template<typename _MatrixType, typename _OrderingType = COLAMDOrdering<typename _MatrixType::Index>>
class Eigen::SparseLU< _MatrixType, _OrderingType >
Sparse supernodal LU factorization for general matrices.
This class implements the supernodal LU factorization for general matrices. It uses the main techniques from the sequential SuperLU package (http://crd-legacy.lbl.gov/~xiaoye/SuperLU/). It handles transparently real and complex arithmetics with single and double precision, depending on the scalar type of your input matrix. The code has been optimized to provide BLAS-3 operations during supernode-panel updates. It benefits directly from the built-in high-performant Eigen BLAS routines. Moreover, when the size of a supernode is very small, the BLAS calls are avoided to enable a better optimization from the compiler. For best performance, you should compile it with NDEBUG flag to avoid the numerous bounds checking on vectors.
An important parameter of this class is the ordering method. It is used to reorder the columns (and eventually the rows) of the matrix to reduce the number of new elements that are created during numerical factorization. The cheapest method available is COLAMD. See the OrderingMethods module for the list of built-in and external ordering methods.
Simple example with key steps
* SparseMatrix<double, ColMajor> A;
* SparseLU<SparseMatrix<scalar, ColMajor>, COLAMDOrdering<Index> > solver;
*
*
* solver.analyzePattern(A);
*
* solver.factorize(A);
*
* x = solver.solve(b);
*
- Warning
- The input matrix A should be in a compressed and column-major form. Otherwise an expensive copy will be made. You can call the inexpensive makeCompressed() to get a compressed matrix.
- Note
- Unlike the initial SuperLU implementation, there is no step to equilibrate the matrix. For badly scaled matrices, this step can be useful to reduce the pivoting during factorization. If this is the case for your matrices, you can try the basic scaling method at "unsupported/Eigen/src/IterativeSolvers/Scaling.h"
- Template Parameters
-
| _MatrixType | The type of the sparse matrix. It must be a column-major SparseMatrix<> |
| _OrderingType | The ordering method to use, either AMD, COLAMD or METIS. Default is COLMAD |
- See Also
- Sparse solvers
-
OrderingMethods module
Inherits SparseLUImpl< _MatrixType::Scalar, _MatrixType::Index >.
| void factorize |
( |
const MatrixType & |
matrix | ) |
|
0: if info = i, and i is
<= A->ncol: U(i,i) is exactly zero. The factorization has
been completed, but the factor U is exactly singular,
and division by zero will occur if it is used to solve a
system of equations.
> A->ncol: number of bytes allocated when memory allocation
failure occurred, plus A->ncol. If lwork = -1, it is
the estimated amount of space needed, plus A->ncol.
References Eigen::NumericalIssue, PlainObjectBase< Derived >::setConstant(), PlainObjectBase< Derived >::setZero(), and Eigen::Success.
Referenced by SparseLU< _MatrixType, _OrderingType >::compute().


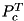 such that
such that 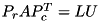
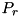 such that
such that 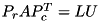
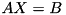 using the current decomposition of A.
using the current decomposition of A.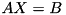 using the current decomposition of A.
using the current decomposition of A.