Table of Contents
This chapter provides general information about MySQL Workbench and how it has changed.
MySQL Workbench is a graphical tool for working with MySQL Servers and databases. MySQL Workbench fully supports MySQL Server versions 5.1 and above. It is also compatible with MySQL Server 5.0, but not every feature of 5.0 may be supported. It does not support MySQL Server versions 4.x.
MySQL Workbench functionality covers five main topics:
SQL Development: Enables you to create and manage connections to database servers. Along with enabling you to configure connection parameters, MySQL Workbench provides the capability to execute SQL queries on the database connections using the built-in SQL Editor.
Data Modeling (Design): Enables you to create models of your database schema graphically, reverse and forward engineer between a schema and a live database, and edit all aspects of your database using the comprehensive Table Editor. The Table Editor provides easy-to-use facilities for editing Tables, Columns, Indexes, Triggers, Partitioning, Options, Inserts and Privileges, Routines and Views.
Server Administration: Enables you to administer MySQL server instances by administering users, performing backup and recovery, inspecting audit data, viewing database health, and monitoring the MySQL server performance.
Data Migration: Allows you to migrate from Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, Sybase ASE, SQLite, SQL Anywhere, PostreSQL, and other RDBMS tables, objects and data to MySQL. Migration also supports migrating from earlier versions of MySQL to the latest releases.
MySQL Enterprise Support: Support for Enterprise products such as MySQL Enterprise Backup and MySQL Audit.
MySQL Workbench is available in two editions, the Community Edition and the Commercial Edition. The Community Edition is available free of charge. The Commercial Edition provides additional Enterprise features, such as access to MySQL Enterprise Backup and MySQL Audit, at low cost. For a complete comparison, see http://www.mysql.com/products/workbench/features.html
For notes detailing changes made in each release of MySQL Workbench, see Appendix G, MySQL Workbench Change History.
This section summarizes how the MySQL Workbench 6 series progressed with each minor release.
For notes detailing the changes in each point release, see the MySQL Workbench Release Notes.
This section summarizes many of the new features added to MySQL Workbench 6.3.x, in relation to MySQL Workbench 6.2.x;.
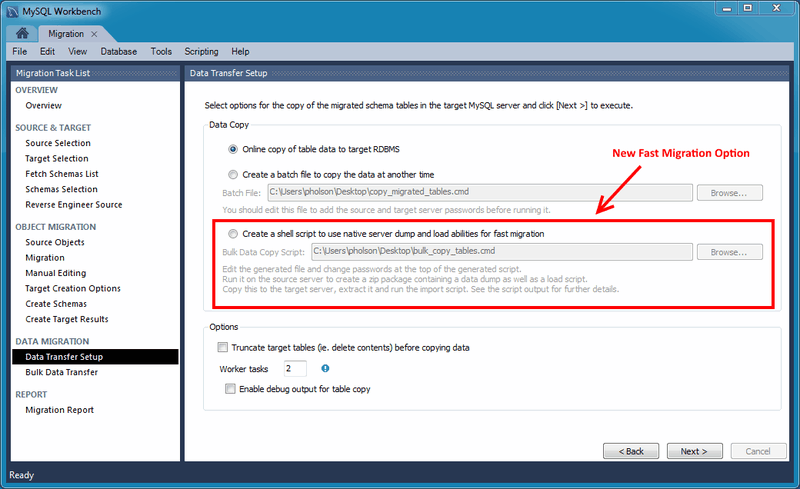
Fast Data Migration
A new "fast migration" option was added to the migration wizard. This is another way to transfer data from one MySQL server to another while performing a migration, and it complements the existing solutions. The premise is to use a generated script on the source server to create a dump that you move to the target machine to perform the import there. This avoids the need to traffic all data through MySQL Workbench, or to have a permanent network connection between the servers. Instead, the dump and restore is performed at maximum speed by using the LOAD DATA call for the MySQL import. The migration wizard automatically creates all necessary scripts for all supported platforms and servers. The generated script creates a self-contained Zip file that must be copied to the target server. You unzip it and execute the provided script to perform the data import.
SSL Certificate Generator
A new SSL certificate generation wizard was added. This new wizard
helps create proper SSL certificates for both MySQL clients and
MySQL servers. Connections in MySQL Workbench are updated with the
certificates by the wizard. This wizard requires OpenSSL to create
the certificates. An example my.cnf /
my.ini file is also generated that utilizes
the generated certificates.
For additional details, see Section 5.3.4, “SSL Wizard (Certificates)”.
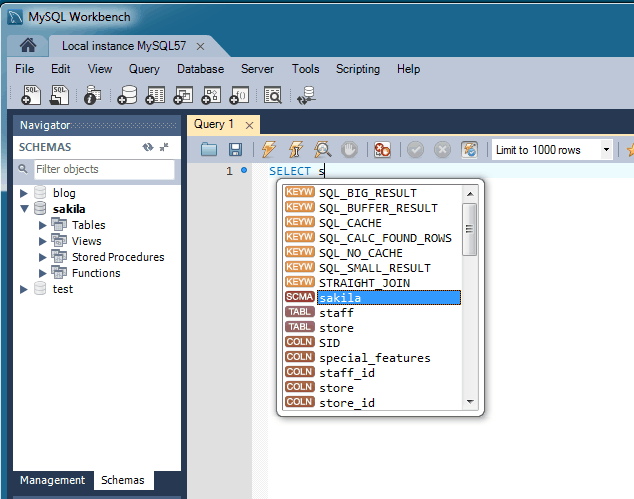
SQL Editor Auto-Completion
The SQL editor auto-completion improvements include the following changes:
It now functions with all statement types, when before only SELECT statements were fully supported.
It now minds the MySQL server version. For example, it now only shows the engines available from the server.
Additional suggestions are now available, such as system variables, engines, table spaces, logfile groups, and more.
New graphics including color coded (and tagged) entries.
It is context aware, as for example it only shows available keywords, columns, and tables.
Improved MySQL 5.7 syntax support.
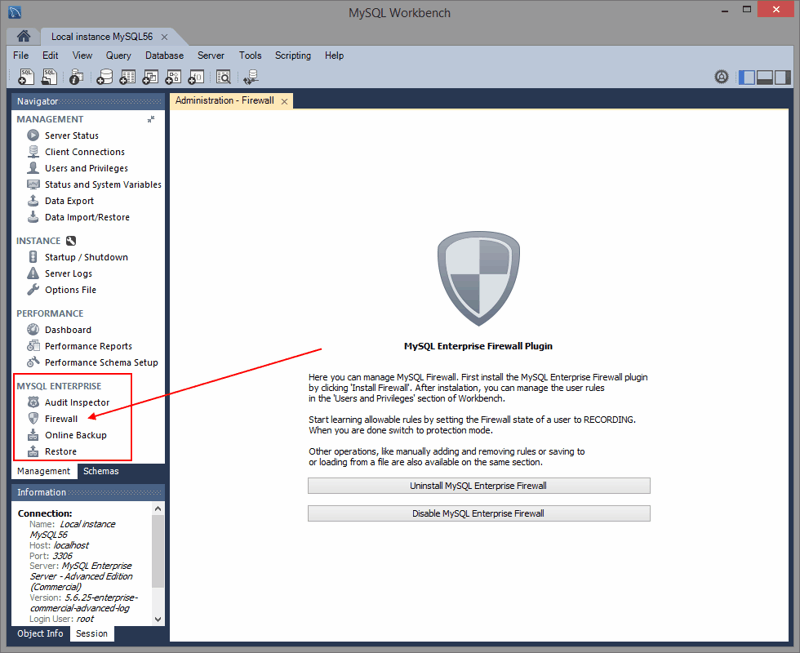
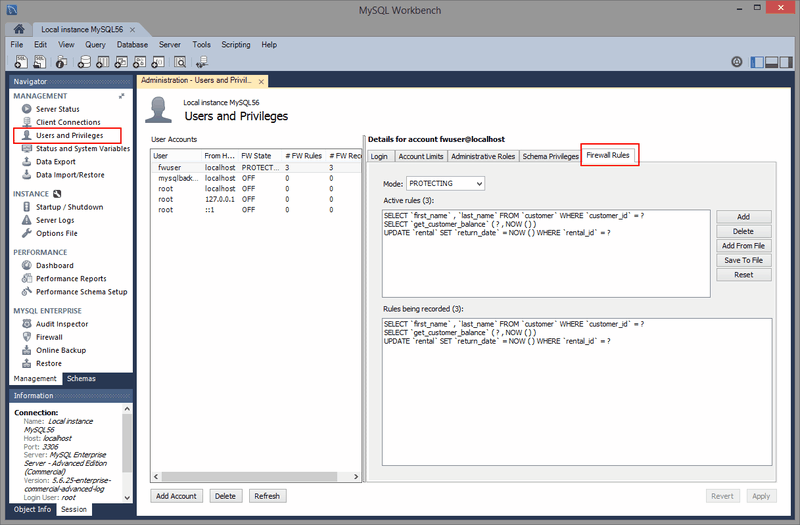
MySQL Enterprise Firewall
MySQL Enterprise Firewall support was added in MySQL Workbench 6.3.4. Use MySQL Workbench to install and enable MySQL Enterprise Firewall, and manage the MySQL Enterprise Firewall rules and variables. For additional information, see Section 6.8, “MySQL Enterprise Firewall Interface”.
MySQL Enterprise Backup
Profile handling now detects mismatches between MySQL Enterprise Backup executables and corresponding profiles.
Improved scheduling logic
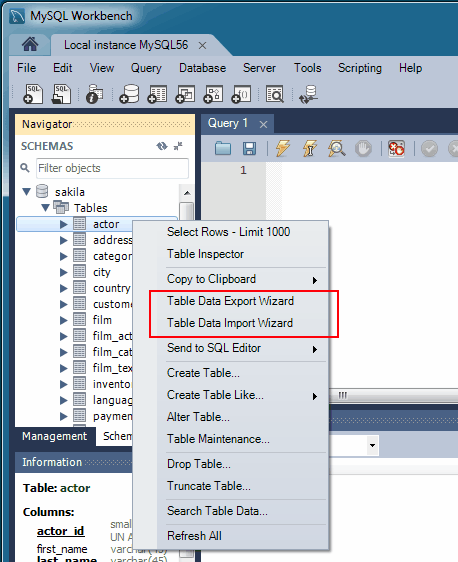
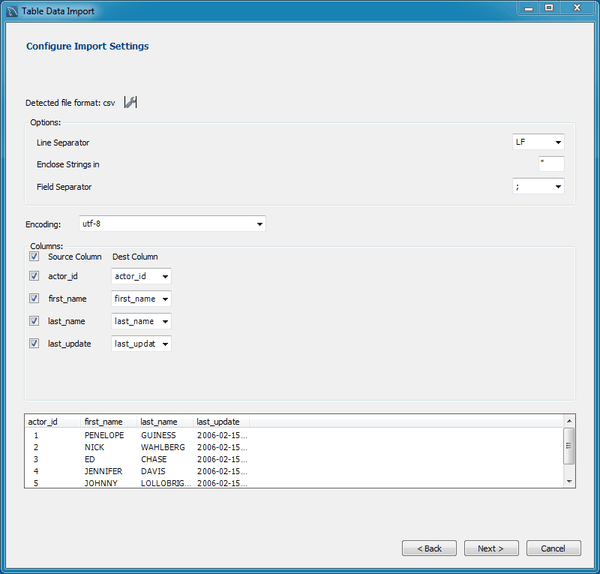
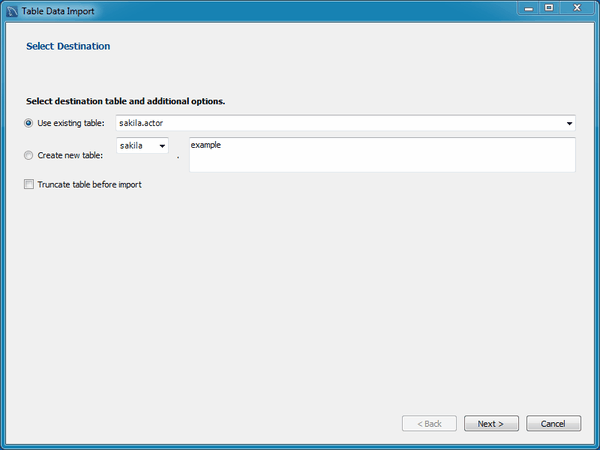
Table Data Export and Import Wizard
A new table data import/export wizard was added. This feature enhances the current CSV import and export feature found in the SQL editor's result set viewer. It supports import and export of CSV and JSON files, and allows a more flexible configuration (separators, column selection, encoding selection, and more). This new wizard does not require an executed statement on a table for a result set to be operated on, as it can now work directly on tables. The wizard can be performed against either a local or remotely connected MySQL server. The import action includes table, column, and type mapping. For additional information, see Section 6.5.1, “Table Data Export and Import Wizard”.
The wizard is accessible from the object browser's context menu.
Additional changes
MySQL Fabric 1.5 is now supported. Older versions of Fabric are no longer supported due to incompatible protocol changes.
OS X builds were switched from 32-bit to 64-bit.
Platforms support changes: 6.3.0: Fedora 21 and Ubuntu 14.10 support was added, Ubuntu 12.10 support was dropped. 6.3.4: Fedora 22 and Ubuntu 15.04 support was added, Ubuntu 14.10 support was dropped.
This section summarizes many of the new features added to MySQL Workbench 6.2.x, in relation to MySQL Workbench 6.1.x;.
SQL Editor
Most of the changes and improvements were made to the SQL editor.
Overlay Icons in the Object Viewer
The schema navigator now includes shortcut buttons for common operations such as table data view, the table editor, and the table/schema inspector.
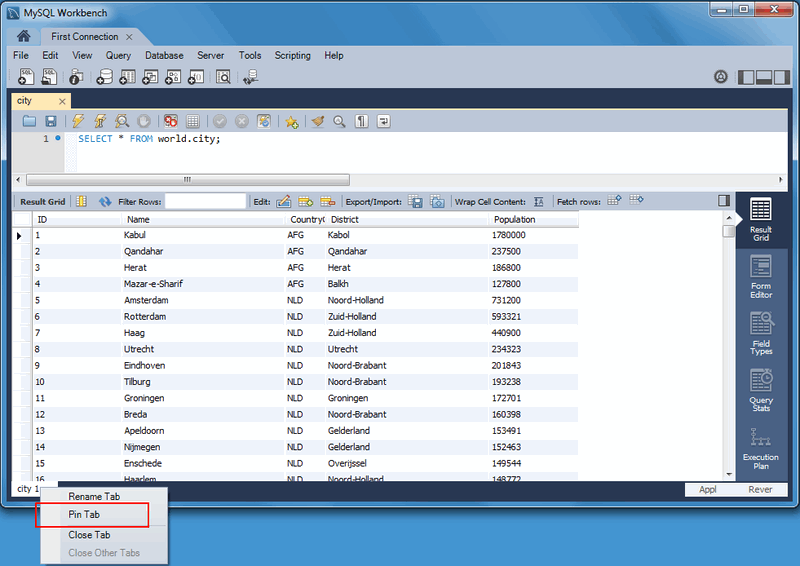
A "Pin Tab" Results Option
Result tabs can now be "pinned" to your result set window.
The "Rename Tab" context menu option is also new. New names are
preserved (and remembered) in your Workbench's
cache/ directory.
Microsoft Access to MySQL Migration
The migration wizard now supports Microsoft Access migration. Select "Microsoft Access" as your source database in the wizard, use MySQL as your target source database, and then execute. For additional information, see Section 10.4, “Microsoft Access Migration”.
MySQL Fabric Integration
MySQL Fabric cluster connectivity was added: Browse, view status, and connect to any MySQL instance in a Fabric Cluster.
This requires Connector/Python and MySQL Utilities 1.4.3+ installed, including the Python module.
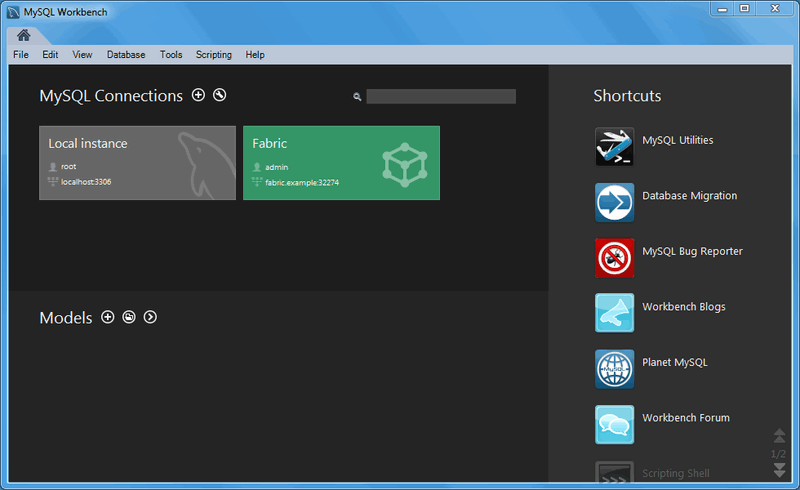
To set up a managed Fabric connection, create a new MySQL connection with the new connection method. The connection tiles have a different look:
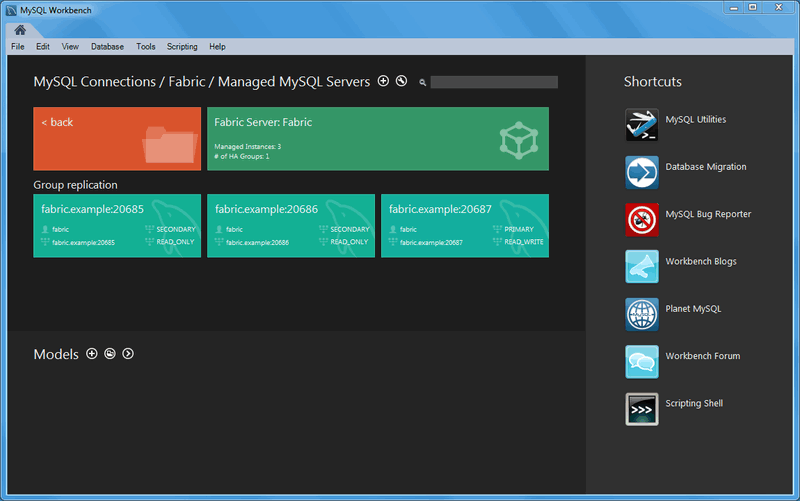
Clicking the new fabric group tile shows the managed connections:
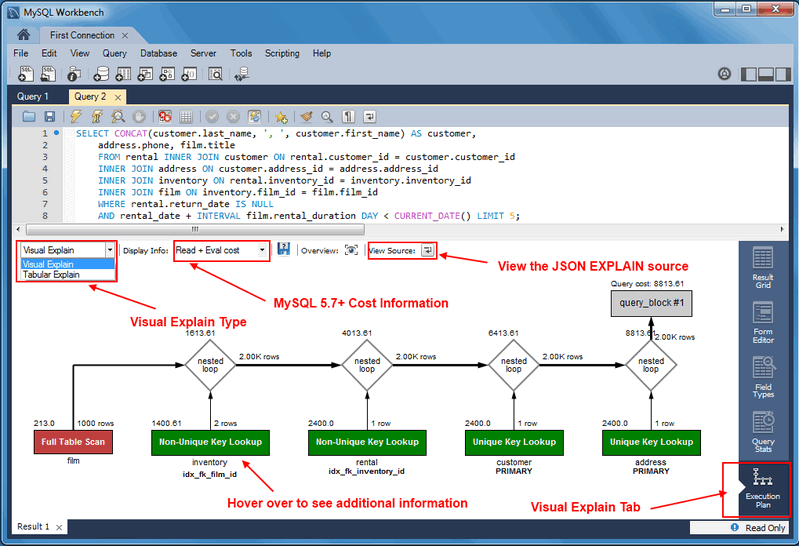
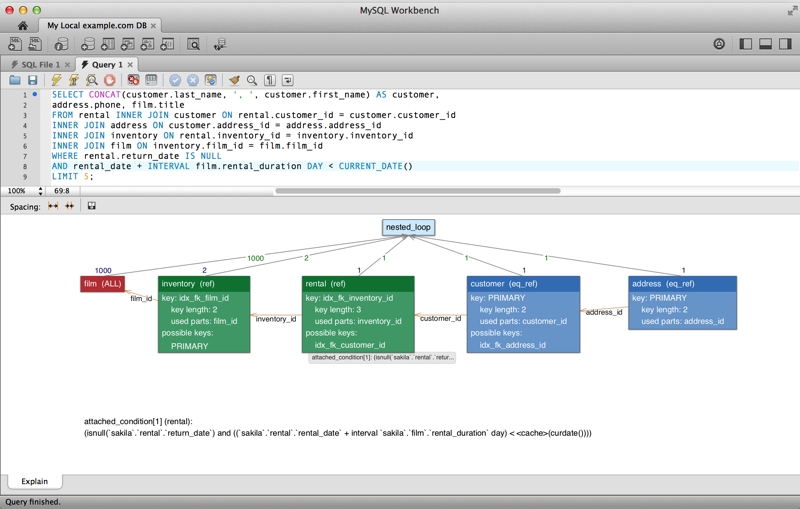
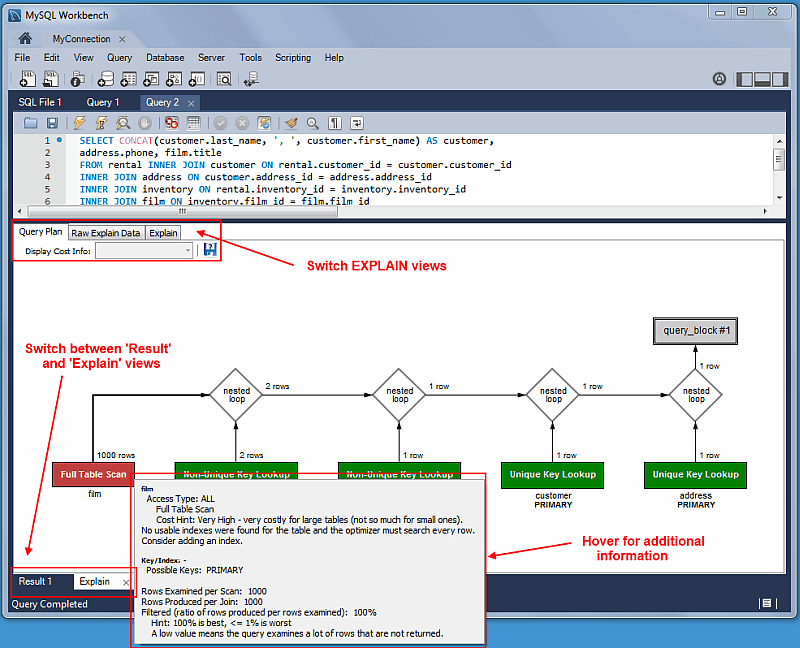
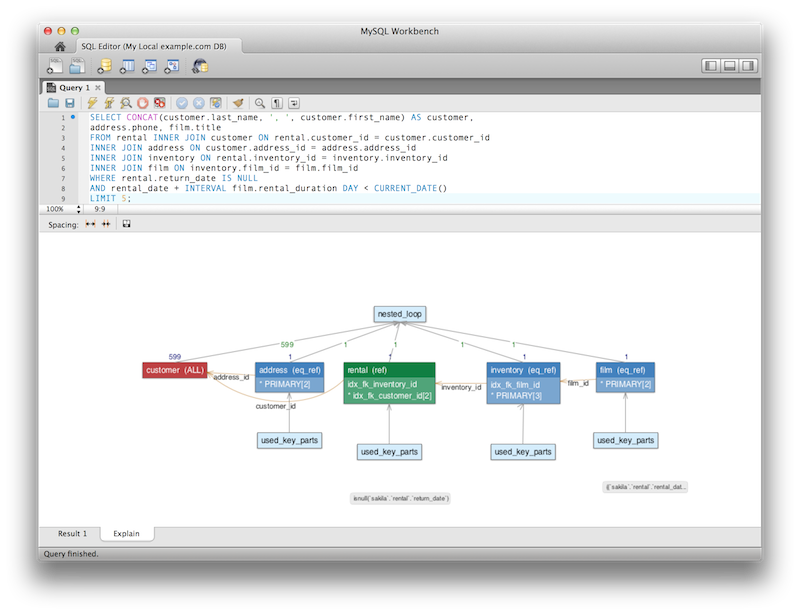
Visual Explain / Execution Plan Improvements
The Visual Explain Execution Plan feature was improved. A list of changes includes:
An "Execution Plan" tab was added to the results view
All statements now offer a "Visual Explain" execution plan
The layout changed, and was improved to allow easier navigation in large query plans
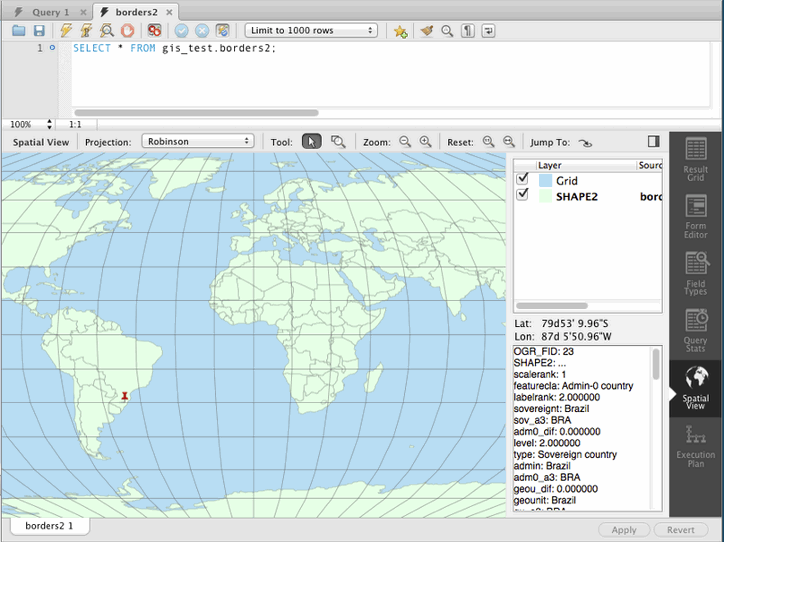
Spatial View Panel
GIS support for InnoDB tables is now supported to make it easier to visualize spatial and geometry data in a geographic context. The new spatial view panel renders data from each row into a separate and selectable element. When clicked, you can view the rest of the data from that row in the textbox. If you have multiple queries with geometry data, you can overlay them onto the same map. View options include the Robinson, Mercator, Equirectangular, and Bonne projection methods.
GIS support for InnoDB tables was added in MySQL server 5.7.
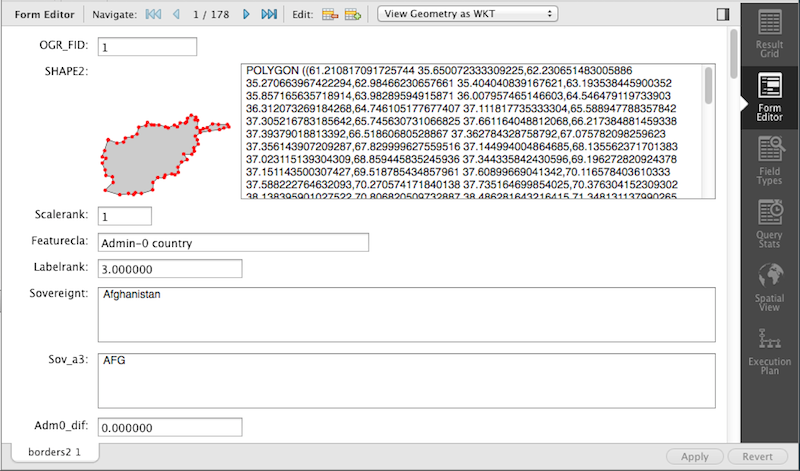
Geometry Data Viewer
The SQL field and form editors were updated to support the
GEOMETRY datatype. You can view geometry data,
such as polygons, from a single row as an image or as text. The
available formats include WKT, GeoJSON, GML, and KML.
Additional New SQL Editor Features
Result Set Widths: resized result set column widths are now preserved and remembered. This data is saved under Workbench's
cache/directory using the schema.table.column format.Opened, closed, and reordered SQL editor tabs are now properly saved and restored. The scroll position and cursor locations are also remembered.
Shared Snippets: these allow multiple users to share SQL code across a shared MySQL connection. They are stored in a schema named .mysqlworkbench on the connected MySQL server. by storing the snippets in a shared MySQL instance. For additional information, see Section 8.1.5, “SQL Snippets tab”.
The full SQL syntax error is now viewable by hovering over the error response message.
The Query Status tab was improved to include graphs and additional information.
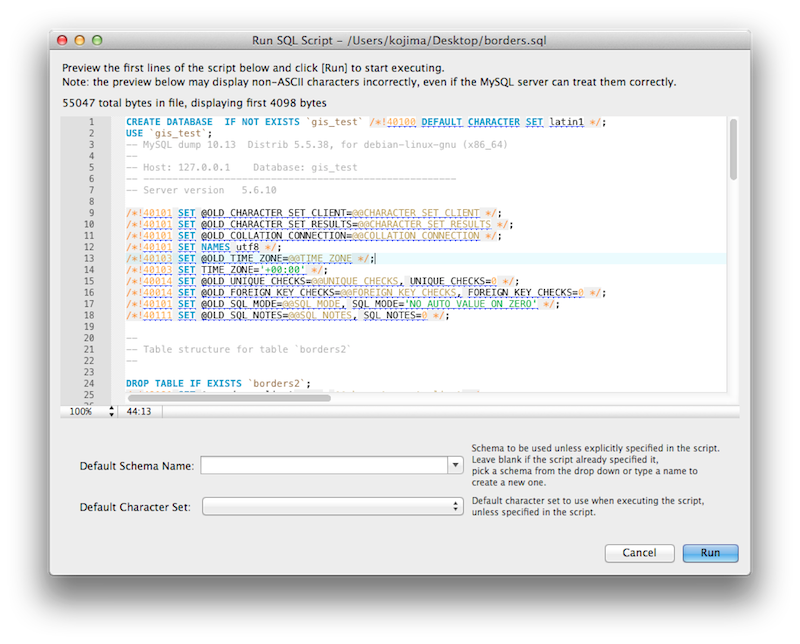
Execute SQL Scripts
The new Run SQL Script dialog executes an SQL script without loading it into the SQL editor. This is useful because loading large scripts for editing can cause performance problems related to increased memory usage and required processing for editor features such as syntax highlighting, syntax checking, and code-folding. The dialog lets you preview a part of the script, optionally specify a default schema, and optionally set the default character set to use for the imported data. The output window shows warnings, messages, and an execution progression bar. Select from the menu to execute this wizard.
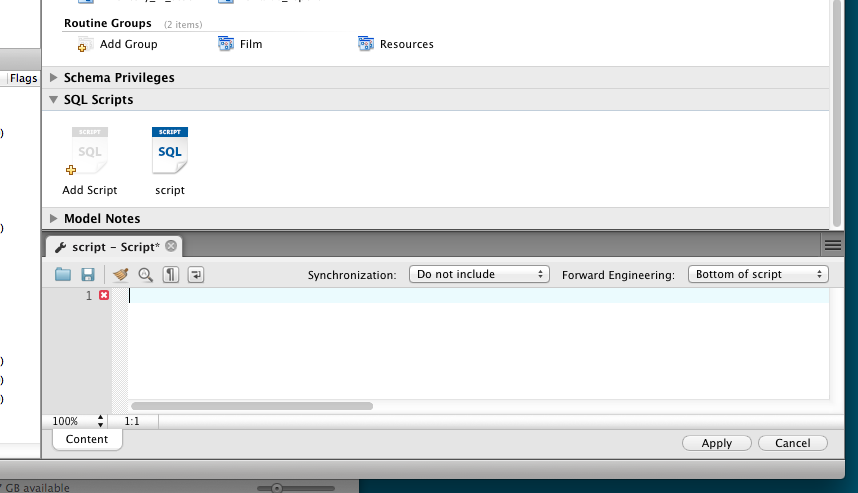
Model Script Attachments
Previously, MySQL Workbench modeling supported attaching SQL script files to models, usually for documentation and organization purposes. You can now include attached SQL files to the output script when performing forward engineering or synchronization operations.
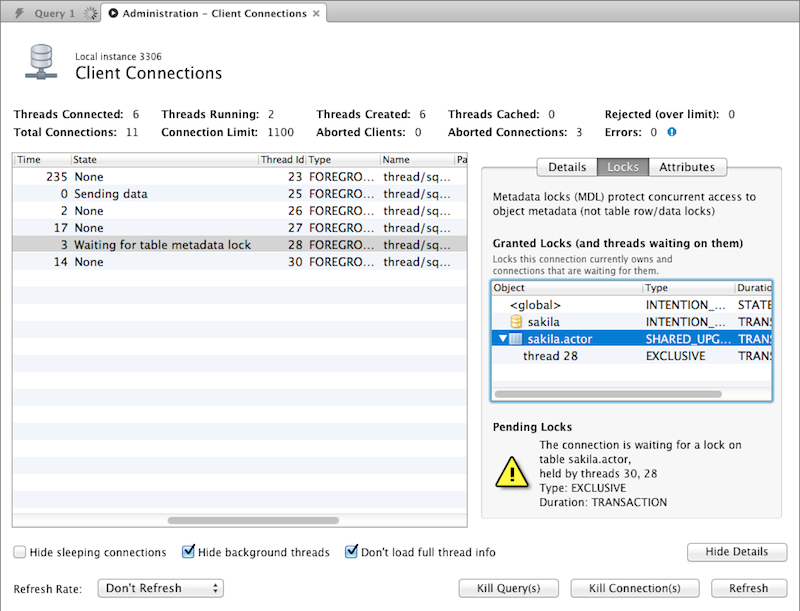
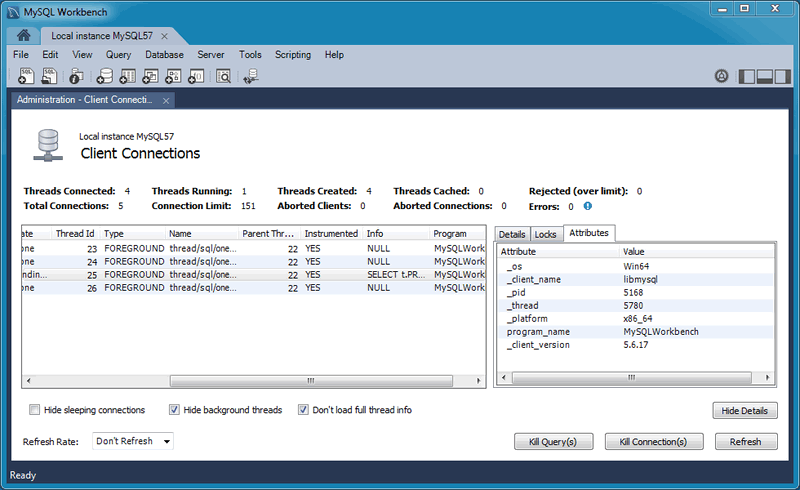
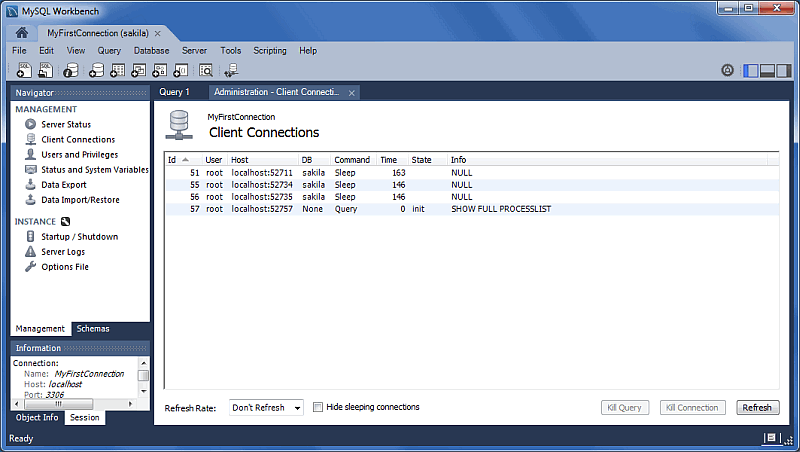
Client Connections and Metadata locks
The Client Connections management window has a new window. This window's three tabs are:
Details: connection details such as Process ID, Type, User, Host, Instrumented, and additional information.
Locks: MySQL uses metadata locking to manage access to objects such as tables and triggers. Sometimes a query might be blocked while being manipulated by another connection from another user. The Locks feature utilizes these MySQL metadata locks (MDL) to show the locked connections that are blocked or being waiting on, and shows information about the locks, what they are waiting for, and what they hold.
NoteThe metadata lock information is provided in the performance schema as of MySQL server 5.7.3.
Attributes: these are connection attributes such as OS, Client Name, Client Version, and Platform.
This feature uses performance schema details from MySQL server 5.7 and above.
For additional information, see Section 5.5, “Client Connections”.
Additional New Features
Performance columns (that display sizes) now have an option to alter the value units. They can be set to KB, MB, or GB. Right-click on a column header and choose Set Display Unit.
The migration wizard can now resume operation if a data copy failed during a database migration from, for example, a timeout or network failure. Click retry the data copy, and MySQL Workbench locates the last row that was copied successfully and attempts to restart the copy from that row.
The MySQL connection password is now remembered across the MySQL Workbench session, even if it not stored in the keychain. This is so you do not need to re-enter it whenever a new MySQL connection is needed.
Under Modeling, the Role Editor now has "Add Everything" and "Check All Privileges" options.
The Preferences layout changed. The tabs were replaced by a list using a horizontal sidebar, and additional category names were added. For additional information, see Section 3.2, “Workbench Preferences”.
Keyboard shortcuts now function in the Scripting Shell.
Model diagram notes can now be resized and automatically rearranged. You can also change the style attributes such as the font, background color, and text color.
This section summarizes many of the new features added to MySQL Workbench 6.1.x, in relation to MySQL Workbench 6.0.x;.
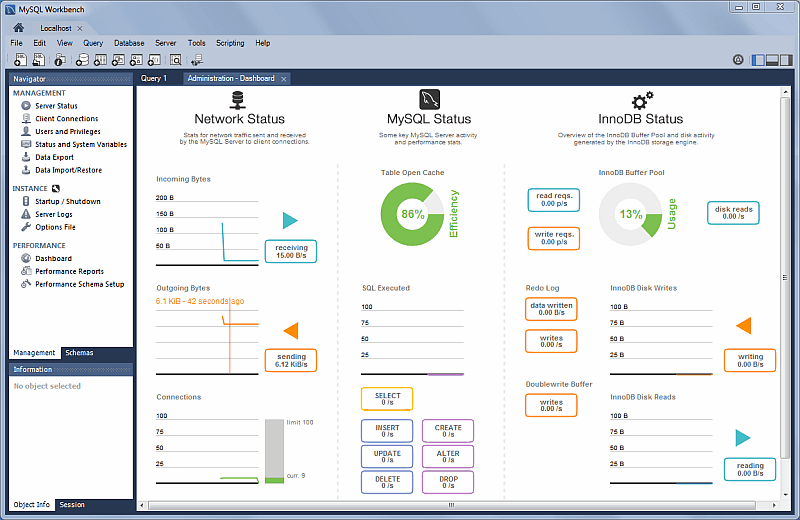
New Navigator PERFORMANCE Section
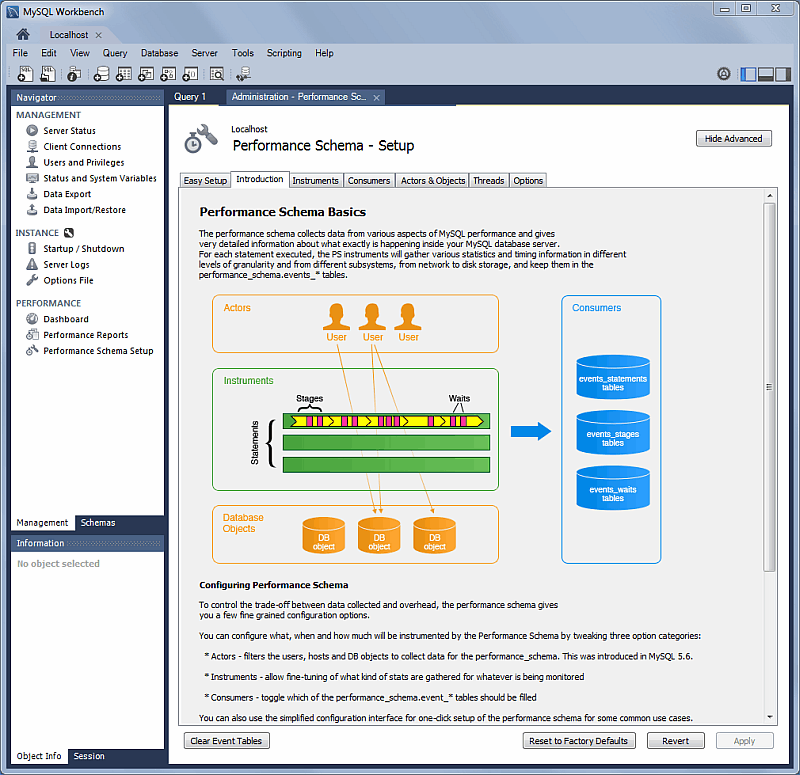
The new PERFORMANCE section includes Dashboard, Performance Reports, and Performance Schema Setup pages. Generally, this new performance reporting feature provides a graphical representation of key statistics from the MySQL server status, and provides an overview of the MySQL server subsystems.
Dashboard
View server performance statistics in a graphical dashboard.
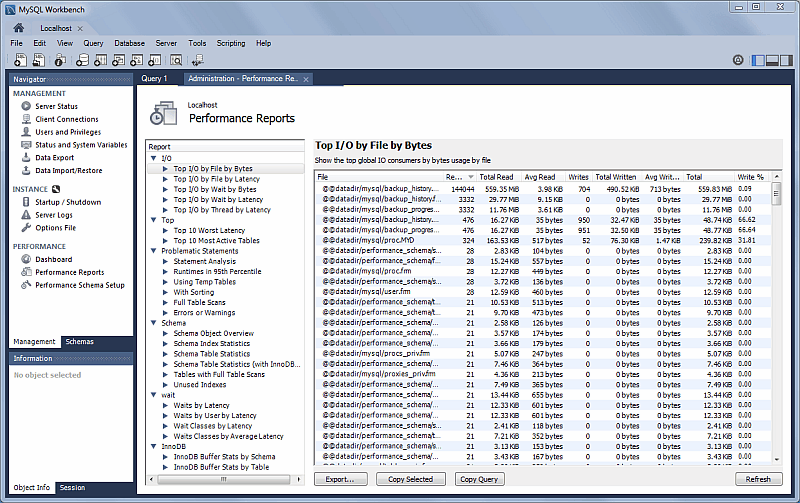
Performance Reports
Performance schema based reports that provide insight into the operation of the MySQL server through many high-level reports.
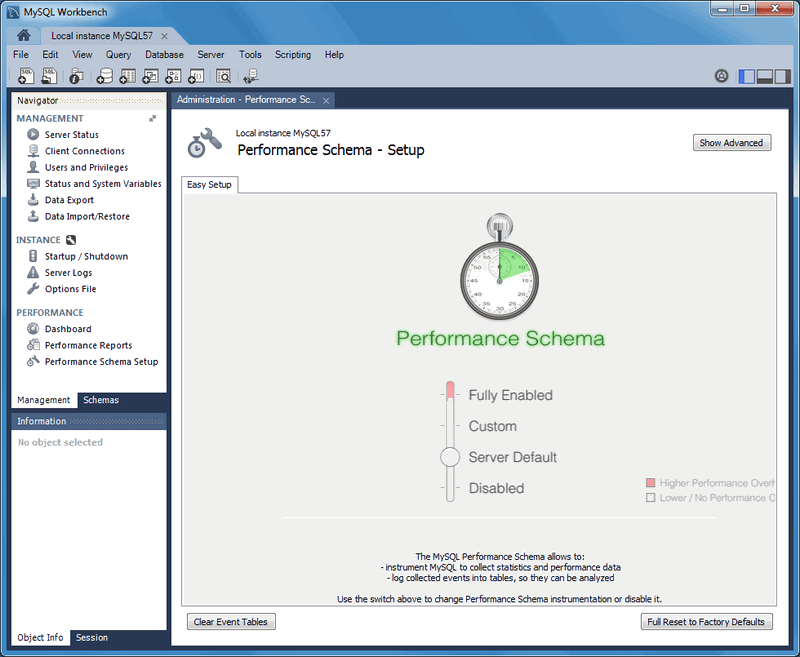
Performance Schema Setup
A GUI for configuring and fine tuning the Performance Schema instrumentation. Initially, this loads an "Easy Setup" page that is enough for most users. Slide the "Performance Schema Full Enabled" slider to YES to enable all available Performance Schema instruments.
Clicking provides methods to fine tune the Performance Schema instrumentation.
For additional information, see Chapter 7, Performance Tools.
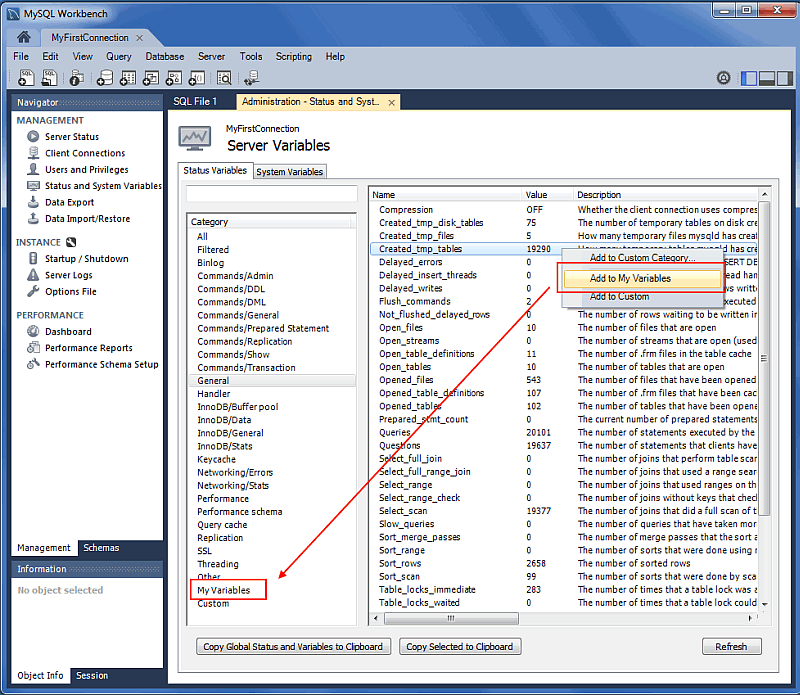
Server Variable Groupings
Variables can now be organized using custom groupings in the Status and System Variables Management tab.
To create a custom group, right-click on a variable and choose either (to create a new category), or an existing custom category. For additional information, see Section 6.4, “Status and System Variables”.
SQL Editor Views
Additional viewing options were added for executed statements:
Result Grid
Available previously, and it remains the default view.
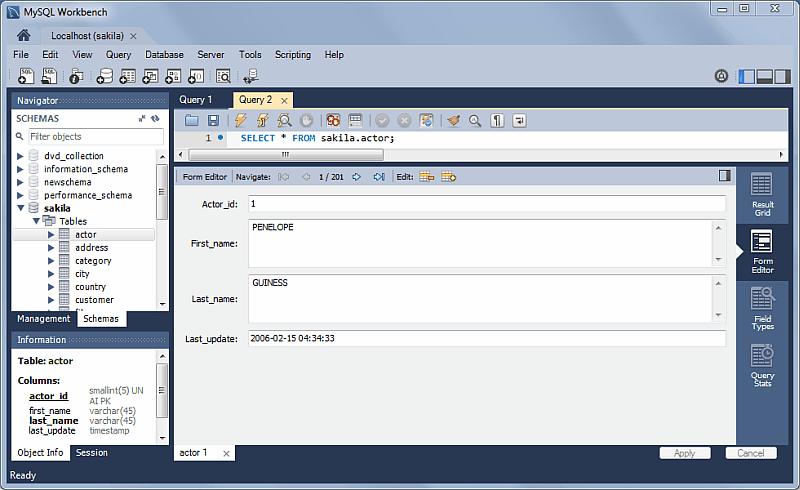
Form Editor
You can now edit records row by row in a form style editor.
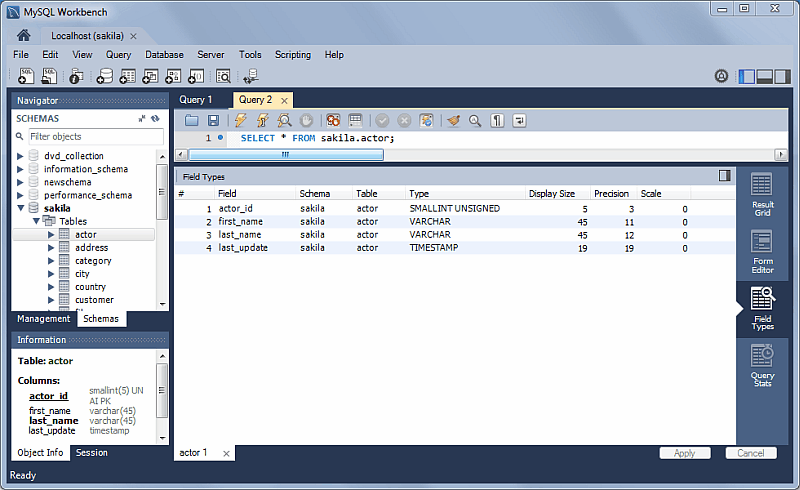
Field Types
Displays information about the selected fields, similar to passing
in --column-type-info from the command line
client.
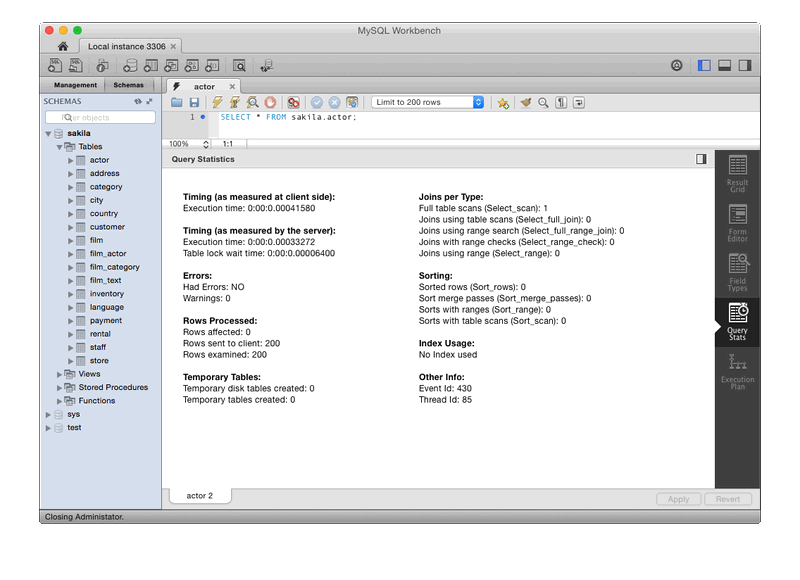
Query Stats
Query statistics are taken from the Performance Schema, and includes information about timing, temporary tables, indexes, joins, and more.
Home Screen Features
Several behavioral improvements were made to the MySQL Workbench Home screen, including:
Connection tiles can now be repositioned by using drag and drop
A script or model file can be dragged into a MySQL connection tile
The following right-click options were added to the connection tiles: and
Right-clicking a blank area in the MySQL Connections area now offers an option to create a
Visual Explain
The layout changed, and additional information is now viewable by
hovering over the fields. It also displays traditional
EXPLAIN output in a separate tab, and the
Raw Explain Data (as JSON) in another. For
MySQL server 5.7+, the new "cost information" (such as
"query_cost" and "sort_cost) is also utilized.
Table Inspector
View table information, similar to the Schema Inspector. This also has a simpler and easier to use interface for analyzing and creating indexes for your tables.
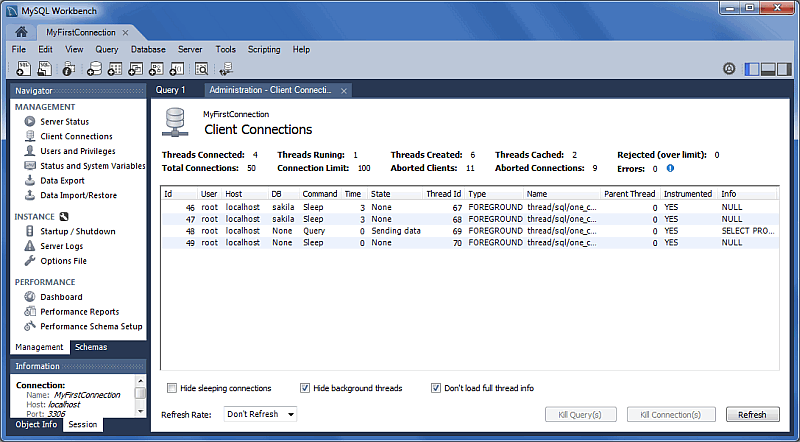
Additional Client Connection Information
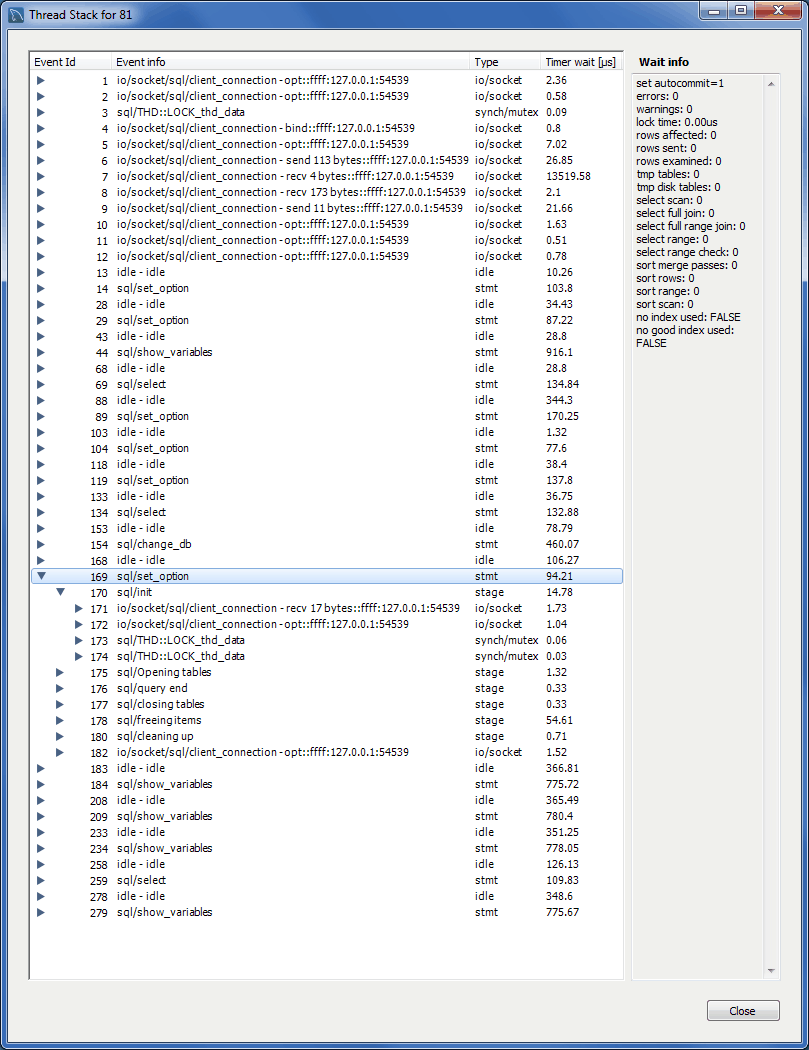
Additional information was added to the Client Connections tab, such as Thread ID, Parent Thread, Instrumented, and Type.
Also, a Thread Stack view option was added by right-clicking a connection entry in the Client Connections tab and choosing .
Additional Miscellaneous Additions
MSAA (Windows Accessibility API) support and High contrast color theme in Microsoft Windows
MySQL Enterprise Backup improvements
Improvements with general performance and overall stability
This section summarizes many of the new features added to MySQL Workbench 6.0.0, in relation to MySQL Workbench 5.2.x;.
A new home screen
A new, modernized Home screen where major functionality of MySQL Workbench can be accessed, including connections to MySQL servers, modeling, migration, and the command-line utilities.
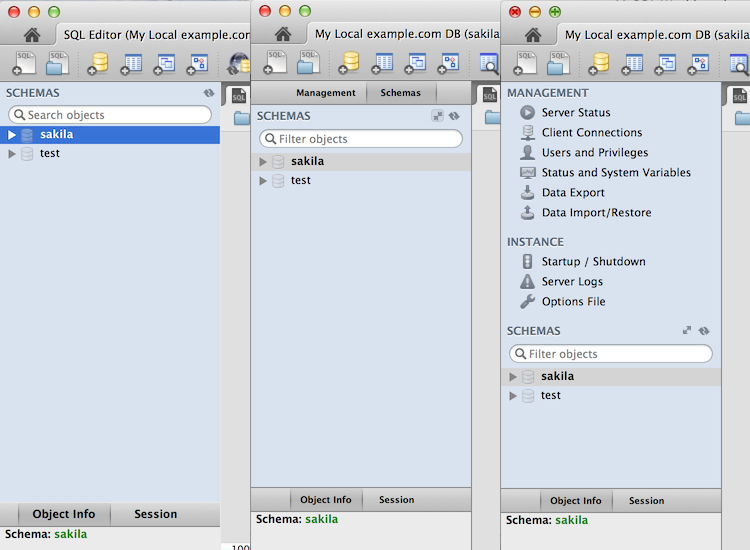
Unified SQL Editor and Administration interface
In the new user interface, the Server Administration functionality (such as start/stop server, managing user accounts etc) is now accessible directly from the SQL Editor interface, located near where the schema information can be browsed and queries executed.
The image below contains three screenshots of the Schema window in the SQL Editor. The first is from MySQL Workbench 5.2, the second is MySQL Workbench 6.0 with the management tab collapsed, and the third shows what the merged management tab looks like. Toggle the merged and tabbed views by clicking the new merge button next to the refresh button.
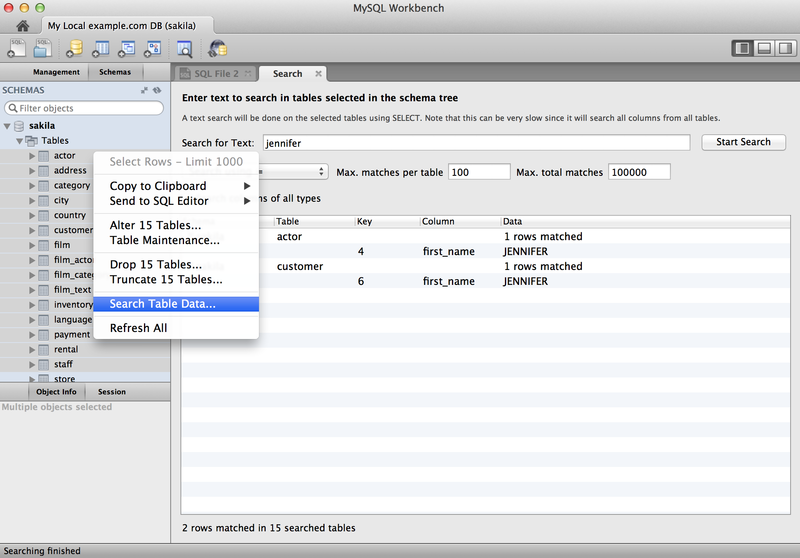
Table data search
You can select schemas and/or tables to perform client-side searches for user specified strings and patterns. To access this new search feature, right click select a schema or a table in the left sidebar and select .
This screenshot demonstrates the search feature, along with an example search. Multiple tables were selected and searched in this example:
For additional information, see Section 8.1.8, “Table Data Search Panel”.
Context Sensitive help for the SQL Editor
Select a keyword or function in your query and after a delay it will show formatted help information from the MySQL Server (equivalent to using the help command from the command-line MySQL Client).
For additional information, see Section 8.1.6, “Context Sensitive Help”.
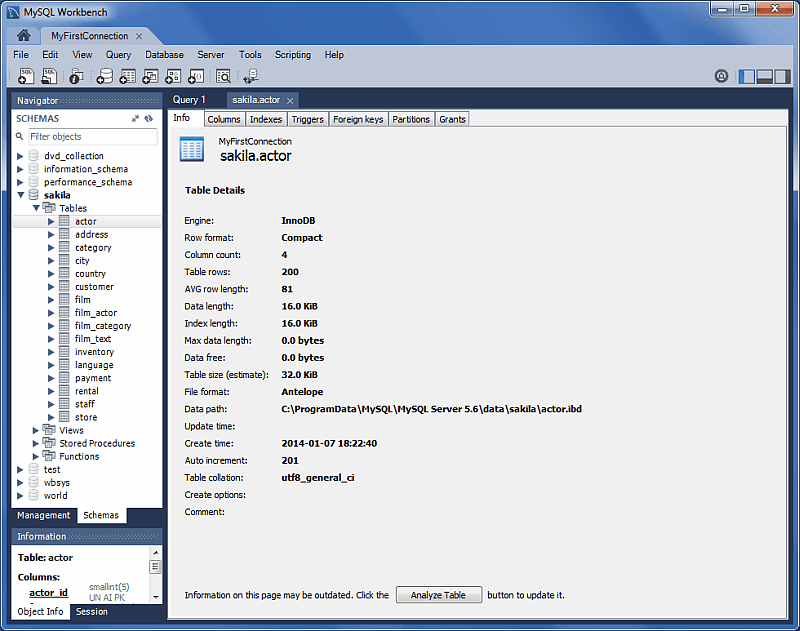
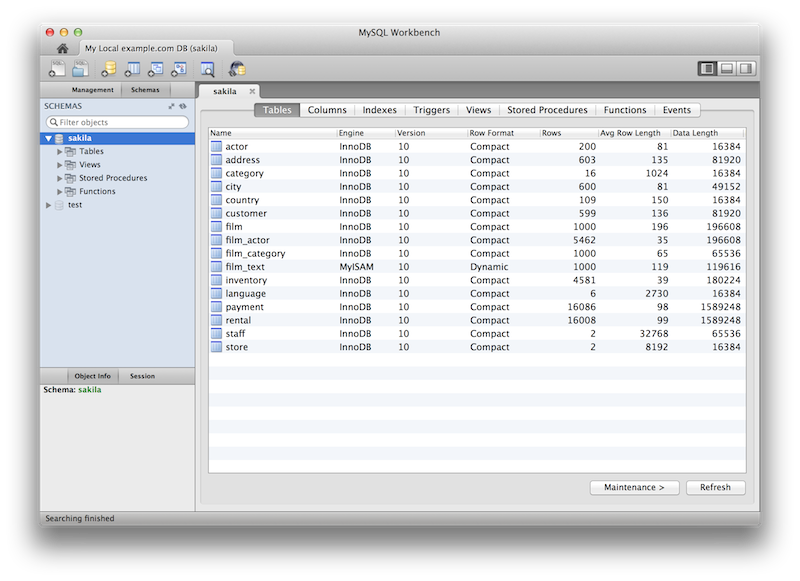
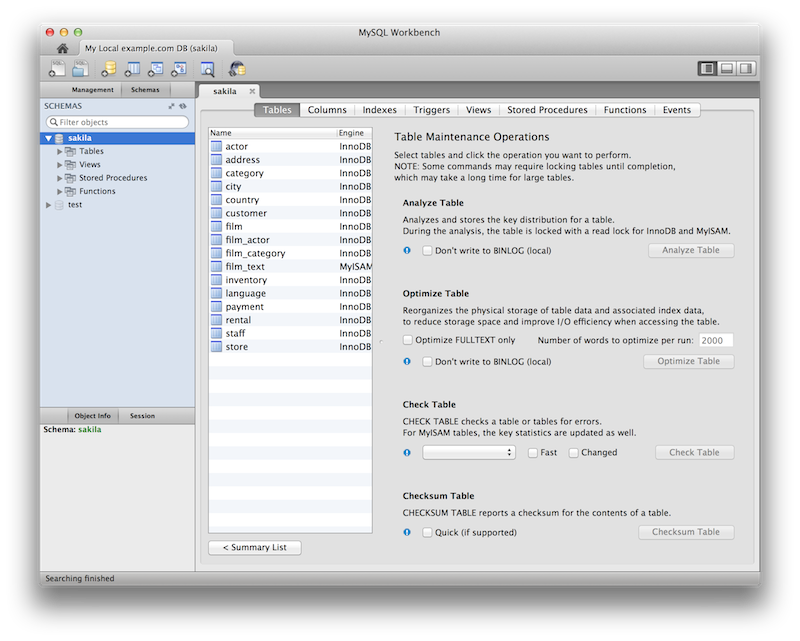
Schema Inspector
New Schema Inspector feature allows you to browse general
information from schema objects. For tables, it's also possible to
perform maintenance tasks such as ANALYZE,
OPTIMIZE, CHECK, and
CHECKSUM TABLE. To access the inspector,
right-click a schema and select the
And choosing for a table:
For additional information, see Schema Inspector.
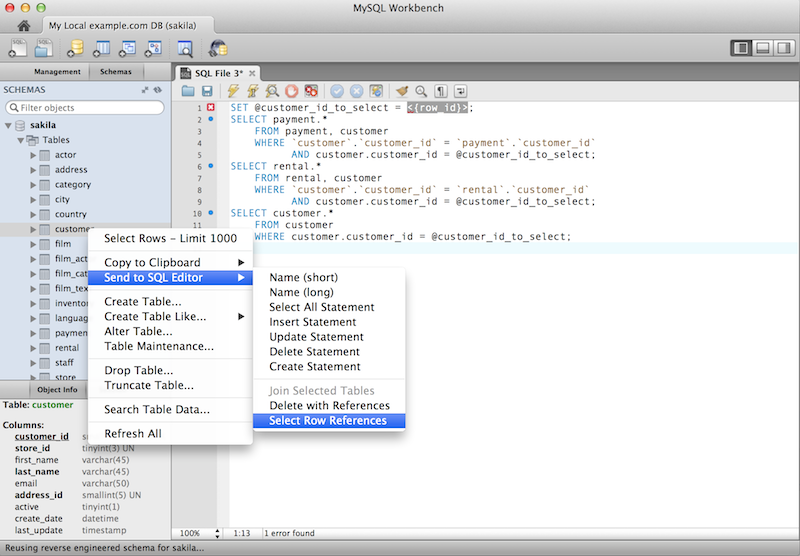
Cascaded DELETE statements generator
You can generate a series of DELETE statements
needed to delete a row from that table, which includes rows from
other tables that reference it, recursively. The
SELECT version allows you to preview what rows
would be deleted. Right click a table and select , .
Table templates
Define templates of tables with commonly used columns, to be used to create new tables in a live connection or in an EER model. In the SQL Editor, choose Create Table Like..., or in Modeling, use the right sidebar. For additional information, see Section 9.6, “Table Templates”.
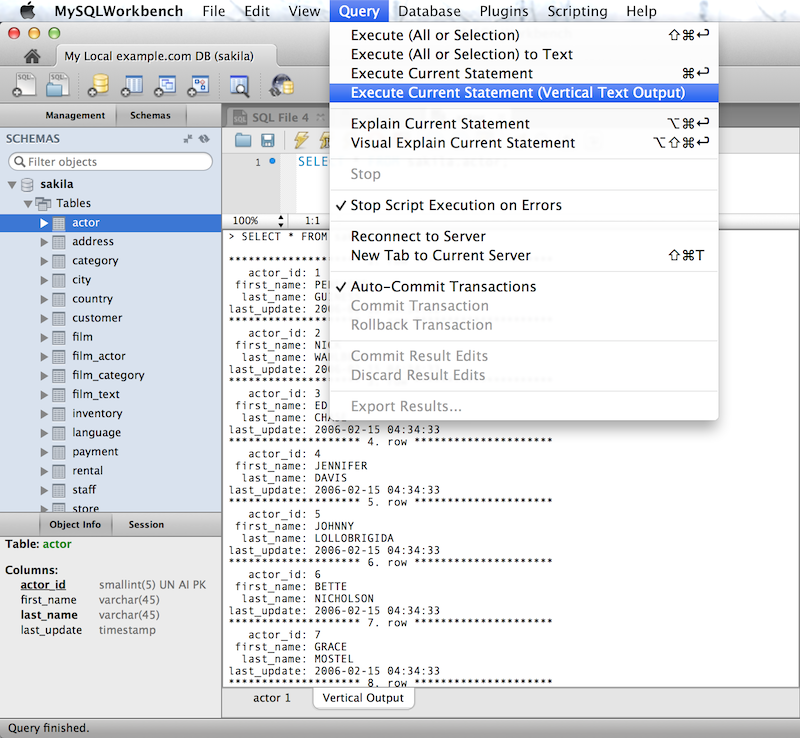
Vertical Text
A Vertical Text output option for queries (equivalent to \G from the command-line Client) was added. To execute, choose , .
Improved Visual Explain
The Visual Explain output was improved.
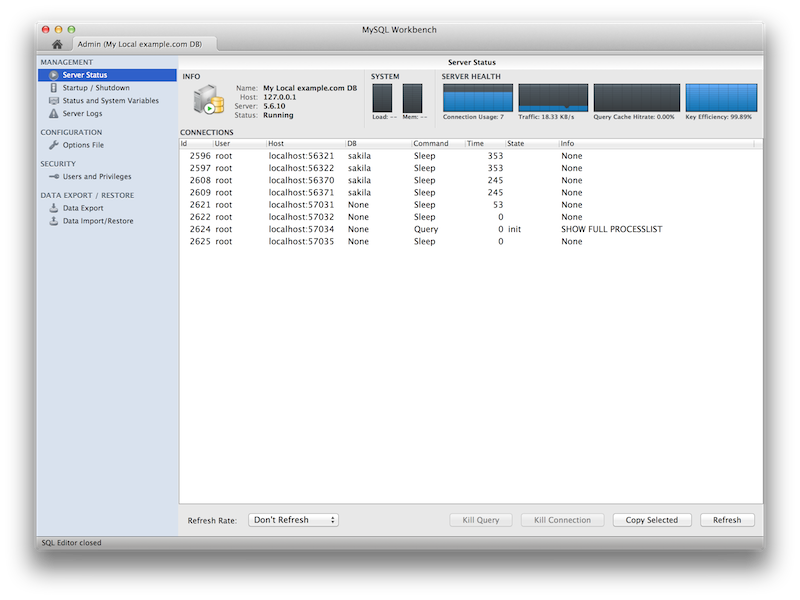
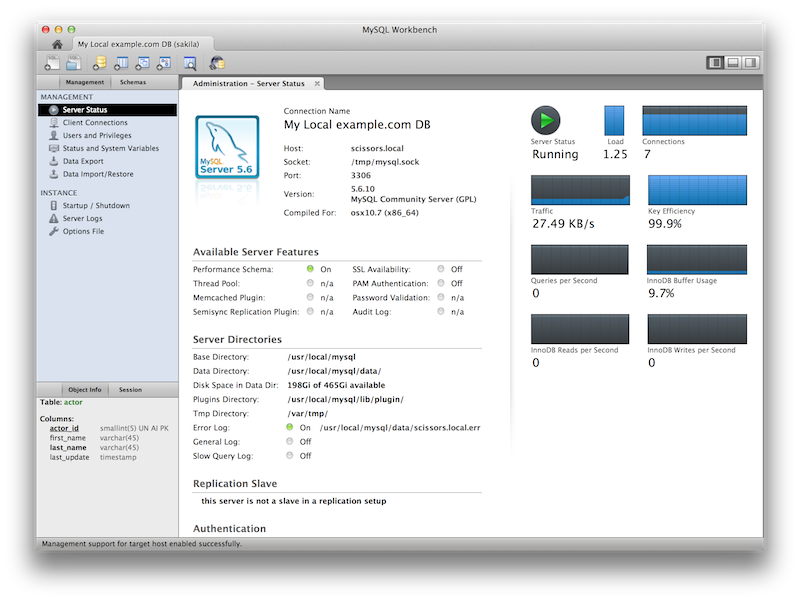
Improved Server Status
Additional server status information was added, and the user interface was improved. Select Server Status from the Management tab to open this window.
Enterprise Features
Support for MySQL Enterprise features in the Commercial edition of MySQL Workbench was added. From within the Management tab for an open connection, look for the following products under the heading MySQL Enterprise:
MySQL Enterprise Backup (MEB): A GUI frontend
for the MEB tool. After installing a commercial version of
MySQL Workbench and MySQL Enterprise Backup, MySQL Workbench will check for and handle the
pre-requisites. Backup recovery is also supported. This plugin
supports MEB with local and remote installations of Linux and OS
X, and locally for MySQL Windows.
MySQL Audit Log Inspector: A GUI for browsing
the contents of generated logs by the commercial Audit Log Plugin.
Powerful filtering and search capabilities are available. Fast
browsing is provided by caching the log data locally in an
encrypted file. This plugin supports MEB with local and remote
installations of Linux and OS X, and locally for MySQL Windows.
Database Migration Features
SQL Anywhere and SQLite are now supported.
MySQL Workbench is available in the following editions:
Community Edition(Open Source, GPL) -- This is the foundation for all other editionsStandard Edition(Commercial)Enterprise Edition(Commercial)
For details about each edition, see http://www.mysql.com/products/workbench/features.html
For more information about the Enterprise edition, visit http://www.mysql.com/enterprise