 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
 |
Eigen
3.2.7
|
Two-sided Jacobi SVD decomposition of a rectangular matrix.
| MatrixType | the type of the matrix of which we are computing the SVD decomposition |
| QRPreconditioner | this optional parameter allows to specify the type of QR decomposition that will be used internally for the R-SVD step for non-square matrices. See discussion of possible values below. |
SVD decomposition consists in decomposing any n-by-p matrix A as a product
![\[ A = U S V^* \]](form_164.png)
where U is a n-by-n unitary, V is a p-by-p unitary, and S is a n-by-p real positive matrix which is zero outside of its main diagonal; the diagonal entries of S are known as the singular values of A and the columns of U and V are known as the left and right singular vectors of A respectively.
Singular values are always sorted in decreasing order.
This JacobiSVD decomposition computes only the singular values by default. If you want U or V, you need to ask for them explicitly.
You can ask for only thin U or V to be computed, meaning the following. In case of a rectangular n-by-p matrix, letting m be the smaller value among n and p, there are only m singular vectors; the remaining columns of U and V do not correspond to actual singular vectors. Asking for thin U or V means asking for only their m first columns to be formed. So U is then a n-by-m matrix, and V is then a p-by-m matrix. Notice that thin U and V are all you need for (least squares) solving.
Here's an example demonstrating basic usage:
Output:
Here is the matrix m: 0.68 0.597 -0.211 0.823 0.566 -0.605 Its singular values are: 1.19 0.899 Its left singular vectors are the columns of the thin U matrix: 0.388 0.866 0.712 -0.0634 -0.586 0.496 Its right singular vectors are the columns of the thin V matrix: -0.183 0.983 0.983 0.183 Now consider this rhs vector: 1 0 0 A least-squares solution of m*x = rhs is: 0.888 0.496
This JacobiSVD class is a two-sided Jacobi R-SVD decomposition, ensuring optimal reliability and accuracy. The downside is that it's slower than bidiagonalizing SVD algorithms for large square matrices; however its complexity is still 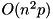 where n is the smaller dimension and p is the greater dimension, meaning that it is still of the same order of complexity as the faster bidiagonalizing R-SVD algorithms. In particular, like any R-SVD, it takes advantage of non-squareness in that its complexity is only linear in the greater dimension.
where n is the smaller dimension and p is the greater dimension, meaning that it is still of the same order of complexity as the faster bidiagonalizing R-SVD algorithms. In particular, like any R-SVD, it takes advantage of non-squareness in that its complexity is only linear in the greater dimension.
If the input matrix has inf or nan coefficients, the result of the computation is undefined, but the computation is guaranteed to terminate in finite (and reasonable) time.
The possible values for QRPreconditioner are:
Public Member Functions | |
| JacobiSVD & | compute (const MatrixType &matrix, unsigned int computationOptions) |
| Method performing the decomposition of given matrix using custom options. More... | |
| JacobiSVD & | compute (const MatrixType &matrix) |
| Method performing the decomposition of given matrix using current options. More... | |
| bool | computeU () const |
| bool | computeV () const |
| JacobiSVD () | |
| Default Constructor. More... | |
| JacobiSVD (Index rows, Index cols, unsigned int computationOptions=0) | |
| Default Constructor with memory preallocation. More... | |
| JacobiSVD (const MatrixType &matrix, unsigned int computationOptions=0) | |
| Constructor performing the decomposition of given matrix. More... | |
| const MatrixUType & | matrixU () const |
| const MatrixVType & | matrixV () const |
| Index | nonzeroSingularValues () const |
| Index | rank () const |
| JacobiSVD & | setThreshold (const RealScalar &threshold) |
| JacobiSVD & | setThreshold (Default_t) |
| const SingularValuesType & | singularValues () const |
| template<typename Rhs > | |
| const internal::solve_retval < JacobiSVD, Rhs > | solve (const MatrixBase< Rhs > &b) const |
| RealScalar | threshold () const |
|
inline |
Default Constructor.
The default constructor is useful in cases in which the user intends to perform decompositions via JacobiSVD::compute(const MatrixType&).
|
inline |
Default Constructor with memory preallocation.
Like the default constructor but with preallocation of the internal data according to the specified problem size.
|
inline |
Constructor performing the decomposition of given matrix.
| matrix | the matrix to decompose |
| computationOptions | optional parameter allowing to specify if you want full or thin U or V unitaries to be computed. By default, none is computed. This is a bit-field, the possible bits are ComputeFullU, ComputeThinU, ComputeFullV, ComputeThinV. |
Thin unitaries are only available if your matrix type has a Dynamic number of columns (for example MatrixXf). They also are not available with the (non-default) FullPivHouseholderQR preconditioner.
| JacobiSVD< MatrixType, QRPreconditioner > & compute | ( | const MatrixType & | matrix, |
| unsigned int | computationOptions | ||
| ) |
Method performing the decomposition of given matrix using custom options.
| matrix | the matrix to decompose |
| computationOptions | optional parameter allowing to specify if you want full or thin U or V unitaries to be computed. By default, none is computed. This is a bit-field, the possible bits are ComputeFullU, ComputeThinU, ComputeFullV, ComputeThinV. |
Thin unitaries are only available if your matrix type has a Dynamic number of columns (for example MatrixXf). They also are not available with the (non-default) FullPivHouseholderQR preconditioner.
References JacobiRotation< Scalar >::transpose().
|
inline |
Method performing the decomposition of given matrix using current options.
| matrix | the matrix to decompose |
This method uses the current computationOptions, as already passed to the constructor or to compute(const MatrixType&, unsigned int).
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
For the SVD decomposition of a n-by-p matrix, letting m be the minimum of n and p, the U matrix is n-by-n if you asked for ComputeFullU, and is n-by-m if you asked for ComputeThinU.
The m first columns of U are the left singular vectors of the matrix being decomposed.
This method asserts that you asked for U to be computed.
Referenced by Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::computeRotationScaling(), Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::computeScalingRotation(), and Eigen::umeyama().
|
inline |
For the SVD decomposition of a n-by-p matrix, letting m be the minimum of n and p, the V matrix is p-by-p if you asked for ComputeFullV, and is p-by-m if you asked for ComputeThinV.
The m first columns of V are the right singular vectors of the matrix being decomposed.
This method asserts that you asked for V to be computed.
Referenced by Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::computeRotationScaling(), Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::computeScalingRotation(), QuaternionBase< Derived >::setFromTwoVectors(), Hyperplane< _Scalar, _AmbientDim, Options >::Through(), and Eigen::umeyama().
|
inline |
|
inline |
*this is the SVD.
|
inline |
Allows to prescribe a threshold to be used by certain methods, such as rank() and solve(), which need to determine when singular values are to be considered nonzero. This is not used for the SVD decomposition itself.
When it needs to get the threshold value, Eigen calls threshold(). The default is NumTraits<Scalar>::epsilon()
| threshold | The new value to use as the threshold. |
A singular value will be considered nonzero if its value is strictly greater than 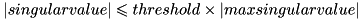 .
.
If you want to come back to the default behavior, call setThreshold(Default_t)
|
inline |
Allows to come back to the default behavior, letting Eigen use its default formula for determining the threshold.
You should pass the special object Eigen::Default as parameter here.
See the documentation of setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
|
inline |
For the SVD decomposition of a n-by-p matrix, letting m be the minimum of n and p, the returned vector has size m. Singular values are always sorted in decreasing order.
Referenced by Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::computeRotationScaling(), Transform< Scalar, Dim, Mode, _Options >::computeScalingRotation(), and Eigen::umeyama().
|
inline |
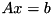 using the current SVD decomposition of A.
using the current SVD decomposition of A.| b | the right-hand-side of the equation to solve. |
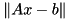 .
.
|
inline |
Returns the threshold that will be used by certain methods such as rank().
See the documentation of setThreshold(const RealScalar&).