Importing Audio
From Audacity Manual
- If you have already saved your audio as an Audacity Project, use or to open the <my_project_name>.aup. Do not attempt to open, import or manipulate any individual AU files. See Audacity Projects for more information.
Audio File Formats Supported by Audacity
The "native" audio formats (importable by Audacity as shipped) are:
- Uncompressed audio formats: most WAV and AIFF files including all PCM variants.
- Compressed audio formats: Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, MP2 and MP3.
You can install the optional FFmpeg library to import a much larger range of audio formats including AC3, AMR(NB), M4A, MP4 and WMA (if the files are not DRM-protected to work only in particular software). FFmpeg will also import audio from most video files or DVDs that are not DRM-protected. On Mac only, Audacity can import M4A, MP4 and MOV files without FFmpeg.
- Older uncompressed file types such as WAV with U-Law or IMA ADPCM encoding are normally supported provided they contain correctly formatted header information.
- If files do not have header information (such as RAW or VOX ADPCM) or have non-standard header information, you can normally import them using .
- WAV files from portable recorders may contain proprietary compressed audio. These should not be imported as Raw Data, but by installing the FFmpeg library.
- LOF files (lists of files) are also supported if the list is correctly formatted and contains supported files.
Four Ways to Import Audio
No matter which method you use to select an audio file, the file is always imported into an Audacity project. Each imported audio file appears in the Audacity project in its own track.
1. File > Open
- This command will behave differently in the following situations:
- With no Audacity project window open, or an Audacity project window open containing (or that has ever contained) at least one track:
If you select the command, then choose one or more audio files (as opposed to an Audacity project file), Audacity will, for each file chosen, open a new project window then import one of the selected audio files into that new project. Thus if you choose, for example, three audio files, Audacity will create three new project windows with each audio file imported into its own project. - With a clean, empty Audacity project window open (one with no tracks in it and that has never contained any tracks):
If you select the command, then choose one or more audio files, Audacity will import the first file into the empty project window, and import subsequent files into new project windows.
- With no Audacity project window open, or an Audacity project window open containing (or that has ever contained) at least one track:
2. File > Recent Files (Open Recent on Mac)
- This command opens a single file from a list of the 12 most recently imported files. The file opens in a new window exactly as .
3. File > Import > Audio
- If you select the command, then choose one or more audio files, Audacity will import the selected file(s) into the existing project. This is the way to get several audio files into one project.
4. Drag and drop
- On Windows and on Macintosh:
- Drag and drop one or more audio files onto the Audacity icon: this is equivalent to .
- Drag and drop one or more audio files into an open Audacity project window: this is equivalent to .
- On Linux:
- Drag and drop one or more audio files onto the Audacity icon: only the first file will open. More than one file dragged and dropped onto the icon will do the same as the command for the first file, but the other files will generate an error message saying that Audacity is already running.
- Drag and drop files into an open Audacity Project window: this is equivalent to .
Importing Uncompressed Audio Files
The two most common uncompressed file types you will encounter are WAV and AIFF.
Uncompressed files can be imported into Audacity in two ways:
- Make a copy before editing (safer)
When this option is chosen Audacity makes a copy of all imported file(s). It is essential that files are copied into the project if the Audacity project is to be moved, opened on another computer, or sent to someone else. This is the default setting. - Read directly from the original (faster)
When this option is chosen Audacity always reads imported files from the computer folder you first imported them from, without copying them into the project. Therefore with this option set, you must not move, rename or delete imported uncompressed files, or the folder they are in. The advantage of this option is that you can begin editing a long file almost immediately, since On-Demand Loading will be used to import the file.
Dependencies
If you import any uncompressed audio files into your project using the "read directly" option, then your project depends on those files. At any time you can check which files your project depends on by clicking on . See the Dependencies Dialog page for details.
When you save a project you can choose whether or not to copy dependent files into the project. See the Projects Preferences page for details.
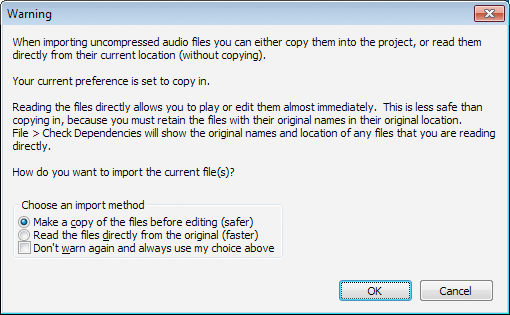
Warning Dialog when Importing Uncompressed Audio Files
The first time you import an uncompressed audio file into Audacity, you will see this dialog.
For each file selected, you can choose:
- Which method to use to import the file.
- Whether to make your choice permanent and never show this warning again.
Importing Compressed Audio Files
When you import a compressed audio file into your project such as MP2, MP3, Ogg Vorbis or FLAC, there is usually no choice between "safer" and "faster" - the file is always copied into the project.
This menu (called "Format" on Mac) contains a list of different file types. Choosing a particular file type in the menu performs two functions.
- The file type choice filters the list of files in the window by restricting it to files of that type.
- The file type choice determines which importer attempts the file first when using the Open or Import Audio dialogs. For example, a WAV file could be imported by Audacity's native WAV importer or by the optional FFmpeg library if this was installed.
Additionally, rules for the order in which different importers attempt files of particular types can be created at Extended Import Preferences with an option to over-ride the Open and Import Audio file type choice. See Import Filtering and Importer Order for more details.