PE 2.0 » Cloud Provisioning » Configuring and Troubleshooting
← Cloud Provisioning: Overview — Index — Cloud Provisioning: Provisioning with VMware →
Configuring and Troubleshooting Cloud Provisioning
Configuring
To create new virtual machines with Puppet Enterprise, you’ll need to first configure the services you’ll be using.
First, create a file called .fog in the home directory of the user who will be provisioning new nodes.
$ touch ~/.fog
This is the configuration file for Fog, the cloud abstraction library that powers PE’s provisioning tools. When filled, it will be a YAML hash containing the locations of your cloud services and the credentials necessary to control them. For example:
:default:
:vsphere_server: vc01.example.com
:vsphere_username: cloudprovisioner
:vsphere_password: abc123
:vsphere_expected_pubkey_hash: 431dd5d0412aab11b14178290d9fcc5acb041d37f90f36f888de0cebfffff0a8
:aws_access_key_id: AKIAIISJV5TZ3FPWU3TA
:aws_secret_access_key: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP1234556/s
Continue reading for explanations of how to find these credentials.
Adding VMware Credentials
To connect to a VMware vSphere server, you must put the following information in your ~/.fog file:
:vsphere_server- The name of your vCenter host (for example:
vc1.example.com). You should already know the value for this setting. :vsphere_username- Your vCenter username. You should already know the value for this setting.
:vsphere_password- Your vCenter password. You should already know the value for this setting.
:vsphere_expected_pubkey_hash- A public key hash for your vSphere server. The value for this setting can be obtained by filling the other three settings and running the following command:
$ puppet node_vmware listThis will result in an error message containing the server’s public key hash…
notice: Connecting ...· err: The remote system presented a public key with hash 431dd5d0412aab11b14178290d9fcc5acb041d37f90f36f888de0cebfffff0a8 but we're expecting a hash of <unset>. If you are sure the remote system is authentic set vsphere_expected_pubkey_hash: <the hash printed in this message> in ~/.fog err: Try 'puppet help node_vmware list' for usage…which can then be entered as the value of this setting.
Adding Amazon Web Services credentials
To connect to Amazon Web Services, you must put the following information in your ~/.fog file:
:aws_access_key_id- Your AWS Access Key ID. See below for how to find this.
:aws_secret_access_key- Your AWS Secret Key ID. See below for how to find this.
You can get find your Amazon Web Services credentials online in your Amazon account. To view them, go to Amazon AWS and click on the Account tab.
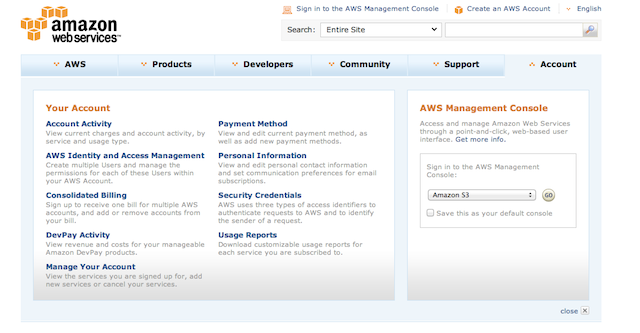
Select the Security Credentials menu and from there choose the “Access Credentials” section; click on the “Access Keys” tab to view your Access Keys.
You need to record two pieces of information: the Access Key ID and the Secret Key ID. To see your Secret Access Key, just click the “Show” link under “Secret Access Key”.
Put both keys in your ~/.fog file as described above.
Additional AWS Configuration
To provision with Puppet, your Amazon Web Services EC2 account will need to have:
- At least one Amazon-managed SSH key pair.
- A security group that allows outbound traffic on ports 8140 and 61613, and inbound SSH traffic (port 22) from the machine being used for provisioning.
You’ll need to provide the names of these resources as arguments when running the provisioning commands.
Key Pairs
To find or create your Amazon SSH key pair, browse to the Amazon Web Service EC2 console.
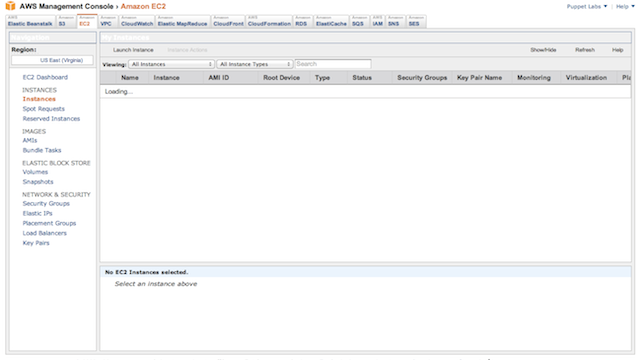
Select the “Key Pairs” menu item from the dashboard. If you don’t have any existing key pairs, you can create one with the “Create Key Pairs” button. Specify a new name for the key pair to create it; the private key file will be automatically downloaded to your host.
Make a note of the name of your key pair, as it is used when creating new instances.
Security Group
To add or edit a security group, select the “Security Groups” menu item from the dashboard. You should see a list of the available security groups. If no groups exist, you can create a new one by clicking the “Create Security Groups” button; otherwise, you can edit an existing group.
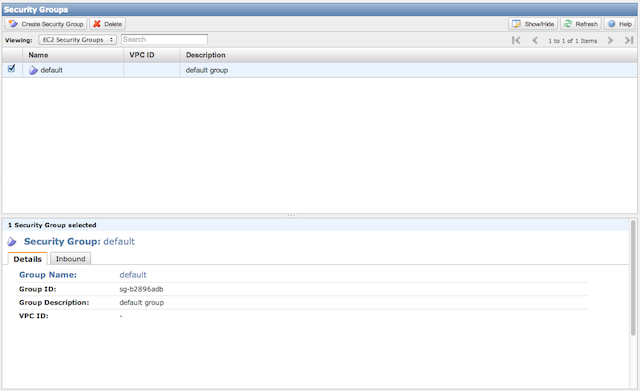
To add the required rules, select the “Inbound” tab and add an SSH rule. You can also specify a specific source to lock the source IP down to an appropriate source IP or network. Click “Add Rule” to add the rule, then click “Apply Rule Changes” to save.
You should also ensure that your security group allows outbound traffic on ports 8140 and 61613. These are the ports PE uses to request configurations and listen for orchestration messages.
Troubleshooting
Missing .fog file or credentials
If you attempt to provision without creating a .fog file or without
populating the file with appropriate credentials:
For VMware you’ll see the following error:
$ puppet node_vmware list
notice: Connecting ...
err: Missing required arguments: vsphere_username, vsphere_password, vsphere_server
err: Try 'puppet help node_vmware list' for usage
For Amazon Web Services you’ll see the following error:
$ puppet node_aws list
err: Missing required arguments: aws_access_key_id,
aws_secret_access_key
err: Try 'puppet help node_aws list' for usage
Add the appropriate file or missing credentials to the file to resolve this issue.
← Cloud Provisioning: Overview — Index — Cloud Provisioning: Provisioning with VMware →