- Introduction to MongoDB >
- Getting Started
Getting Started¶
MongoDB Atlas is a cloud-hosted service for provisioning, running, monitoring, and maintaining MongoDB deployments. It is a fast, easy, and free way to get started with MongoDB. To install and run MongoDB locally, see Install MongoDB.
- Mongo Shell
- Compass
- Python
- Node.js
The following tutorial uses
mongo shell to connect to an Atlas free-tier cluster, insert
data, and perform query operations.
MongoDB Compass is the GUI for MongoDB. The following tutorial uses MongoDB Compass to connect to an Atlas free-tier cluster, insert data, and perform query operations.
The following tutorial uses the PyMongo Python driver to connect to an Atlas free-tier cluster, insert data, and perform query operations.
The following tutorial uses the MongoDB Node.js Driver to connect to an Atlas free-tier cluster, then perform insert and query operations.
To learn more about the MongoDB query language and other MongoDB fundamentals, sign up for M001: MongoDB Basics.
Create an Atlas user account.¶
To get started with MongoDB Atlas, create your user account and log in to Atlas.
Create an Atlas Group.¶
Choose a name for your group.
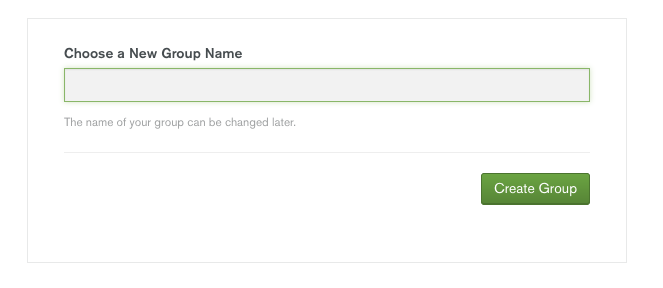
Groups manage related MongoDB deployments. To create additional Atlas groups, click on your user name in the upper-right hand corner and select My Groups. Click the Add Group button.
Create a cluster.¶
MongoDB deployments, or “clusters” in Atlas, can be either a replica set or a sharded cluster.
To create a cluster, go to the Clusters view and click the Add New Cluster or Build a New Cluster button.
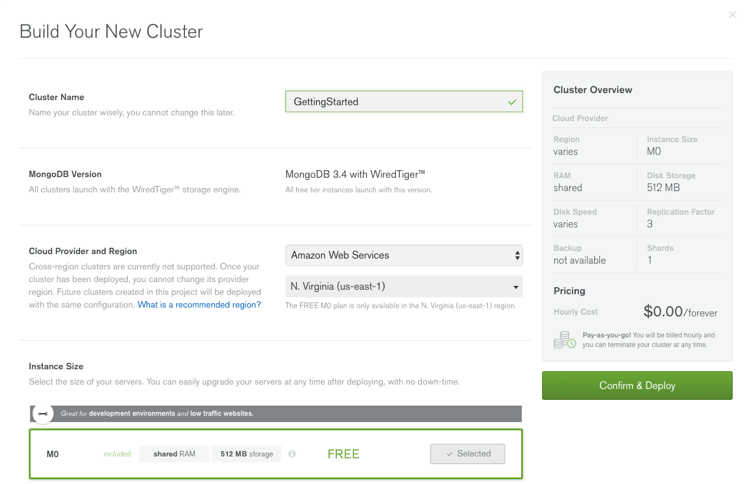
Enter a Cluster Name.
Click the Select button for Instance Size
M0for Atlas Free Tier.Enter a Username and Password.
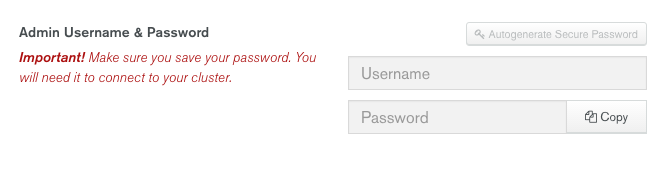
These fields appear only if no MongoDB user exists for your Atlas group. If you created users in the group beforehand these fields will not appear.
Click Confirm & Deploy.
Setup security.¶
Atlas only allows client connections to the cluster from entries in the group’s whitelist. To add an entry to the whitelist:
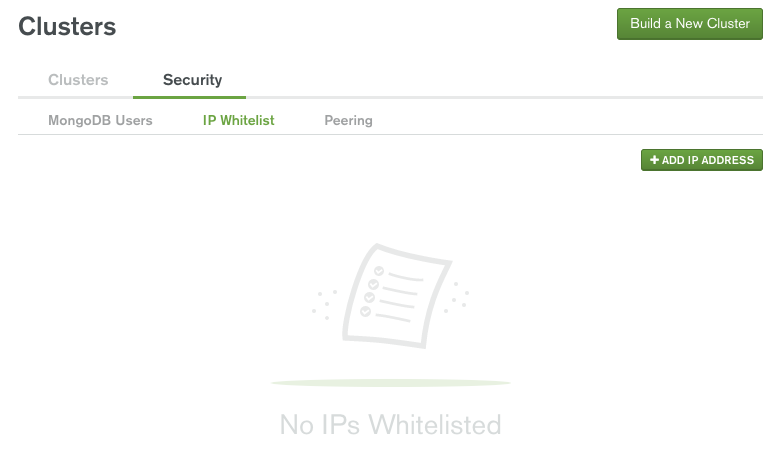
- Click the Security tab from the Clusters view.
- Click IP Whitelist, then Add IP Address. You may either enter the IP address manually in the Whitelist Entry field or click the Add Current IP Address button.
- Click Confirm and wait for Atlas to update the firewall.
Download the connecting client.¶
- Mongo Shell
- Compass
- Python
- Node.js
To download the mongo Shell:
- Click the Connect button from the Clusters view.
- Under the Connect with the Mongo Shell section, select your operating system from the dropdown and click Download Shell.
- Extract the download to the desired location or install the
mongoshell depending on your operating system. - Optionally, add the
<mongodb-install-directory>/binto your operating system’sPATHor environment variables.
For more operating system specific installation information, see Installation.
Download MongoDB Compass from the download center and install it.
Install the PyMongo
driver via pip:
python -m pip install pymongo
For more information, see Installing Pymongo.
First create your project using npm init then install the
MongoDB Node.js Driver via npm:
npm install mongodb --save
For more information, see the Node.js driver Quick Start documentation.
Get the URI connection string.¶
From the MongoDB Atlas Clusters view:
- Click the Connect button to view the URI Connection String.
- Copy the connection string to the clipboard.
- Paste the connection string somewhere and replace
<PASSWORD>with the password for the user created earlier, and<DATABASE>with the name of the database to which you wish to connect. In the following examples, thetestdatabase is used. - Copy the modified URI to the clipboard.
Connect to the cluster.¶
Using the URI string from the previous step, connect to the Atlas cluster:
- Mongo Shell
- Compass
- Python
- Node.js
<mongodb-install-directory>/bin/mongo "mongodb://user123:[email protected]:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-01-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-02-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017/test?ssl=true&replicaSet=GettingStarted-shard-0&authSource=admin"
Alternatively, if you added <mongodb-install-directory>/bin to
the PATH then you may run:
mongo "mongodb://user123:[email protected]:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-01-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-02-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017/test?ssl=true&replicaSet=GettingStarted-shard-0&authSource=admin"
For Windows, run:
"C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.4\bin\mongo.exe" "mongodb://user123:[email protected]:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-01-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-02-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017/test?ssl=true&replicaSet=GettingStarted-shard-0&authSource=admin"
Launch MongoDB Compass with the URI from the previous step copied to the clipboard.
A dialog box will prompt you to use the URI to fill out the connect form. Click Yes.
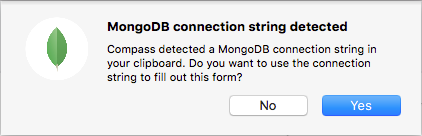
Enter the Password.
Optionally enter a Favorite Name and click Create Favorite to save these settings under Favorites to connect more quickly in future sessions.

Click Connect.
from pymongo import MongoClient
client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://user123:[email protected]:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-01-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-02-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017/test?ssl=true&replicaSet=GettingStarted-shard-0&authSource=admin")
db = client.test
# Paste the following examples here
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var uri = "mongodb://user123:[email protected]:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-01-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017,gettingstarted-shard-00-02-hyjsm.mongodb.net:27017/test?ssl=true&replicaSet=GettingStarted-shard-0&authSource=admin";
MongoClient.connect(uri, function(err, db) {
// Paste the following examples here
db.close();
});
Documents and Collections¶
MongoDB stores data as BSON documents (binary represenatation of JSON) in collections. MongoDB databases hold collections of documents.
Insert Documents¶
- Mongo Shell
- Compass
- Python
- Node.js
db.collection.insertMany() can insert multiple
documents into a collection. Pass an
array of documents to the method.
The following example inserts new documents into the inventory
collection:
db.inventory.insertMany([
// MongoDB adds the _id field with an ObjectId if _id is not present
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, status: "A",
size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blank", "red" ] },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, status: "A",
size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, tags: [ "red", "blank" ] },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, status: "D",
size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, tags: [ "red", "blank", "plain" ] },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, status: "D",
size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blank", "red" ] },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, status: "A",
size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blue" ] }
]);
insertMany() returns a document that includes
the newly inserted documents _id field values. See the
reference for an example.
Use db.collection.insertOne() to insert a single document.
Click Create Database.
Enter “retail” for the Database Name and “inventory” for the Collection Name then click Create Database.
From the Collections tab, click the “inventory” collection link.
Click the Insert Document button.
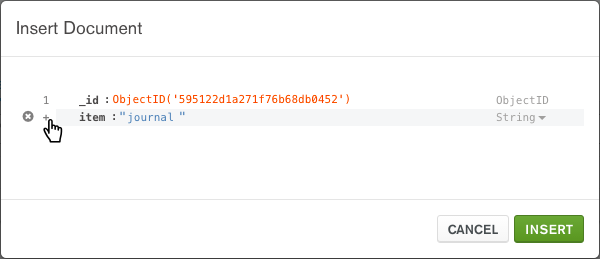
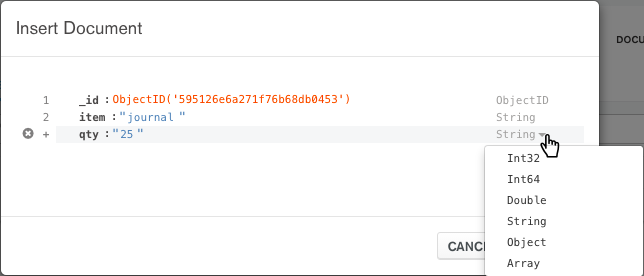
Insert the following document by entering the
fieldsandvalues, then selecting the appropriate types from the dropdowns. Add fields by clicking the last line number, then clicking Add Field After ….{ item: "journal", qty: 25, status: "A", size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blank", "red" ] }
- For
Objecttypes, add nested fields by clicking the last field’s number and selecting Add Field After …. - For
Arraytypes, add additional elements to the array by clicking the last element’s line number and selecting Add Array Element After ….
- For
Repeat steps 4 and 5 to add additional documents:
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, status: "A", size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, tags: [ "red", "blank" ] }, { item: "paper", qty: 100, status: "D", size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, tags: [ "red", "blank", "plain" ] }, { item: "planner", qty: 75, status: "D", size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blank", "red" ] }, { item: "postcard", qty: 45, status: "A", size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blue" ] }
pymongo.collection.Collection.insert_many() can insert
multiple documents into a collection.
Pass an array of documents to the method.
The following example inserts new documents into the inventory
collection:
db.inventory.insert_many([
# MongoDB adds the _id field with an ObjectId if _id is not present
{ "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "status": "A",
"size": { "h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm" }, "tags": [ "blank", "red" ] },
{ "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "status": "A",
"size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "tags": [ "red", "blank" ] },
{ "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "status": "D",
"size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "tags": [ "red", "blank", "plain" ] },
{ "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "status": "D",
"size": { "h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm" }, "tags": [ "blank", "red" ] },
{ "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "status": "A",
"size": { "h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm" }, "tags": [ "blue" ] }
])
insert_many() returns a
document that includes the newly inserted documents _id field
values. See the reference for an example.
Use pymongo.collection.Collection.insert_one() to insert a
single document.
Collection.insertMany() can insert multiple documents into a collection. Pass an array of documents to the method.
The following example inserts new documents into the inventory
collection:
db.collection('inventory').insertMany([
// MongoDB adds the _id field with an ObjectId if _id is not present
{ item: "journal", qty: 25, status: "A",
size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blank", "red" ] },
{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, status: "A",
size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, tags: [ "red", "blank" ] },
{ item: "paper", qty: 100, status: "D",
size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, tags: [ "red", "blank", "plain" ] },
{ item: "planner", qty: 75, status: "D",
size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blank", "red" ] },
{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, status: "A",
size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, tags: [ "blue" ] }
])
.then(function(result) {
// process result
})
insertMany() returns a
document that includes the newly inserted documents _id field
values. See the reference for an example.
Use Collection.insertOne() to insert a single document.
For more information and examples, see Insert Documents in the CRUD section.
Query Documents¶
Select All Documents¶
- Mongo Shell
- Compass
- Python
- Node.js
To select all documents in the collection, pass an empty document as the
query filter document to the
db.collection.find() method:
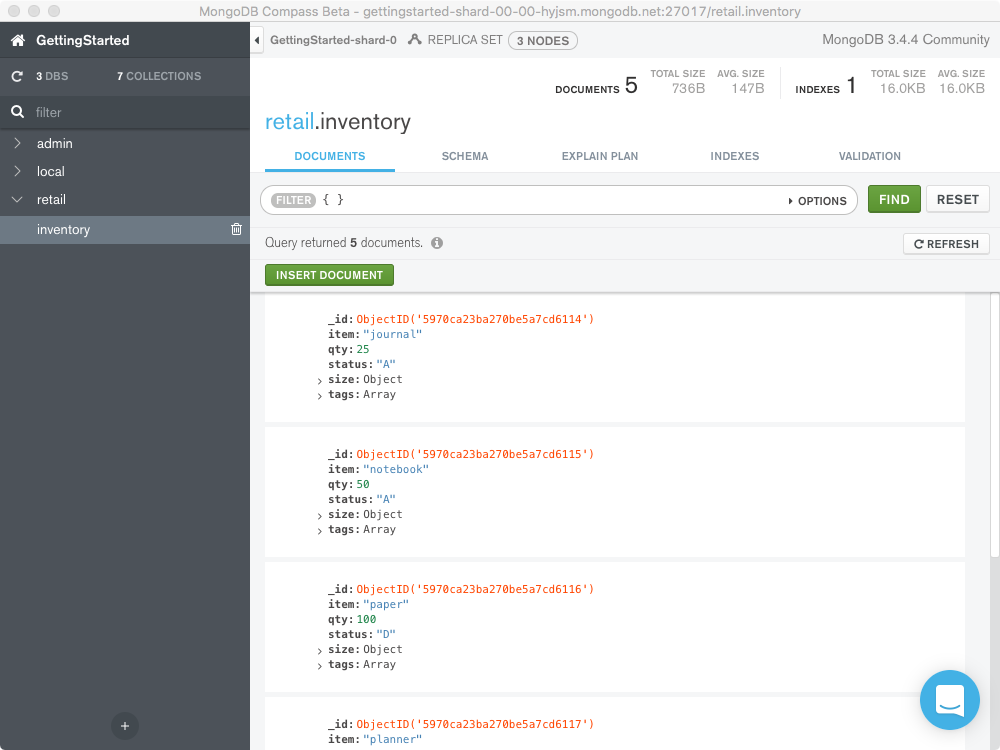
Select the inventory collection from the Collections
tab or the left-hand pane. By default, all documents are selected and
additional documents are loaded by scrolling down.
To explicitly select all documents in the collection, pass an empty
query filter document { } to
the Filter input and click Find.
To select all documents in the collection, pass an empty document as the
query filter document to the
pymongo.collection.Collection.find() method:
To select all documents in the collection, pass an empty document as the query filter document to the Collection.find() method:
- Mongo Shell
- Python
- Java (Sync)
- Node.js
- PHP
- Other
db.inventory.find( {} )
cursor = db.inventory.find({})
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(new Document());
var cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({});
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([]);
FindPublisher<Document> findPublisher = collection.find(new Document());
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Empty;
var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( {} );
client[:inventory].find({})
var findObservable = collection.find(Document())
- Mongo Shell
- Compass
- Python
- Node.js
To query for documents that match specific equality conditions, pass the
find() method a query filter document
with the <field>: <value> of the desired documents. The following example
selects from the inventory collection all documents where the status
equals "D":
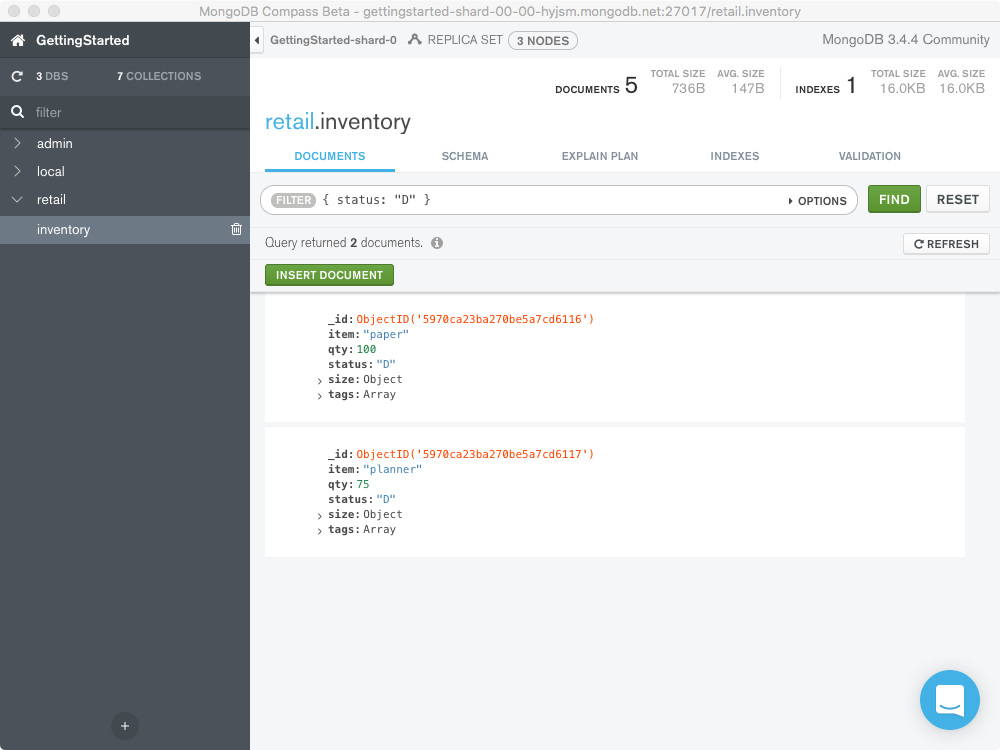
To query for documents that match specific equality conditions, pass
a query filter document to the
Filter with the <field>: <value> of the desired
documents. The following query filter document selects all documents
where the status equals "D" from the inventory collection:
{ status: "D" }
To query for documents that match specific equality conditions, pass the
find() method a
query filter document with the
<field>: <value> of the desired documents. The following example
selects from the inventory collection all documents where the
status equals "D":
To query for documents that match specific equality conditions, pass the
find() method a
query filter document with the
<field>: <value> of the desired documents. The following example
selects from the inventory collection all documents where the
status equals "D":
- Mongo Shell
- Python
- Java (Sync)
- Node.js
- PHP
- Other
db.inventory.find( { status: "D" } )
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": "D"})
findIterable = collection.find(eq("status", "D"));
var cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ status: "D" });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['status' => 'D']);
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("status", "D"));
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("status", "D");
var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { status => "D" } );
client[:inventory].find(status: 'D')
findObservable = collection.find(equal("status", "D"))
Match an Embedded Document¶
Equality matches on the whole embedded document require an exact
match of the specified <value> document, including the field order. For
example, the following query selects all documents where the field size
equals the document { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }:
- Mongo Shell
- Python
- Java (Sync)
- Node.js
- PHP
- Other
db.inventory.find( { size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } } )
cursor = db.inventory.find(
{"size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")])})
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }")));
var cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({
size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }
});
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size' => ['h' => 14, 'w' => 21, 'uom' => 'cm']]);
FindPublisher<Document> findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }")));
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 14 }, { "w", 21 }, { "uom", "cm" } });
var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
# Subdocument key order matters in this example so we have
# to use Tie::IxHash instead of a regular, unordered Perl hash.
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find(
{ size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 14, w => 21, uom => "cm" ) }
);
client[:inventory].find(size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' })
var findObservable = collection.find(equal("size", Document("h" -> 14, "w" -> 21, "uom" -> "cm")))
- Compass
{ size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } }
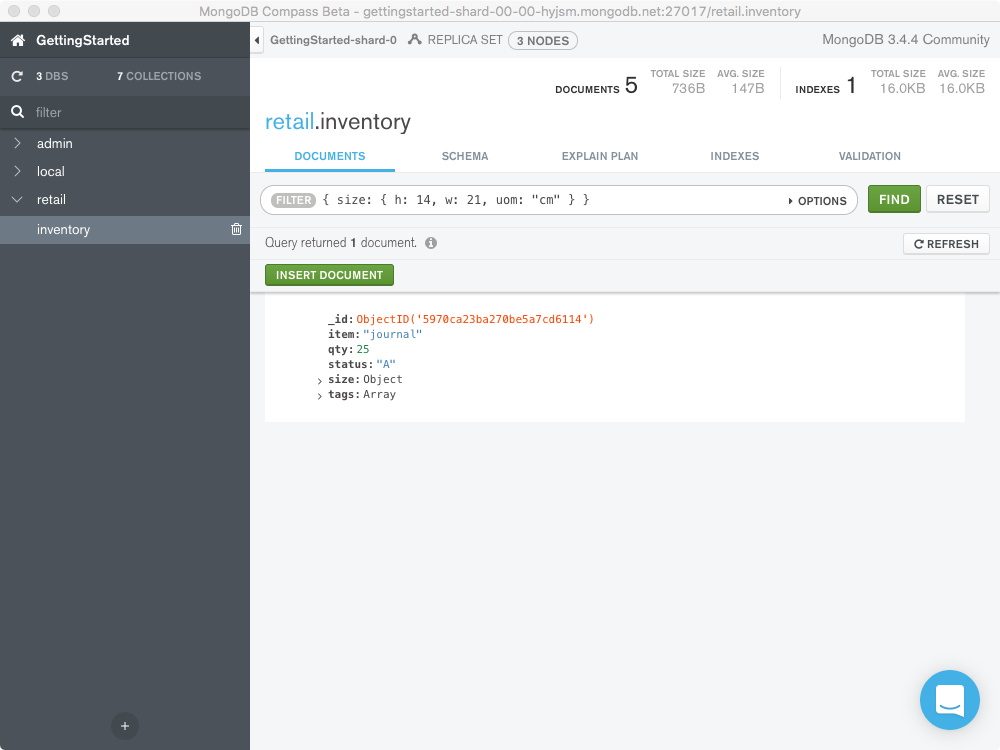
Match a Field in an Embedded Document¶
The following example selects all documents where the field uom
nested in the size field equals the string value "in":
- Mongo Shell
- Python
- Java (Sync)
- Node.js
- PHP
- Other
db.inventory.find( { "size.uom": "in" } )
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.uom": "in"})
findIterable = collection.find(eq("size.uom", "in"));
var cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({
"size.uom": "in"
});
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size.uom' => 'in']);
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size.uom", "in"));
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size.uom", "in");
var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { "size.uom" => "in" } );
client[:inventory].find('size.uom' => 'in')
findObservable = collection.find(equal("size.uom", "in"))
- Compass
{ "size.uom": "in" }

Match an Element in an Array¶
The following example queries for all documents where tags is an
array that contains the string "red" as one of its elements:
- Mongo Shell
- Python
- Java (Sync)
- Node.js
- PHP
- Other
db.inventory.find( { tags: "red" } )
cursor = db.inventory.find({"tags": "red"})
findIterable = collection.find(eq("tags", "red"));
var cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({
tags: "red"
});
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['tags' => 'red']);
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("tags", "red"));
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("tags", "red");
var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { tags => "red" } );
client[:inventory].find(tags: 'red')
findObservable = collection.find(equal("tags", "red"))
- Compass
{ tags: "red" }
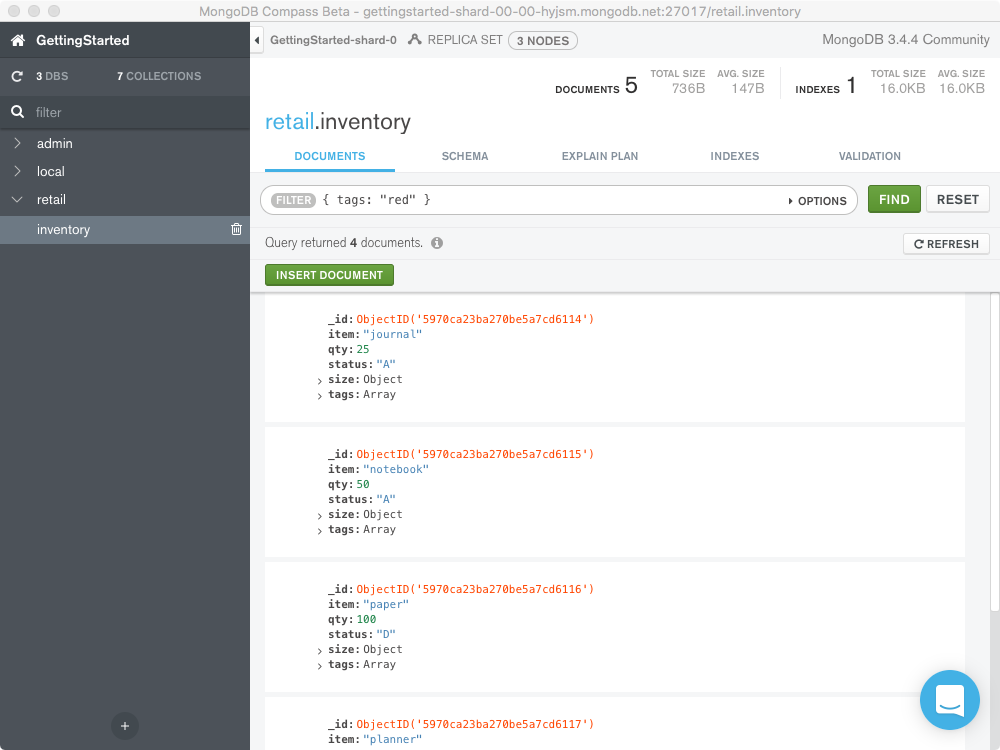
Match an Array Exactly¶
The following example queries for all documents where the field tags
value is an array with exactly two elements, "red" and "blank",
in the specified order:
- Mongo Shell
- Python
- Java (Sync)
- Node.js
- PHP
- Other
db.inventory.find( { tags: ["red", "blank"] } )
cursor = db.inventory.find({"tags": ["red", "blank"]})
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(eq("tags", asList("red", "blank")));
var cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({
tags: [ "red", "blank" ]
});
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['tags' => ['red', 'blank']]);
FindPublisher<Document> findPublisher = collection.find(eq("tags", asList("red", "blank")));
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("tags", new[] { "red", "blank" });
var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { tags => [ "red", "blank" ] } );
client[:inventory].find(tags: ['red', 'blank'])
var findObservable = collection.find(equal("tags", Seq("red", "blank")))
- Compass
{ tags: ["red", "blank"] }
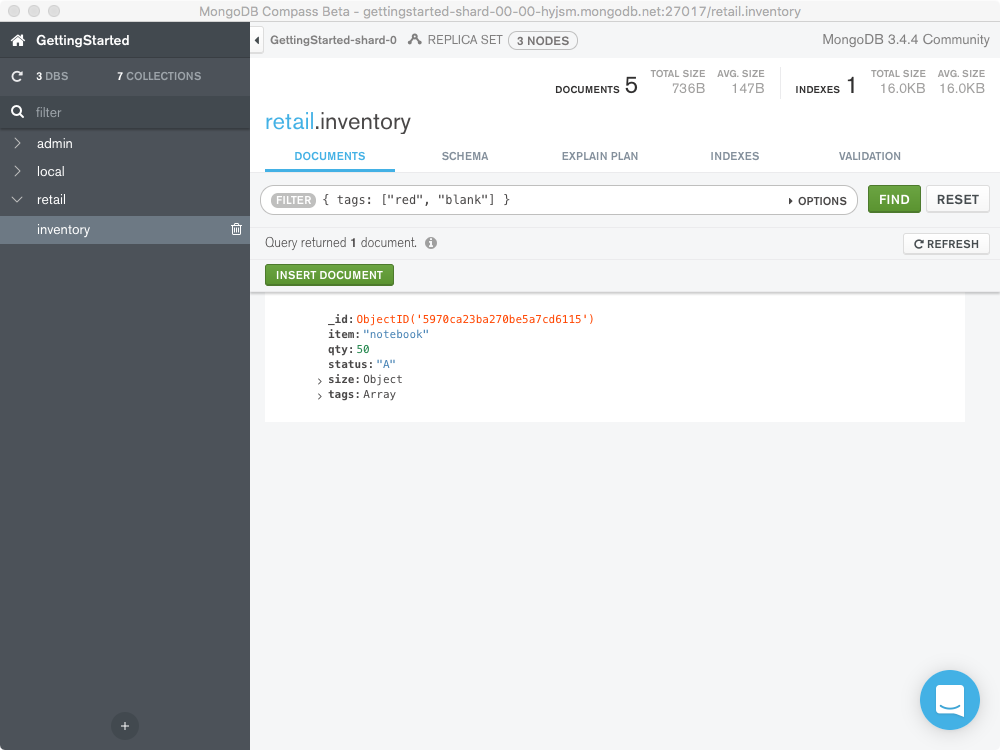
For more information and query examples, see Query Documents in the CRUD section.
To update or delete documents, see Update Documents and Delete Documents.
Next Steps¶
Once you complete the Getting Started Guide, you may find the following course and topics useful:
To learn more about the MongoDB query language and other MongoDB fundamentals, sign up for M001: MongoDB Basics.
| Introduction | Developers | Administrators | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|