 |
OpenCV
3.0.0-dev
Open Source Computer Vision
|
 |
OpenCV
3.0.0-dev
Open Source Computer Vision
|
Classes | |
| class | cv::LineSegmentDetector |
| Line segment detector class. More... | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | cv::LineSegmentDetectorModes { cv::LSD_REFINE_NONE = 0, cv::LSD_REFINE_STD = 1, cv::LSD_REFINE_ADV = 2 } |
Functions | |
| void | cv::Canny (InputArray image, OutputArray edges, double threshold1, double threshold2, int apertureSize=3, bool L2gradient=false) |
| Finds edges in an image using the Canny algorithm [24] . More... | |
| void | cv::cornerEigenValsAndVecs (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int blockSize, int ksize, int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT) |
| Calculates eigenvalues and eigenvectors of image blocks for corner detection. More... | |
| void | cv::cornerHarris (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int blockSize, int ksize, double k, int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT) |
| Harris corner detector. More... | |
| void | cv::cornerMinEigenVal (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int blockSize, int ksize=3, int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT) |
| Calculates the minimal eigenvalue of gradient matrices for corner detection. More... | |
| void | cv::cornerSubPix (InputArray image, InputOutputArray corners, Size winSize, Size zeroZone, TermCriteria criteria) |
| Refines the corner locations. More... | |
| Ptr< LineSegmentDetector > | cv::createLineSegmentDetector (int _refine=LSD_REFINE_STD, double _scale=0.8, double _sigma_scale=0.6, double _quant=2.0, double _ang_th=22.5, double _log_eps=0, double _density_th=0.7, int _n_bins=1024) |
| Creates a smart pointer to a LineSegmentDetector object and initializes it. More... | |
| void | cv::goodFeaturesToTrack (InputArray image, OutputArray corners, int maxCorners, double qualityLevel, double minDistance, InputArray mask=noArray(), int blockSize=3, bool useHarrisDetector=false, double k=0.04) |
| Determines strong corners on an image. More... | |
| void | cv::HoughCircles (InputArray image, OutputArray circles, int method, double dp, double minDist, double param1=100, double param2=100, int minRadius=0, int maxRadius=0) |
| Finds circles in a grayscale image using the Hough transform. More... | |
| void | cv::HoughLines (InputArray image, OutputArray lines, double rho, double theta, int threshold, double srn=0, double stn=0, double min_theta=0, double max_theta=CV_PI) |
| Finds lines in a binary image using the standard Hough transform. More... | |
| void | cv::HoughLinesP (InputArray image, OutputArray lines, double rho, double theta, int threshold, double minLineLength=0, double maxLineGap=0) |
| Finds line segments in a binary image using the probabilistic Hough transform. More... | |
| void | cv::preCornerDetect (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ksize, int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT) |
| Calculates a feature map for corner detection. More... | |
Variants of Line Segment Detector
| void cv::Canny | ( | InputArray | image, |
| OutputArray | edges, | ||
| double | threshold1, | ||
| double | threshold2, | ||
| int | apertureSize = 3, |
||
| bool | L2gradient = false |
||
| ) |
Finds edges in an image using the Canny algorithm [24] .
The function finds edges in the input image image and marks them in the output map edges using the Canny algorithm. The smallest value between threshold1 and threshold2 is used for edge linking. The largest value is used to find initial segments of strong edges. See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canny_edge_detector
| image | 8-bit input image. |
| edges | output edge map; single channels 8-bit image, which has the same size as image . |
| threshold1 | first threshold for the hysteresis procedure. |
| threshold2 | second threshold for the hysteresis procedure. |
| apertureSize | aperture size for the Sobel operator. |
| L2gradient | a flag, indicating whether a more accurate \(L_2\) norm \(=\sqrt{(dI/dx)^2 + (dI/dy)^2}\) should be used to calculate the image gradient magnitude ( L2gradient=true ), or whether the default \(L_1\) norm \(=|dI/dx|+|dI/dy|\) is enough ( L2gradient=false ). |
| void cv::cornerEigenValsAndVecs | ( | InputArray | src, |
| OutputArray | dst, | ||
| int | blockSize, | ||
| int | ksize, | ||
| int | borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT |
||
| ) |
Calculates eigenvalues and eigenvectors of image blocks for corner detection.
For every pixel \(p\) , the function cornerEigenValsAndVecs considers a blockSize \(\times\) blockSize neighborhood \(S(p)\) . It calculates the covariation matrix of derivatives over the neighborhood as:
\[M = \begin{bmatrix} \sum _{S(p)}(dI/dx)^2 & \sum _{S(p)}dI/dx dI/dy \\ \sum _{S(p)}dI/dx dI/dy & \sum _{S(p)}(dI/dy)^2 \end{bmatrix}\]
where the derivatives are computed using the Sobel operator.
After that, it finds eigenvectors and eigenvalues of \(M\) and stores them in the destination image as \((\lambda_1, \lambda_2, x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2)\) where
The output of the function can be used for robust edge or corner detection.
| src | Input single-channel 8-bit or floating-point image. |
| dst | Image to store the results. It has the same size as src and the type CV_32FC(6) . |
| blockSize | Neighborhood size (see details below). |
| ksize | Aperture parameter for the Sobel operator. |
| borderType | Pixel extrapolation method. See cv::BorderTypes. |
| void cv::cornerHarris | ( | InputArray | src, |
| OutputArray | dst, | ||
| int | blockSize, | ||
| int | ksize, | ||
| double | k, | ||
| int | borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT |
||
| ) |
Harris corner detector.
The function runs the Harris corner detector on the image. Similarly to cornerMinEigenVal and cornerEigenValsAndVecs , for each pixel \((x, y)\) it calculates a \(2\times2\) gradient covariance matrix \(M^{(x,y)}\) over a \(\texttt{blockSize} \times \texttt{blockSize}\) neighborhood. Then, it computes the following characteristic:
\[\texttt{dst} (x,y) = \mathrm{det} M^{(x,y)} - k \cdot \left ( \mathrm{tr} M^{(x,y)} \right )^2\]
Corners in the image can be found as the local maxima of this response map.
| src | Input single-channel 8-bit or floating-point image. |
| dst | Image to store the Harris detector responses. It has the type CV_32FC1 and the same size as src . |
| blockSize | Neighborhood size (see the details on cornerEigenValsAndVecs ). |
| ksize | Aperture parameter for the Sobel operator. |
| k | Harris detector free parameter. See the formula below. |
| borderType | Pixel extrapolation method. See cv::BorderTypes. |
| void cv::cornerMinEigenVal | ( | InputArray | src, |
| OutputArray | dst, | ||
| int | blockSize, | ||
| int | ksize = 3, |
||
| int | borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT |
||
| ) |
Calculates the minimal eigenvalue of gradient matrices for corner detection.
The function is similar to cornerEigenValsAndVecs but it calculates and stores only the minimal eigenvalue of the covariance matrix of derivatives, that is, \(\min(\lambda_1, \lambda_2)\) in terms of the formulae in the cornerEigenValsAndVecs description.
| src | Input single-channel 8-bit or floating-point image. |
| dst | Image to store the minimal eigenvalues. It has the type CV_32FC1 and the same size as src . |
| blockSize | Neighborhood size (see the details on cornerEigenValsAndVecs ). |
| ksize | Aperture parameter for the Sobel operator. |
| borderType | Pixel extrapolation method. See cv::BorderTypes. |
| void cv::cornerSubPix | ( | InputArray | image, |
| InputOutputArray | corners, | ||
| Size | winSize, | ||
| Size | zeroZone, | ||
| TermCriteria | criteria | ||
| ) |
Refines the corner locations.
The function iterates to find the sub-pixel accurate location of corners or radial saddle points, as shown on the figure below.
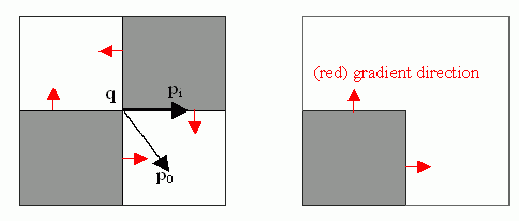
Sub-pixel accurate corner locator is based on the observation that every vector from the center \(q\) to a point \(p\) located within a neighborhood of \(q\) is orthogonal to the image gradient at \(p\) subject to image and measurement noise. Consider the expression:
\[\epsilon _i = {DI_{p_i}}^T \cdot (q - p_i)\]
where \({DI_{p_i}}\) is an image gradient at one of the points \(p_i\) in a neighborhood of \(q\) . The value of \(q\) is to be found so that \(\epsilon_i\) is minimized. A system of equations may be set up with \(\epsilon_i\) set to zero:
\[\sum _i(DI_{p_i} \cdot {DI_{p_i}}^T) - \sum _i(DI_{p_i} \cdot {DI_{p_i}}^T \cdot p_i)\]
where the gradients are summed within a neighborhood ("search window") of \(q\) . Calling the first gradient term \(G\) and the second gradient term \(b\) gives:
\[q = G^{-1} \cdot b\]
The algorithm sets the center of the neighborhood window at this new center \(q\) and then iterates until the center stays within a set threshold.
| image | Input image. |
| corners | Initial coordinates of the input corners and refined coordinates provided for output. |
| winSize | Half of the side length of the search window. For example, if winSize=Size(5,5) , then a \(5*2+1 \times 5*2+1 = 11 \times 11\) search window is used. |
| zeroZone | Half of the size of the dead region in the middle of the search zone over which the summation in the formula below is not done. It is used sometimes to avoid possible singularities of the autocorrelation matrix. The value of (-1,-1) indicates that there is no such a size. |
| criteria | Criteria for termination of the iterative process of corner refinement. That is, the process of corner position refinement stops either after criteria.maxCount iterations or when the corner position moves by less than criteria.epsilon on some iteration. |
| Ptr<LineSegmentDetector> cv::createLineSegmentDetector | ( | int | _refine = LSD_REFINE_STD, |
| double | _scale = 0.8, |
||
| double | _sigma_scale = 0.6, |
||
| double | _quant = 2.0, |
||
| double | _ang_th = 22.5, |
||
| double | _log_eps = 0, |
||
| double | _density_th = 0.7, |
||
| int | _n_bins = 1024 |
||
| ) |
Creates a smart pointer to a LineSegmentDetector object and initializes it.
The LineSegmentDetector algorithm is defined using the standard values. Only advanced users may want to edit those, as to tailor it for their own application.
| _refine | The way found lines will be refined, see cv::LineSegmentDetectorModes |
| _scale | The scale of the image that will be used to find the lines. Range (0..1]. |
| _sigma_scale | Sigma for Gaussian filter. It is computed as sigma = _sigma_scale/_scale. |
| _quant | Bound to the quantization error on the gradient norm. |
| _ang_th | Gradient angle tolerance in degrees. |
| _log_eps | Detection threshold: -log10(NFA) > log_eps. Used only when advancent refinement is chosen. |
| _density_th | Minimal density of aligned region points in the enclosing rectangle. |
| _n_bins | Number of bins in pseudo-ordering of gradient modulus. |
| void cv::goodFeaturesToTrack | ( | InputArray | image, |
| OutputArray | corners, | ||
| int | maxCorners, | ||
| double | qualityLevel, | ||
| double | minDistance, | ||
| InputArray | mask = noArray(), |
||
| int | blockSize = 3, |
||
| bool | useHarrisDetector = false, |
||
| double | k = 0.04 |
||
| ) |
Determines strong corners on an image.
The function finds the most prominent corners in the image or in the specified image region, as described in [126]
The function can be used to initialize a point-based tracker of an object.
| image | Input 8-bit or floating-point 32-bit, single-channel image. |
| corners | Output vector of detected corners. |
| maxCorners | Maximum number of corners to return. If there are more corners than are found, the strongest of them is returned. |
| qualityLevel | Parameter characterizing the minimal accepted quality of image corners. The parameter value is multiplied by the best corner quality measure, which is the minimal eigenvalue (see cornerMinEigenVal ) or the Harris function response (see cornerHarris ). The corners with the quality measure less than the product are rejected. For example, if the best corner has the quality measure = 1500, and the qualityLevel=0.01 , then all the corners with the quality measure less than 15 are rejected. |
| minDistance | Minimum possible Euclidean distance between the returned corners. |
| mask | Optional region of interest. If the image is not empty (it needs to have the type CV_8UC1 and the same size as image ), it specifies the region in which the corners are detected. |
| blockSize | Size of an average block for computing a derivative covariation matrix over each pixel neighborhood. See cornerEigenValsAndVecs . |
| useHarrisDetector | Parameter indicating whether to use a Harris detector (see cornerHarris) or cornerMinEigenVal. |
| k | Free parameter of the Harris detector. |
| void cv::HoughCircles | ( | InputArray | image, |
| OutputArray | circles, | ||
| int | method, | ||
| double | dp, | ||
| double | minDist, | ||
| double | param1 = 100, |
||
| double | param2 = 100, |
||
| int | minRadius = 0, |
||
| int | maxRadius = 0 |
||
| ) |
Finds circles in a grayscale image using the Hough transform.
The function finds circles in a grayscale image using a modification of the Hough transform.
Example: :
| image | 8-bit, single-channel, grayscale input image. |
| circles | Output vector of found circles. Each vector is encoded as a 3-element floating-point vector \((x, y, radius)\) . |
| method | Detection method, see cv::HoughModes. Currently, the only implemented method is HOUGH_GRADIENT |
| dp | Inverse ratio of the accumulator resolution to the image resolution. For example, if dp=1 , the accumulator has the same resolution as the input image. If dp=2 , the accumulator has half as big width and height. |
| minDist | Minimum distance between the centers of the detected circles. If the parameter is too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one. If it is too large, some circles may be missed. |
| param1 | First method-specific parameter. In case of CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the higher threshold of the two passed to the Canny edge detector (the lower one is twice smaller). |
| param2 | Second method-specific parameter. In case of CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the accumulator threshold for the circle centers at the detection stage. The smaller it is, the more false circles may be detected. Circles, corresponding to the larger accumulator values, will be returned first. |
| minRadius | Minimum circle radius. |
| maxRadius | Maximum circle radius. |
| void cv::HoughLines | ( | InputArray | image, |
| OutputArray | lines, | ||
| double | rho, | ||
| double | theta, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| double | srn = 0, |
||
| double | stn = 0, |
||
| double | min_theta = 0, |
||
| double | max_theta = CV_PI |
||
| ) |
Finds lines in a binary image using the standard Hough transform.
The function implements the standard or standard multi-scale Hough transform algorithm for line detection. See http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/hough.htm for a good explanation of Hough transform.
| image | 8-bit, single-channel binary source image. The image may be modified by the function. |
| lines | Output vector of lines. Each line is represented by a two-element vector \((\rho, \theta)\) . \(\rho\) is the distance from the coordinate origin \((0,0)\) (top-left corner of the image). \(\theta\) is the line rotation angle in radians ( \(0 \sim \textrm{vertical line}, \pi/2 \sim \textrm{horizontal line}\) ). |
| rho | Distance resolution of the accumulator in pixels. |
| theta | Angle resolution of the accumulator in radians. |
| threshold | Accumulator threshold parameter. Only those lines are returned that get enough votes ( \(>\texttt{threshold}\) ). |
| srn | For the multi-scale Hough transform, it is a divisor for the distance resolution rho . The coarse accumulator distance resolution is rho and the accurate accumulator resolution is rho/srn . If both srn=0 and stn=0 , the classical Hough transform is used. Otherwise, both these parameters should be positive. |
| stn | For the multi-scale Hough transform, it is a divisor for the distance resolution theta. |
| min_theta | For standard and multi-scale Hough transform, minimum angle to check for lines. Must fall between 0 and max_theta. |
| max_theta | For standard and multi-scale Hough transform, maximum angle to check for lines. Must fall between min_theta and CV_PI. |
| void cv::HoughLinesP | ( | InputArray | image, |
| OutputArray | lines, | ||
| double | rho, | ||
| double | theta, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| double | minLineLength = 0, |
||
| double | maxLineGap = 0 |
||
| ) |
Finds line segments in a binary image using the probabilistic Hough transform.
The function implements the probabilistic Hough transform algorithm for line detection, described in [95]
See the line detection example below:
This is a sample picture the function parameters have been tuned for:

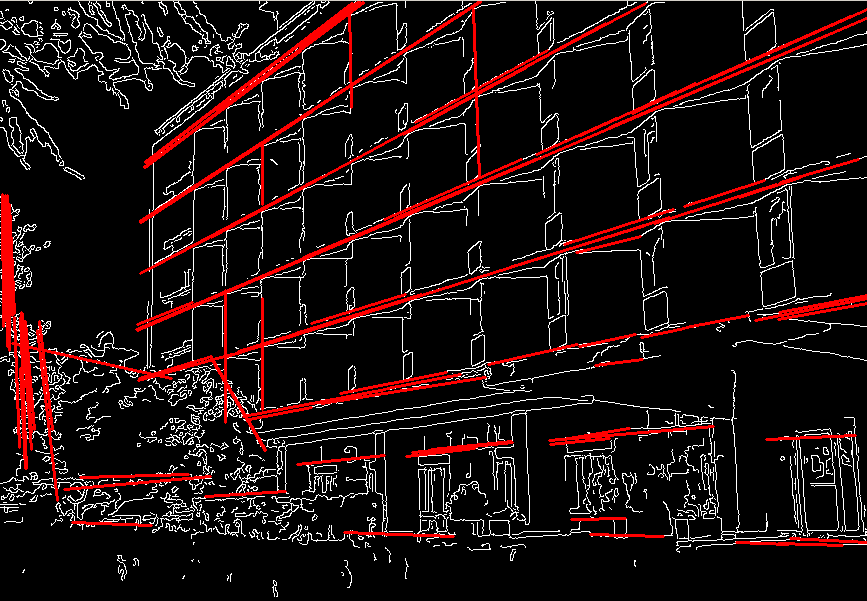
And this is the output of the above program in case of the probabilistic Hough transform:

| image | 8-bit, single-channel binary source image. The image may be modified by the function. |
| lines | Output vector of lines. Each line is represented by a 4-element vector \((x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2)\) , where \((x_1,y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) are the ending points of each detected line segment. |
| rho | Distance resolution of the accumulator in pixels. |
| theta | Angle resolution of the accumulator in radians. |
| threshold | Accumulator threshold parameter. Only those lines are returned that get enough votes ( \(>\texttt{threshold}\) ). |
| minLineLength | Minimum line length. Line segments shorter than that are rejected. |
| maxLineGap | Maximum allowed gap between points on the same line to link them. |
| void cv::preCornerDetect | ( | InputArray | src, |
| OutputArray | dst, | ||
| int | ksize, | ||
| int | borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT |
||
| ) |
Calculates a feature map for corner detection.
The function calculates the complex spatial derivative-based function of the source image
\[\texttt{dst} = (D_x \texttt{src} )^2 \cdot D_{yy} \texttt{src} + (D_y \texttt{src} )^2 \cdot D_{xx} \texttt{src} - 2 D_x \texttt{src} \cdot D_y \texttt{src} \cdot D_{xy} \texttt{src}\]
where \(D_x\), \(D_y\) are the first image derivatives, \(D_{xx}\), \(D_{yy}\) are the second image derivatives, and \(D_{xy}\) is the mixed derivative.
The corners can be found as local maximums of the functions, as shown below:
| src | Source single-channel 8-bit of floating-point image. |
| dst | Output image that has the type CV_32F and the same size as src . |
| ksize | Aperture size of the Sobel . |
| borderType | Pixel extrapolation method. See cv::BorderTypes. |
 1.8.9.1
1.8.9.1