
Table of Contents
Nuxeo DM is both content management and collaborative work oriented.
The application is organized in domains, that contain workspaces, templates and sections. Documents are created and distributed in these workspaces and sections. The actions available to users in workspaces and sections are determined by access rights.
This section presents the different kind of spaces available in Nuxeo DM. The management of these spaces is presented in the chapter Functional management of Nuxeo DM.
A domain is a thematic space created by the site administrator at the site root. Domains contain workspaces, templates and sections. They enable you to make your site organization more accurate and precise.
When you log in to the site, you are directed to a page where the list of the available domains is displayed.
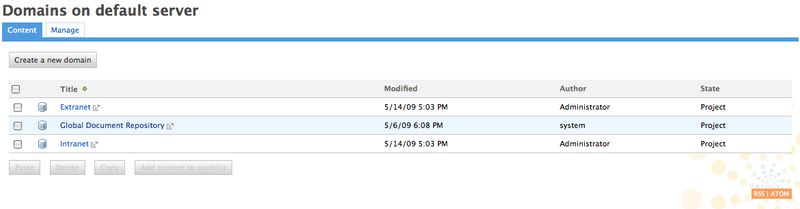
Only the site administrators can create new domains. Members of the application are automatically granted reading rights in the new domain.
When the site administrator creates a domain, three root spaces are automatically created inside it:
Workspaces,
Sections,
Templates.
You must create your workspaces and sections in these root spaces.
Workspaces are dedicated to content creation and modification. There are two types of workspaces:
collaborative workspaces,
personal workspaces.
Collborative workspaces are workspaces meant for collaborative work, that is to say that the workspace's content is meant to be shared and modified by several users. Collaborative workspaces are workspaces created in the root space called Workspaces and shared between users. Once the documents are ready for distribution, they must be published in a section.
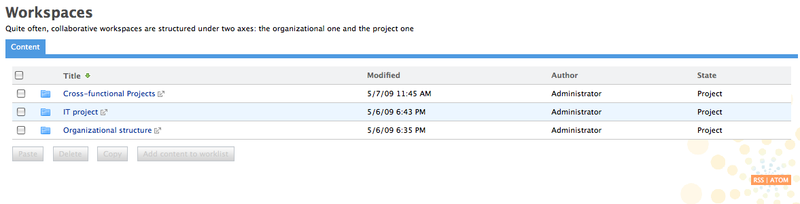
Users have a personal workspace, in which they can create and edit documents. The management of personal workspaces is the same as for collaborative workspaces. By default a personal workspace is accessible only by its owner, but users can give access to it to other users if they want to.
Personal workspaces are accessible in the header of the application.

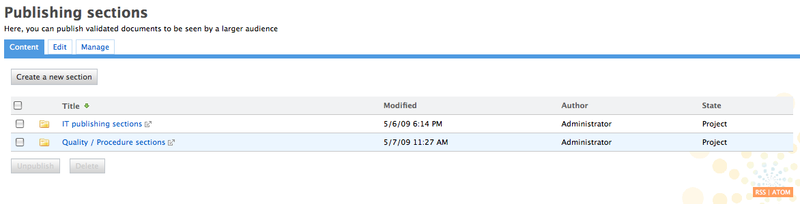
Sections are the areas where you place the documents created in a workspace when they are ready for distribution to the public or a wider audience. Documents published in sections can only be read. You cannot create or edit documents in sections.
You must create sections in the root space called Sections. You can add as many sub-sections as you wish and organize them the way you want. The structures of Workspaces and Sections are independent and thus can be completely different.
The access rights from sections and workspaces are different too: it enables the distribution of documents to a larger audience than the one that participate to the document creation.
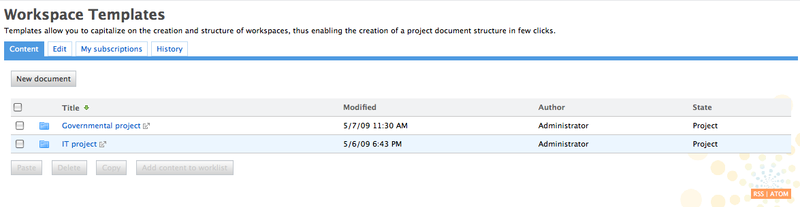
Templates are spaces that can be used as a pattern to create other spaces. They are only available for workspaces. You can create content in it (either folders or documents), as in a regular workspace. When you use the template to create a new workspace, the new workspace gets the structure (folders and documents) defined in the template.
Nuxeo DM enables you to create various types of content, either office automation documents, multimedia documents or tools to ease communication between users.
Nuxeo DM includes several collaborative document types:
Workspaces: workspaces are the basic space in which you can create, share and edit content. You can create as many sub-workspaces as you need to organise your application. You can create any type of content in workspaces.
Folders: Folders are repertories that can contain several documents. The types of document that you can create in a folder are more limited than in a workspace.
Forum: forums are discussion space organized in topics.
Picture book: picture books are spaces in which you can see and edit pictures.
Email folder: folder in which you can fetch mails from any inbox, thus automatically creating documents in your folder with the email's attachements.
Website: displays a workspace conteny as a website in which you can easily create pages and contextual links.
Access rights are permissions granted to users in the different spaces of the application. These access rights determine the actions available to users.
To make rights management easier, Nuxeo DM allow groups of users. You can thus give an ensemble of users the same access rights in a single manipulation.
Access rights can be defined for a whole domain, but also just for a workspace or a section. The rights granted or denied in a space are applied to all its content, including the sub-spaces. This is called rights inheritance. Rights inheritance spares you the declaration of access rights in every single space of the application.
There are four different types of access rights:
reading right,
writing right,
removing right,
management right.
A user who is granted reading rights can read the documents created in the space. He can also read the content's metadata and history, add comments on the document and annotate it.
By default, all users have reading rights on the application's content.
Writing rights enable users to consult, create and edit content in the space. For instance, a user with writing rights can add relations on a document, or start a workflow.
Removing rights enable users to delete content in a space, either documents or sub-spaces.

Users with management rights can consult, create and edit content, but they can also edit the space and manage its access rights.
