Contributed by Bob May, maintained by Irina Filippova
December 2007
Developer Guide to the BPEL Designer
|
|
One of the primary means of orchestrating web services is the use of Business Process Execution Language (BPEL). This guide explores ways in which the IDE enables you to edit, compile, and deploy BPEL processes compliant with the WS-BPEL 2.0 specification. Using the BPEL Designer feature of the IDE, you can easily create and edit BPEL processes, deploy them to the BPEL Service Engine, and run these processes in test or debug modes.
To better understand the BPEL Designer features provided by the NetBeans IDE 6.0 release, see the following tutorials:
For readability, some images have been provided in thumbnail format. Click those images to see a larger version.
This document consists of several sections, each related to a particular feature of the BPEL Designer included in the NetBeans IDE. A list of sections is given in the Contents.
The Java Business Integration (JBI) runtime environment provides the runtime capability for SOA tools in the IDE. The JBI runtime environment includes several components that interact using a services model. This model is based on Web Services Description Language (WSDL) 2.0. Components that supply or consume services within the JBI environment are referred to as Service Engines. One of these components is the BPEL Service Engine that provides services for executing business processes. Components that provide access to services that are external to the JBI environment are called Binding Components.
The JBI components are installed as part of the GlassFish application server, which is packaged with the NetBeans IDE.
To view the installed or deployed JBI components:
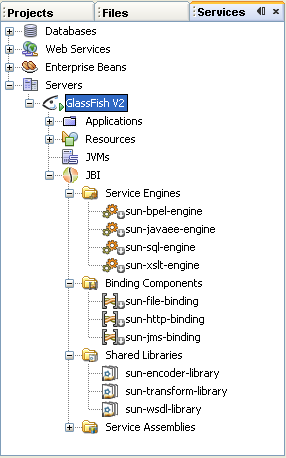
For a detailed overview of the Java Business Integration concept and a description of JBI nodes, see the JBI Component Technical Overview.
The BPEL Service Engine is a JSR 208-compliant JBI runtime component that provides services for executing WS-BPEL 2.0 compliant business processes. The BPEL Service Engine provides runtime services for deploying BPEL processes. To deploy a BPEL process, you need to add it as a JBI module to a Composite Application project.
The BPEL Service Engine starts together with the Application Server. Thus, before deploying and performing test runs of a Composite Application project, make sure that the Application Server is started.
To check the status of the GlassFish V2 Application Server:
To configure the GlassFish V2 Application Server:
To start the GlassFish V2 Application Server:
The BPEL Service Engine is represented as sun-bpel-engine in the Services window of the IDE, under the GlassFish V2 > JBI nodes.
See the BPEL Service Engine User's Guide for details about the BPEL Service Engine and supported BPEL 2.0 language constructs.
The Composite Application project is used to create a Service Assembly that can be deployed to the Java Business Integration (JBI) runtime environment. Within the Composite Application project, you can:
To deploy a Composite Application to the BPEL Service Engine, it must include a JBI module created from a BPEL Module project. Within a Composite Application Project that includes a JBI module, you can also create and execute test cases that can then be run against the deployed BPEL processes.
For more information about working with Composite Application projects, see The BPEL Module Project and Testing and Debugging BPEL Processes sections of this guide.