CMake Build Configuration
Configuring medium-sized to large CMake projects in Qt Creator can be a challenge due to the number of variables that you need to pass to CMake to configure the project correctly. To make this easier, Qt Creator creates an initial configuration for you based on the kit settings and displays it in Initial Configuration in the Build Settings of the project. Alternatively, you can use CMake presets to configure CMake.
The Configure field displays the effective CMake call that Qt Creator constructs using the values of the Build directory and Build type fields.
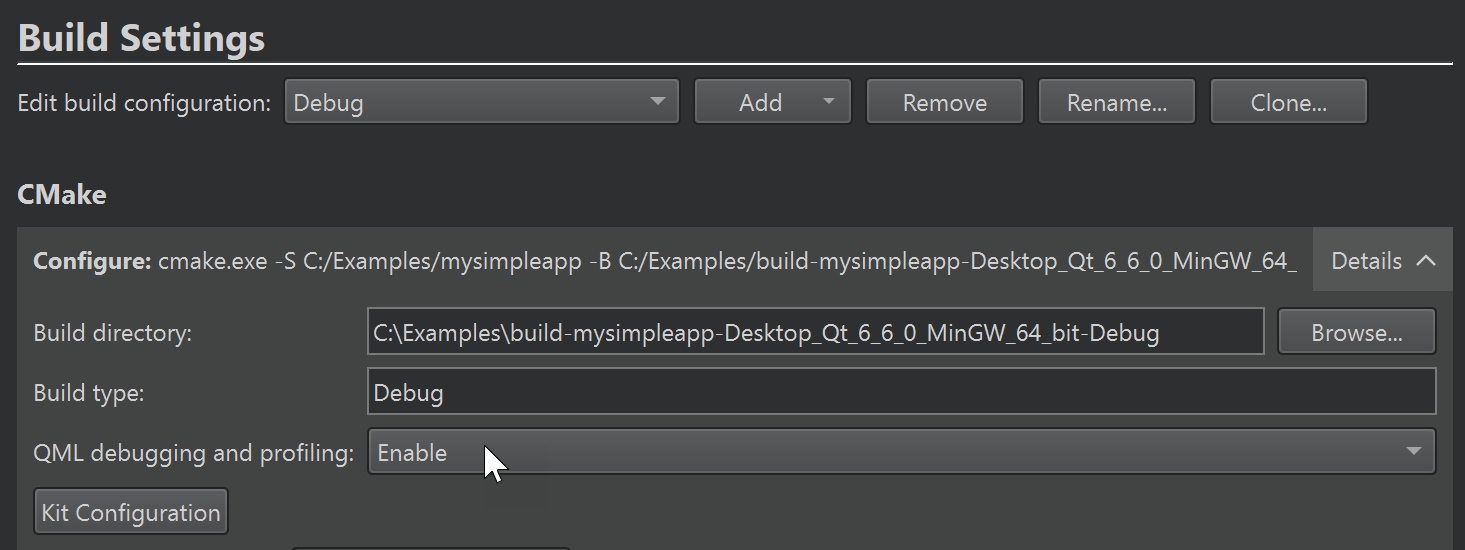
You can specify additional CMake options, such as --find-debug, --trace-expand, or --warn-uninitialized, in Additional CMake options. For more information about the options, click the link in the field name or see CMake: cmake(1).
Select Kit Configuration to edit the CMake settings for the build and run kit selected for the project.
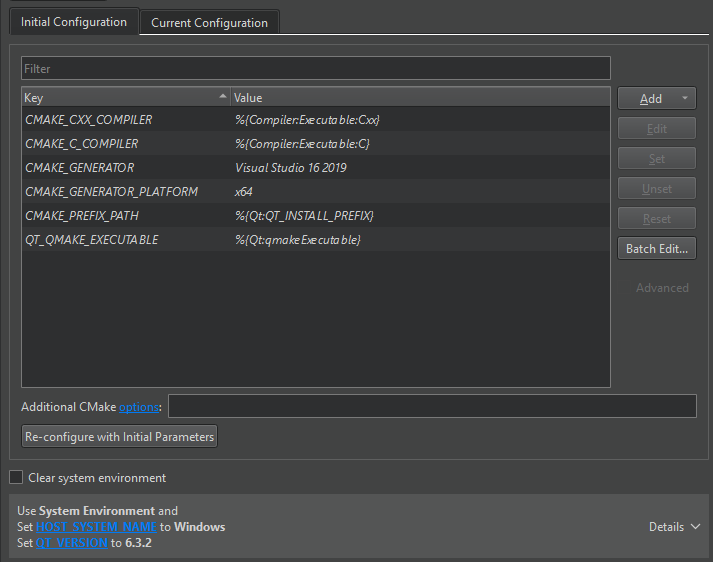
Initial Configuration
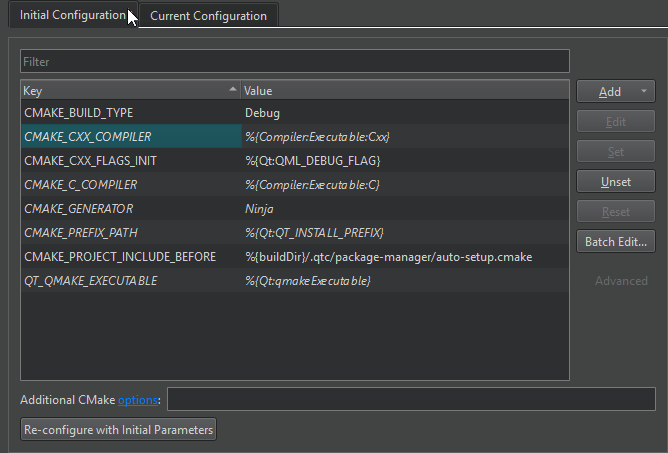
Initial Configuration lists the variables that Qt Creator uses to configure the CMake project for the first time. It shows the default values that come from the kit's CMake configuration in italics. Qt Creator saves the initial configuration list of variables in the project's source directory as the CMakeLists.txt.user file.
Current Configuration
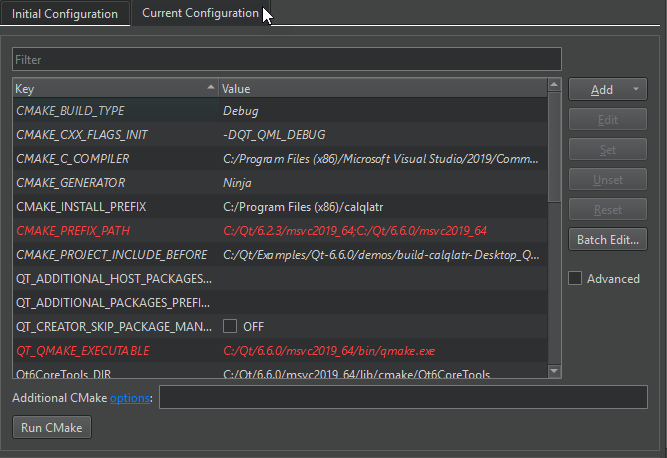
Current Configuration lists the CMake variables in the cmake-file-api JSON export in the .cmake/api/v1/reply directory. It shows the variables that come from the initial configuration in italics and mismatched values in red.
After selecting the Run CMake button, you can view and change the actual values of the variables that Qt Creator passes to CMake. The Key column lists variable names, and the Value column lists their current values. For more information about the variables, select Help in the context menu or see CMake: cmake-variables(7). For more information about Qt-specific variables, see CMake Variable Reference.
CMake Presets
You can use CMake presets files to specify common configure, build, and test options and share them with others. CMakePresets.json has options for project-wide builds, whereas CMakeUserPresets.json has options for your local builds.
Create the presets files in the format described in cmake-presets(7) and store them in project's root directory.
Qt Creator supports presets up to version 3 (introduced in CMake 3.21), but does not enforce version checking. It reads and uses all the fields from version 3 if present. It does not support test presets.
You can import the presets the first time you open a project, when no CMakeLists.txt.user file exists or you have disabled all kits in the project. To update changes to the CMakePresets.json file, delete the CMakeLists.txt.user file.
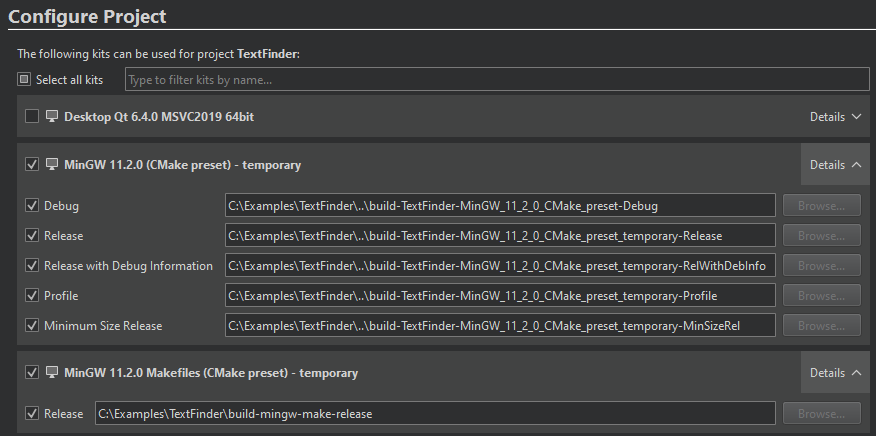
You can view the presets in the Initial Configuration field and in the environment configuration field below it.
Configure Presets
The following configure presets instruct CMake to use the default generator on the platform and specify the build directory for all build types. NOT_COMMON_VALUE is displayed in Initial Parameters and AN_ENVIRONMENT_FLAG in the environment configuration field.
{
"version": 1,
"configurePresets": [
{
"name": "preset",
"displayName": "preset",
"binaryDir": "${sourceDir}/build/preset",
"cacheVariables": {
"NOT_COMMON_VALUE": "NOT_COMMON_VALUE"
},
"environment": {
"AN_ENVIRONMENT_FLAG": "1"
}
}
]
}MinGW Example
The following example configures a Qt project with:
- MinGW compiler
- build directory –
<sourceDir>/build-release - build type –
CMAKE_BUILD_TYPEasRelease - generator – MinGW Makefiles
- path to a CMake executable
- path to the Qt installation via
CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH
{
"version": 1,
"configurePresets": [
{
"name": "mingw",
"displayName": "MinGW 11.2.0",
"generator": "MinGW Makefiles",
"binaryDir": "${sourceDir}/build-release",
"cmakeExecutable": "C:/Qt/Tools/CMake_64/bin/cmake.exe",
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE": "Release",
"CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH": "C:/Qt/6.4.0/mingw_64"
},
"environment": {
"PATH": "C:/Qt/Tools/mingw1120_64/bin;$penv{PATH}"
}
}
]
}To speed up the process on Windows, specify the CMAKE_C_COMPILER and CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER in the cacheVariables section.
Ninja Generator Example
The following configure and build presets set Ninja Multi-Config as the generator, add Debug and Release build steps, and specify the path to ninja.exe as a value of the CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM variable:
{
"version": 2,
"configurePresets": [
{
"name": "ninja-nmc",
"displayName": "Ninja Multi-Config MinGW",
"generator": "Ninja Multi-Config",
"binaryDir": "${sourceDir}/build",
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE": "Debug;Release",
"CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH": "C:/Qt/6.4.0/mingw_64"
"CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM": "C:/Qt/Tools/Ninja/ninja.exe"
},
"environment": {
"PATH": "c:/Qt/Tools/mingw1120_64/bin;$penv{PATH}"
}
}
],
"buildPresets": [
{
"name": "release",
"displayName": "Ninja Release",
"configurePreset": "ninja-nmc",
"configuration": "Release"
},
{
"name": "debug",
"displayName": "Ninja Debug",
"configurePreset": "ninja-nmc",
"configuration": "Debug"
}
]
}This example assumes that the CMake executable path is set in Edit > Preferences > CMake > Tools.
MSVC Example
When using MSVC compilers with NMAKE Makefiles, Ninja, or Ninja Multi-Config generators, you can use the external strategy for the architecture and toolset fields. This lets Qt Creator set up the Visual C++ environment before invoking CMake.
For example:
"generator": "Ninja Multi-Config",
"toolset": {
"value": "v142,host=x64",
"strategy": "external"
},
"architecture": {
"value": "x64",
"strategy": "external"
},If you use MSVC compilers with non-VS generators and have several compilers in the PATH, you might also have to specify the compiler to use in cacheVariables or environmentVariables:
"generator": "Ninja Multi-Config",
"toolset": {
"value": "v142,host=x64",
"strategy": "external"
},
"architecture": {
"value": "x64",
"strategy": "external"
},
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_C_COMPILER": "cl.exe",
"CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER": "cl.exe"
}Using Conditions
The following configure presets are used if they match condition. That is, if the hostSystemName equals Linux, the linux presets are used and if it equals Windows, the windows presets are used.
{
"version": 3,
"configurePresets": [
{
"name": "linux",
"displayName": "Linux GCC",
"binaryDir": "${sourceDir}/build",
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH": "$env{HOME}/Qt/6.4.0/gcc_64"
},
"condition": {
"type": "equals",
"lhs": "${hostSystemName}",
"rhs": "Linux"
}
},
{
"name": "windows",
"displayName": "Windows MSVC",
"binaryDir": "${sourceDir}/build",
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH": "$env{SYSTEMDRIVE}/Qt/6.4.0/msvc2019_64"
},
"condition": {
"type": "equals",
"lhs": "${hostSystemName}",
"rhs": "Windows"
}
}
]
}Multi-Config Support
Qt Creator supports Multi-config generators, such as Xcode, Visual Studio, and Ninja Multi-Config. This means that you need to configure CMake only once, have only one build directory, and can switch between build types faster.
However, this means that Qt Creator can no longer simply parse the first CMake file-api JSON export. Therefore, the value of the Build type field must match that of the CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE variable for the single configuration generators (Ninja, Makefile) to determine, which generator to use.
When developing with Qt 6 for iOS, only the Xcode generator is supported.
Modifying Variable Values
You can view and edit the actual values of the variables that are passed to CMake in Initial Configuration or Current Configuration.

You can select several variables and apply an action to them. To clear the selection, click anywhere in the view.
To change the environment variable values for the CMake build environment, select Batch Edit. For more information, see Batch Editing.
To build using the current configuration, select Run CMake. While building, the button text changes to Stop CMake. Select the button to cancel the current build.
Adding Variables
To add variables, select Add, and then select the type of the variable that you are adding: Boolean, String, Directory, or File.
To change the type of the selected variable, right-click the variable name in the Key column, and then select Force to bool, Force to file, Force to directory, or Force to string in the context menu.
To copy the name or value of the selected variable to the clipboard, select Copy in the context menu.
Changing Variable Values
To change the value of a variable, double-click it, or select it, and then select Edit. If the initial, current, and kit configuration get out of sync, select Apply Kit Value or Apply Initial Configuration Value in the context menu in Initial Configuration or Current Configuration.
To reset all the changes that you made, select Reset.
The variable values that you change are passed via -D<option>=<value> to CMake, which stores the options in the CMakeCache.txt file. This means that if you remove the build directory, all the custom variables that are not part of the initial CMake configuration are also removed.
To reconfigure a project using the changed variable values, select Build > Clear CMake Configuration, which removes the CMakeCache.txt file. This enables you to do a full rebuild.
Removing Variables
To remove the selected variables, select Unset. To undo the removal, select Set.
Viewing Advanced Variables
To view all variables, select the Advanced check box.
To view all variables by default, select Edit > Preferences > CMake > General > Show advanced options by default.
Re-configuring with Initial Variables
To reset CMake variables to the initial ones, select Re-configure with Initial Variables in Initial Configuration. Qt Creator deletes the current CMake configuration and runs CMake. The initial configuration values are stored in the CMakeLists.txt.user file, so deleting a build directory does not delete the initial configuration.
To be asked before Qt Creator resets the changes, select Edit > Preferences > CMake > General > Ask before re-configuring with initial parameters.
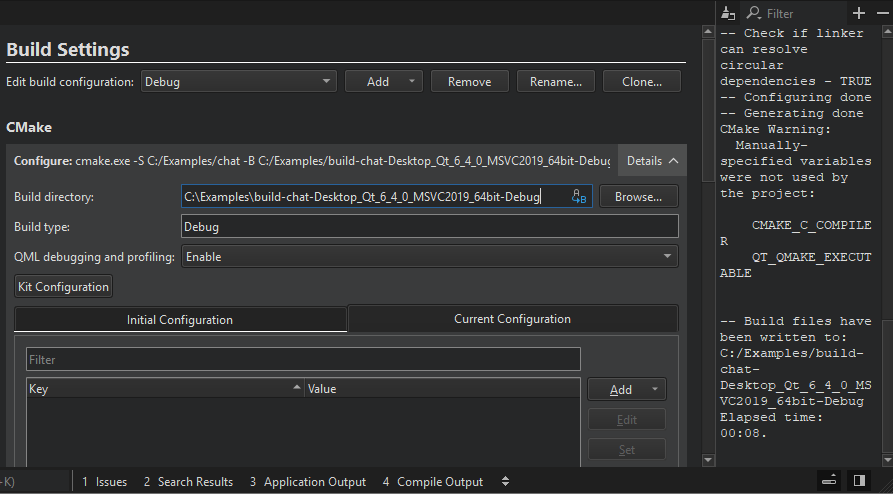
Viewing CMake Output
Output from CMake is displayed next to the Build Settings and Run Settings panes in the Projects mode.
To clear the search results, select the  (Clear) button.
(Clear) button.
You can enter a string in the Filter field to filter output. To specify filtering options, select the 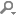 button. You can filter output by using regular expressions or case-sensitivity. Select Show Non-matching Lines to hide the lines that match the filter.
button. You can filter output by using regular expressions or case-sensitivity. Select Show Non-matching Lines to hide the lines that match the filter.
Press Ctrl+F to search for a string from the output.
To increase or decrease the output text size, select  (Zoom In) or
(Zoom In) or  (Zoom Out), or press Ctrl++ or Ctrl+-.
(Zoom Out), or press Ctrl++ or Ctrl+-.
To hide the output, select the ![]() (Hide/Show Right Sidebar) button or press Alt+Shift+0.
(Hide/Show Right Sidebar) button or press Alt+Shift+0.
CMake Build Steps
Qt Creator builds CMake projects by running cmake . --build, which then runs the CMake generator specified in the project configuration: make, mingw32-make, nmake, or ninja, for example. The CMake generator produces project files for Qt Creator. Multi-config generators are also supported.
You can add arguments to pass to CMake and the generator and targets for the build command in Build Steps.
Note: While the other CMake generators are installed together with Qt, you usually need to install Ninja yourself.
Using Ninja as a CMake Generator
To use Ninja with CMake, you must install it and select it as the CMake generator in the build and run kit:
- Install Ninja.
- Add the path to the Ninja executable to the value of the PATH system variable.
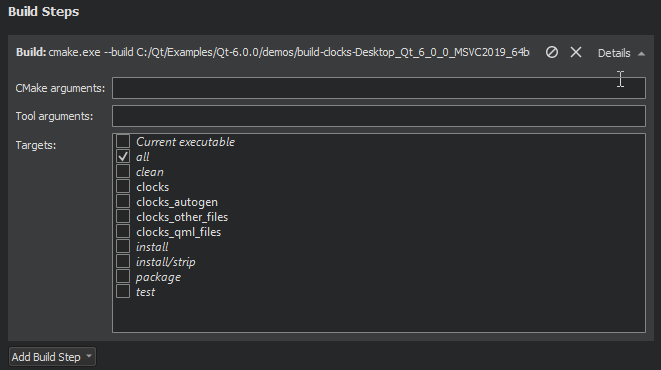
- In Projects > Build & Run > Build > Build Settings, select Kit Configuration.
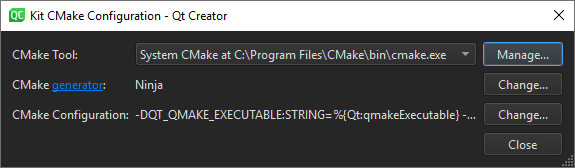
- Select Change next to the CMake generator field to open the CMake Generator dialog.
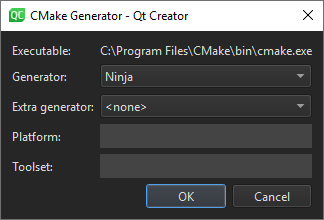
- In Generator, select Ninja.
- Select OK to save your changes and close the dialog.
- Select Close to close the Kit CMake Configuration dialog and return to Build Settings.
Note: To make sure that old build artifacts don't get in the way the first time you build the project after the change, select Build > Rebuild Project. This cleans up the build directory and performs a new build.
Using CMake with Conan
Qt Creator can automatically set up the Conan package manager for use with CMake.
Select Edit > Preferences > CMake General > Package manager auto setup to set the value of the CMAKE_PROJECT_INCLUDE_BEFORE variable to the path to a CMake script that installs dependencies from a conanfile.txt, conanfile.py, or vcpkg.json file in the project source directory.
QTC_RUN Environment Variable
Qt Creator sets the environment variable QTC_RUN to 1 when executing the cmake process.
This enables the CMake code to detect if it's being executed from Qt Creator.
CMake Clean Steps
When building with CMake, you can add arguments to pass to CMake and the generator and targets for the clean command in Clean Steps.
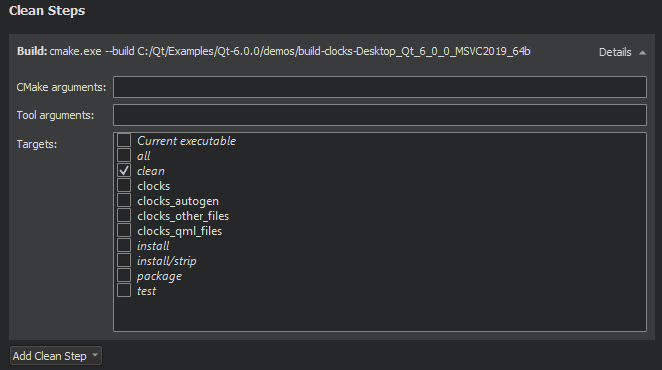
The build errors and warnings are parsed and displayed in Issues.
© 2023 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.