Scilab 6.0.0
Ajuda do Scilab >> CACSD > Control Design > Linear Quadratic > lqg
lqg
LQG compensator
Syntax
[K]=lqg(P,r)
Arguments
- P
syslinlist (augmented plant) in state-space form- r
1x2 row vector = (number of measurements, number of inputs) (dimension of the 2,2 part of
P)- K
syslinlist (controller)
Description
lqg computes the linear optimal LQG (H2) controller for the
"augmented" plant P=syslin('c',A,B,C,D) (continuous time) or
P=syslin('d',A,B,C,D) (discrete time).
The function lqg2stan returns P and r given the
nominal plant, weighting terms and variances of noises.
K is given by the following ABCD matrices:
[A+B*Kc+Kf*C+Kf*D*Kc,-Kf,Kc,0] where Kc=lqr(P12)
is the controller gain and Kf=lqe(P21) is the filter gain.
See example in lqg2stan.
Examples
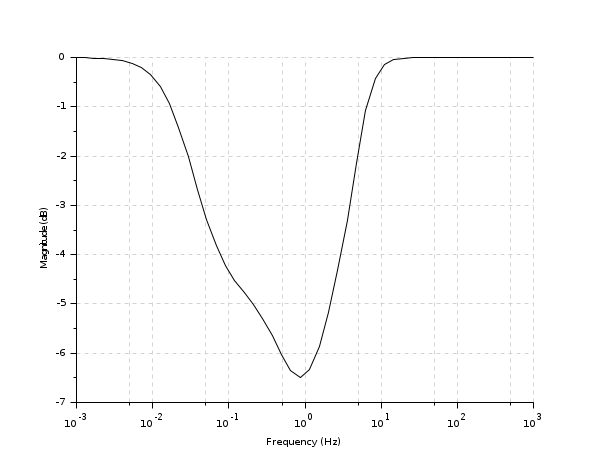
s=poly(0,'s'); Plant=syslin('c',[1/(s+1)*s/(s-1)^2]); //Nominal Plant P22=tf2ss(Plant); //...in state-space form [ny,nu,nx]=size(P22); rand('seed',0);rand('normal'); bigQ=rand(nx+nu,nx+nu); bigQ=bigQ*bigQ'; bigR=rand(nx+ny,nx+ny); bigR=bigR*bigR'; //random weighting matrices [Plqg,r]=lqg2stan(P22,bigQ,bigR); //LQG pb as a standard problem Klqg=lqg(Plqg,r); //Controller spec(h_cl(Plqg,r,Klqg)) //Check internal stability [Slqg,Rlqg,Tlqg]=sensi(P22,Klqg); //Sensitivity functions frq=logspace(-3,3); //10^-3 to 10^3 y=svplot(Slqg); //Computes singular values; gainplot(frq,y) //Plot sing. values

Comments
Add a comment:
Please login to comment this page.