The Android search framework provides the ability for your application to provide suggestions while the user types into the Android search dialog. In this guide, you'll learn how to create custom suggestions. These are suggestions based on custom data provided by your application. For example, if your application is a word dictionary, you can suggest words from the dictionary that match the text entered so far. These are the most valuable suggestions because you can effectively predict what the user wants and provide instant access to it. Once you provide custom suggestions, you then make them available to the system-wide Quick Search Box, providing access to your content from outside your application.
Before you begin, you need to have implemented the Android search dialog for searches in your application. If you haven't done this, see Using the Android Search Dialog.
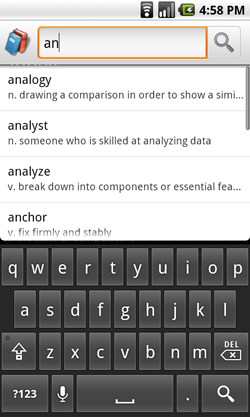
When the user selects a custom suggestions, the Search Manager will send a customized Intent to
your searchable Activity. Whereas a normal search query will send an Intent with the ACTION_SEARCH action, you can instead define your custom suggestions to use
ACTION_VIEW (or any other action), and also include additional data
that's relevant to the selected suggestion. Continuing
the dictionary example, when the user selects a suggestion, your application can immediately
open the definition for that word, instead of searching the dictionary for matches.
To provide custom suggestions, you need to do the following:
SQLiteDatabase) for your
suggestions and format the table with required columns.Intent to be sent when the user selects a
suggestion (including a custom action and custom data). Just like the Search Manager handles the rendering of the search dialog, it will also do the work to display all search suggestions below the search dialog. All you need to do is provide a source from which the suggestions can be retrieved.
Note: If you're not familiar with creating Content Providers, please read the Content Providers developer guide before you continue.
When the Search Manager identifies that your Activity is searchable and also provides search suggestions, the following procedure will take place as soon as the user types into the Android search box:
Cursor that points to all
suggestions that are relevant to the search query text.At this point, the following may happen:
ACTION_SEARCH
Intent.To add support for custom suggestions, add the android:searchSuggestAuthority attribute
to the <searchable> element in your searchable configuration file. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<searchable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="my.package.MyCustomSuggestionProvider" >
</searchable>
You may require some additional attributes, depending on the type of Intent you attach to each suggestion and how you want to format queries to your content provider. The other optional attributes are discussed in the relevant sections below.
Creating a content provider for custom suggestions requires previous knowledge about Content
Providers that's covered in the Content Provider developer
guide. For the most part, a content provider for custom suggestions is the
same as any other content provider. However, for each suggestion you provide, the respective row in
the Cursor must include specific columns that the Search Manager
understands.
When the user starts typing into the search dialog, the Search Manager will query your Content
Provider for suggestions by calling query() each time
a letter is typed. In your implementation of query(), your
content provider must search your suggestion data and return a Cursor that points to the rows you determine to be good suggestions.
The following two sections describe how the Search Manager will send requests to your Content
Provider and how you can handle them, and define the columns that the Search Manager understands and
expects to be provided in the Cursor returned with each query.
When the Search Manager makes a request for suggestions from your content provider, it will call
query(Uri, String[], String, String[], String). You must
implement this method in your content provider so that it will search your suggestions and return a
Cursor that contains the suggestions you deem relevant.
Here's a summary of the parameters that the Search Manager will pass to your query() method
(listed in order):
uriUri, formatted as:
content://your.authority/optional.suggest.path/SUGGEST_URI_PATH_QUERY
The default behavior is for Search Manager to pass this URI and append it with the query text. For example:
content://your.authority/optional.suggest.path/SUGGEST_URI_PATH_QUERY/puppies
The query text on the end will be encoded using URI encoding rules, so you may need to decode it.
The optional.suggest.path portion is only included in the URI if you have set
such a path in your searchable configuration file with the android:searchSuggestPath
attribute. This is only needed if you use the same content provider for multiple searchable
activities, in which case you need to disambiguate the source of the suggestion query.
Note that SUGGEST_URI_PATH_QUERY is not the literal
string provided in the URI, but a constant that you should use if you need to refer to this
path.
projectionselectionandroid:searchSuggestSelection attribute of
your searchable configuration file, or null if you have not declared the android:searchSuggestSelection attribute. More about this below.selectionArgsandroid:searchSuggestSelection attribute in your searchable configuration. If
you have not declared android:searchSuggestSelection, then this parameter is null. More
about this below.sortOrderAs you may have realized, there are two ways by which the Search Manager can send you the search
query text. The default manner is for the query text to be included as the last path of the content
URI that is passed in the uri parameter. However, if you include a selection value in your
searchable configuration's android:searchSuggestSelection attribute, then the query text will instead be passed as the first
element of the selectionArgs string array. Both options are summarized below.
By default, the query will be appended as the last segment of the uri
parameter (a Uri object). To retrieve the query text in this case, simply use
getLastPathSegment(). For example:
String query = uri.getLastPathSegment().toLowerCase();
This will return the last segment of the Uri, which is the query text entered in the search dialog.
Instead of using the URI, you may decide it makes more sense for your query() method to
receive everything it needs to perform the look-up and you want the
selection and selectionArgs parameters to carry values. In this case, you can
add the android:searchSuggestSelection attribute to your searchable configuration with your
SQLite selection string. In this selection string, you can include a question mark ("?") as
a placeholder for the actual search query. This selection string will be delivered as the
selection string parameter, and the query entered into the search dialog will be delivered
as the first element in the selectionArgs string array parameter.
For example, here's how you might form the android:searchSuggestSelection attribute to
create a full-text search statement:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<searchable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="my.package.MyCustomSuggestionProvider"
android:searchSuggestIntentAction="android.Intent.action.VIEW"
android:searchSuggestSelection="word MATCH ?">
</searchable>
When you then receive the selection and selectionArgs parameters in your ContentProvider.query()
method, they will carry the selection ("word MATCH ?") and the query text, respectively. When
these are passed to an SQLite query method, they will be synthesized together (replacing the question mark with the query
text, wrapped in single-quotes). Note that if you chose this method and need to add any wildcards to
your query text, you must do so by appending (and/or prefixing) them to the selectionArgs
parameter, because this is the value that will be wrapped in quotes and inserted in place of the
question mark.
Tip: If you don't want to define a selection clause in
the android:searchSuggestSelection attribute, but would still like to receive the query
text in the selectionArgs parameter, simply provide a non-null value for the android:searchSuggestSelection attribute. This will trigger the query to be passed in selectionArgs and you can ignore the selection parameter. In this way, you can instead
define the actual selection clause at a lower level so that your content provider doesn't have to
handle it.
If your search suggestions are not stored in a table format using the columns required by the
Search Manager, then you can search your suggestion data for matches and then format them
into the necessary table on the fly. To do so, create a MatrixCursor using
the required column names and then add a row for each suggestion using addRow(Object[]). Return the final product from your Content
Provider's query() method.
When you return suggestions to the Search Manager with a Cursor, the
Search Manager expects there to be specific columns in each row. So, regardless of whether you
decide to store
your suggestion data in an SQLite database on the device, a database on a web server, or another
format on the device or web, you must format the suggestions as rows in a table and
present them with a Cursor. There are several columns that the Search
Manager will understand, but only two are required:
_IDSUGGEST_COLUMN_TEXT_1The following columns are all optional (and most will be discussed further in the following sections, so you may want to skip this list for now):
SUGGEST_COLUMN_TEXT_2SUGGEST_COLUMN_ICON_1SUGGEST_COLUMN_ICON_2SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_ACTIONandroid:searchSuggestIntentAction field in your searchable configuration. At
least one of these
must be present for the suggestion to generate an Intent. Note: If your action is the same for all
suggestions, it is more efficient to specify the action using android:searchSuggestIntentAction and omit this column from the Cursor .SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATAandroid:searchSuggestIntentData field in your searchable configuration. If neither
source is provided,
the Intent's data field will be null. Note: If your data is the same for all suggestions, or can be
described using a constant part and a specific ID, it is more efficient to specify it using android:searchSuggestIntentData and omit this column from the Cursor .
SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA_IDandroid:searchSuggestIntentData attribute in the searchable configuration has already
been set to an appropriate base string.SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_EXTRA_DATAEXTRA_DATA_KEY key.SUGGEST_COLUMN_QUERYQUERY key. Required if suggestion's action is ACTION_SEARCH, optional otherwise.SUGGEST_COLUMN_SHORTCUT_IDSUGGEST_NEVER_MAKE_SHORTCUT, the result will
not be stored as a shortcut.
Otherwise, the shortcut id will be used to check back for for an up to date suggestion using
SUGGEST_URI_PATH_SHORTCUT.SUGGEST_COLUMN_SPINNER_WHILE_REFRESHINGSUGGEST_COLUMN_ICON_2
while the shortcut of this suggestion is being refreshed in Quick Search Box.Again, most of these columns will be discussed in the relevant sections below, so don't worry if they don't make sense to you now.
When the user selects a suggestion from the list that appears below the search
dialog (instead of performing a search), the Search Manager will send
a custom Intent to your searchable Activity. You must define both the
action and data for the Intent.
The most common Intent action for a custom suggestion is ACTION_VIEW, which is appropriate when
you want to open something, like the definition for a word, a person's contact information, or a web
page. However, the Intent action can be whatever you want and can even be different for each
suggestion.
To declare an Intent action that will be the same for all suggestions, define the action in
the android:searchSuggestIntentAction attribute of your searchable configuration file. For
example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<searchable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="my.package.MySuggestionProvider"
android:searchSuggestIntentAction="android.Intent.action.VIEW" >
</searchable>
If you want to declare an Intent action that's unique for each suggestion, add the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_ACTION column to
your suggestions table and, for each suggestion, place in it the action to use (such as
"android.Intent.action.VIEW").
You can also combine these two techniques. For instance, you can include the android:searchSuggestIntentAction attribute with an action to be used with all suggestions by
default, then override this action for some suggestions by declaring a different action in the
SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_ACTION column. If you do not include
a value in the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_ACTION column, then the
Intent provided in the android:searchSuggestIntentAction attribute will be used.
Note: If you do not include the
android:searchSuggestIntentAction attribute in your searchable configuration, then you
must include a value in the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_ACTION
column for every suggestion, or the Intent will fail.
When the user selects a suggestion, your searchable Activity will receive the Intent with the
action you've defined (as discussed in the previous section), but the Intent must also carry
data in order for your Activity to identify which suggestions was selected. Specifically,
the data should be something unique for each suggestion, such as the row ID for the suggestion in
your suggestions table. When the Intent is received,
you can retrieve the attached data with getData() or getDataString().
There are two ways to define the data that is included with the Intent:
SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA column of your suggestions table.android:searchSuggestIntentData
attribute of the searchable configuration and the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA_ID column of your
suggestions table, respectively.The first option is straight-forward. Simply provide all necessary data information for each
Intent in the suggestions table by including the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA column and then populating it with unique
data for each row. The data from this column will be attached to the Intent exactly as it
is found in this column. You can then retrieve it with with getData()
or getDataString().
Tip: It's usually easiest to use the table's row ID as the
Intent data because it's always unique. And the easiest way to do that is by using the
SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA column name as an alias for the row ID
column. See the Searchable Dictionary sample
app for an example in which SQLiteQueryBuilder is used to
create a projection map of column names to aliases.
The second option is to fragment your data URI into the common piece and the unique piece.
Declare the piece of the URI that is common to all suggestions in the android:searchSuggestIntentData attribute of your searchable configuration. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<searchable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="my.package.MySuggestionProvider"
android:searchSuggestIntentAction="android.Intent.action.VIEW"
android:searchSuggestIntentData="content://my.package/datatable" >
</searchable>
Now include the final path for each suggestion (the unique part) in the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA_ID
column of your suggestions table. When the user selects a suggestion, the Search Manager will take
the string from android:searchSuggestIntentData, append a slash ("/") and then add the
respective value from the SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA_ID column to
form a complete content URI. You can then retrieve the Uri with with getData().
If you need to express even more information with your Intent, you can add another table column,
SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_EXTRA_DATA, which can store additional
information about the suggestion. The data saved in this column will be placed in EXTRA_DATA_KEY of the Intent's extra Bundle.
Now that your search dialog provides custom search suggestions with custom formatted Intents, you
need your searchable Activity to handle these Intents as they are delivered once the user selects a
suggestion. (This is, of course, in addition to handling the ACTION_SEARCH Intent, which your searchable Activity already does.)
Accepting the new Intent is rather self-explanatory, so we'll skip straight to an example:
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (Intent.ACTION_SEARCH.equals(intent.getAction())) {
// Handle the normal search query case
String query = intent.getStringExtra(SearchManager.QUERY);
doSearch(query);
} else if (Intent.ACTION_VIEW.equals(intent.getAction())) {
// Handle a suggestions click (because my suggestions all use ACTION_VIEW)
Uri data = intent.getData());
showResult(rowId);
}
In this example, the Intent action is ACTION_VIEW and the data carries a complete URI pointing to the suggested
item, as synthesized by the android:searchSuggestIntentData string and SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA_ID column. The URI is then passed to a local
method that will query the content provider for the item specified by the URI and show it.
If the user navigates through the suggestions list using the device directional controls, the text in the search dialog won't change, by default. However, you can temporarily rewrite the user's query text as it appears in the text box with a query that matches the currently selected suggestion. This enables the user to see what query is being suggested (if appropriate) and then select the search box and edit the query before dispatching it as a search.
You can rewrite the query text in the following ways:
android:searchMode attribute to your searchable configuration with the
"queryRewriteFromText" value. In this case, the content from the suggestion's SUGGEST_COLUMN_TEXT_1
column will be used to rewrite the query text.android:searchMode attribute to your searchable configuration with the
"queryRewriteFromData" value. In this case, the content from the suggestion's
SUGGEST_COLUMN_INTENT_DATA column will be used to rewrite the
query text. Note that this should only
be used with Uri's or other data formats that are intended to be user-visible, such as HTTP URLs.
Internal Uri schemes should not be used to rewrite the query in this way.SUGGEST_COLUMN_QUERY column of your suggestions table. If this column is
present and contains a value for the current suggestion, it will be used to rewrite the query text
(and override either of the previous implementations).Once your application is configured to provide custom search suggestions, making them available
to the globally-accessible Quick Search Box is as easy as modifying your searchable configuration to
include android:includeInGlobalSearch as "true".
The only scenario in which additional work will be required is if your content provider for
custom suggestions requires a permission for read access. In which case, you need to add a special
<path-permission> element for the provider to grant Quick Search Box read access to your
content provider. For example:
<provider android:name="MySuggestionProvider"
android:authorities="my.package.authority"
android:readPermission="com.example.provider.READ_MY_DATA"
android:writePermission="com.example.provider.WRITE_MY_DATA">
<path-permission android:pathPrefix="/search_suggest_query"
android:readPermission="android.permission.GLOBAL_SEARCH" />
</provider>
In this example, the provider restricts read and write access to the content. The
<path-permission> element amends the restriction by granting read access to content
inside the "/search_suggest_query" path prefix when the "android.permission.GLOBAL_SEARCH" permission exists. This grants access to Quick Search Box
so that it may query your content provider for suggestions.
Content providers that enforce no permissions are already available to the search infrastructure.
When your application is configured to provide suggestions in Quick Search Box, it is not actually enabled to provide suggestions in Quick Search Box, by default. It is the user's choice whether to include suggestions from your application in the Quick Search Box. To enable search suggestions from your application, the user must open "Searchable items" (in Settings > Search) and enable your application as a searchable item.
Each application that is available to Quick Search Box has an entry in the Searchable items
settings page. The entry includes the name of the application and a short description of what
content can be searched from the application and made available for suggestions in Quick Search Box.
To define the description text for your searchable application, add the android:searchSettingsDescription attribute to your searchable configuration. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<searchable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="my.package.MySuggestionProvider"
android:searchSuggestIntentAction="android.Intent.action.VIEW"
android:includeInGlobalSearch="true"
android:searchSettingsDescription="@string/search_description" >
</searchable>
The string for android:searchSettingsDescription should be as concise as possible and
state the content that is searchable. For example, "Artists, albums, and tracks" for a music
application, or "Saved notes" for a notepad application. Providing this description is important so
the user knows what kind of suggestions will be provided. This attribute should always be included
when android:includeInGlobalSearch is "true".
Remember that the user must visit this settings menu to enable search suggestions for your application before your search suggestions will appear in Quick Search Box. As such, if search is an important aspect of your application, then you may want to consider a way to message this to your users — perhaps with a note the first time they launch the app about how to enable search suggestions for Quick Search Box.
Suggestions that the user selects from Quick Search Box may be automatically made into shortcuts. These are suggestions that the Search Manager has copied from your content provider so it can quickly access the suggestion without the need to re-query your content provider.
By default, this is enabled for all suggestions retrieved by Quick Search Box, but if your
suggestion data may change over time, then you can request that the shortcuts be refreshed. For
instance, if your suggestions refer to dynamic data, such as a contact's presence status, then you
should request that the suggestion shortcuts be refreshed when shown to the user. To do so,
include the SUGGEST_COLUMN_SHORTCUT_ID in your suggestions table.
Using this column, you can
configure the shortcut behavior for each suggestion in the following ways:
Provide a value in the SUGGEST_COLUMN_SHORTCUT_ID column
and the suggestion will be
re-queried for a fresh version of the suggestion each time the shortcut is displayed. The shortcut
will be quickly displayed with whatever data was most recently available until the refresh query
returns, after which the suggestion will be dynamically refreshed with the new information. The
refresh query will be sent to your content provider with a URI path of SUGGEST_URI_PATH_SHORTCUT
(instead of SUGGEST_URI_PATH_QUERY). The Cursor you return should
contain one suggestion using the
same columns as the original suggestion, or be empty, indicating that the shortcut is no
longer valid (in which case, the suggestion will disappear and the shortcut will be removed).
If a suggestion refers to data that could take longer to refresh, such as a network based
refresh, you may also add the SUGGEST_COLUMN_SPINNER_WHILE_REFRESHING column to your suggestions
table with a value
of "true" in order to show a progress spinner for the right hand icon until the refresh is complete.
(Any value other than "true" will not show the progress spinner.)
Provide a value of SUGGEST_NEVER_MAKE_SHORTCUT in the
SUGGEST_COLUMN_SHORTCUT_ID column. In
this case, the suggestion will never be copied into a shortcut. This should only be necessary if you
absolutely do not want the previously copied suggestion to appear at all. (Recall that if you
provide a normal value for the column then the suggestion shortcut will appear only until the
refresh query returns.)
Simply leave the SUGGEST_COLUMN_SHORTCUT_ID empty for each
suggestion that will not change and can be saved as a shortcut.
Of course, if none of your suggestions will ever change, then you do not need the
SUGGEST_COLUMN_SHORTCUT_ID column at all.
Note: Quick Search Box will ultimately decide whether to shortcut your app's suggestions, considering these values as a strong request from your application.
Once your application's search results are made available to Quick Search Box, how they surface to the user for a particular query will be determined as appropriate by Quick Search Box ranking. This may depend on how many other apps have results for that query, and how often the user has selected on your results compared to those of the other apps. There is no guarantee about how ranking will occur, or whether your app's suggestions will show at all for a given query. In general, you can expect that providing quality results will increase the likelihood that your app's suggestions are provided in a prominent position, and apps that provide lower quality suggestions will be more likely to be ranked lower and/or not displayed.
See the Searchable Dictionary sample app for a complete demonstration of custom search suggestions.