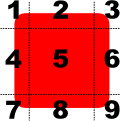
When the image is scaled, regions of the source image are scaled or tiled to create the displayed border image in the following way:
- The corners (regions 1, 3, 7, and 9) are not scaled at all.
- Regions 2 and 8 are scaled according to horizontalTileMode.
- Regions 4 and 6 are scaled according to verticalTileMode.
- The middle (region 5) is scaled according to both horizontalTileMode and verticalTileMode.
The regions of the image are defined using the border property group, which describes the distance from each edge of the source image to use as a border.
Example Usage
The following examples show the effects of the different modes on an image. Guide lines are overlaid onto the image to show the different regions of the image as described above.
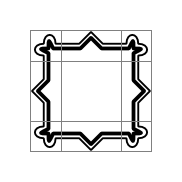
An unscaled image is displayed using an Image element. The border property is used to determine the parts of the image that will lie inside the unscaled corner areas and the parts that will be stretched horizontally and vertically.
Image {
source: "pics/borderframe.png"
}
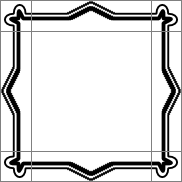
A BorderImage element is used to display the image, and it is given a size that is larger than the original image. Since the horizontalTileMode property is set to BorderImage.Stretch, the parts of image in regions 2 and 8 are stretched horizontally. Since the verticalTileMode property is set to BorderImage.Stretch, the parts of image in regions 4 and 6 are stretched vertically.
BorderImage {
width: 180; height: 180
border { left: 30; top: 30; right: 30; bottom: 30 }
horizontalTileMode: BorderImage.Stretch
verticalTileMode: BorderImage.Stretch
source: "pics/borderframe.png"
}
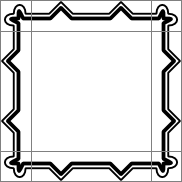
Again, a large BorderImage element is used to display the image. With the horizontalTileMode property set to BorderImage.Repeat, the parts of image in regions 2 and 8 are tiled so that they fill the space at the top and bottom of the element. Similarly, the verticalTileMode property is set to BorderImage.Repeat, the parts of image in regions 4 and 6 are tiled so that they fill the space at the left and right of the element.
BorderImage {
width: 180; height: 180
border { left: 30; top: 30; right: 30; bottom: 30 }
horizontalTileMode: BorderImage.Repeat
verticalTileMode: BorderImage.Repeat
source: "pics/borderframe.png"
}
In some situations, the width of regions 2 and 8 may not be an exact multiple of the width of the corresponding regions in the source image. Similarly, the height of regions 4 and 6 may not be an exact multiple of the height of the corresponding regions. It can be useful to use BorderImage.Round instead of BorderImage.Repeat in cases like these.
The BorderImage example shows how a BorderImage can be used to simulate a shadow effect on a rectangular item.
Quality and Performance
By default, any scaled regions of the image are rendered without smoothing to improve rendering speed. Setting the smooth property improves rendering quality of scaled regions, but may slow down rendering.
The source image may not be loaded instantaneously, depending on its original location. Loading progress can be monitored with the progress property.
See also Image and AnimatedImage.
Property Documentation
The 4 border lines (2 horizontal and 2 vertical) break the image into 9 sections, as shown below:

Each border line (left, right, top, and bottom) specifies an offset in pixels from the respective edge of the source image. By default, each border line has a value of 0.
For example, the following definition sets the bottom line 10 pixels up from the bottom of the image:
border.bottom: 10
The border lines can also be specified using a .sci file.
horizontalTileMode : enumeration |
verticalTileMode : enumeration |
This property describes how to repeat or stretch the middle parts of the border image.
- BorderImage.Stretch - Scales the image to fit to the available area.
- BorderImage.Repeat - Tile the image until there is no more space. May crop the last image.
- BorderImage.Round - Like Repeat, but scales the images down to ensure that the last image is not cropped.
read-onlyprogress : real |
This property holds the progress of image loading, from 0.0 (nothing loaded) to 1.0 (finished).
See also status.
smooth : bool |
Set this property if you want the image to be smoothly filtered when scaled or transformed. Smooth filtering gives better visual quality, but is slower. If the image is displayed at its natural size, this property has no visual or performance effect.
By default, this property is set to false.
Note: Generally scaling artifacts are only visible if the image is stationary on the screen. A common pattern when animating an image is to disable smooth filtering at the beginning of the animation and enable it at the conclusion.
source : url |
This property holds the URL that refers to the source image.
BorderImage can handle any image format supported by Qt, loaded from any URL scheme supported by Qt.
It can also handle .sci files, which are a QML-specific format. A .sci file uses a simple text-based format that specifies the borders, the image file and the tile rules.
The following .sci file sets the borders to 10 on each side for the image picture.png:
border.left: 10 border.top: 10 border.bottom: 10 border.right: 10 source: picture.png
The URL may be absolute, or relative to the URL of the component.
See also QDeclarativeImageProvider.
read-onlystatus : enumeration |
This property describes the status of image loading. It can be one of:
- BorderImage.Null - no image has been set
- BorderImage.Ready - the image has been loaded
- BorderImage.Loading - the image is currently being loaded
- BorderImage.Error - an error occurred while loading the image
See also progress.