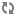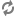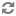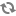Contents
Compute uses the nova-scheduler service to determine how to
dispatch compute and volume requests. For example, the
nova-scheduler service determines which host a VM should launch
on. The term host in the context of filters means a physical node
that has a nova-compute
service running on it. You can configure the scheduler through a
variety of options.
Just as shown by above figure, nova-scheduler interacts with other components through queue and central database repo. For scheduling, queue is the essential communications hub.
All compute nodes (also known as hosts in terms of OpenStack) periodically publish their status, resources available and hardware capabilities to nova-scheduler through the queue. nova-scheduler then collects this data and uses it to make decisions when a request comes in.
By default, the compute scheduler is configured as a filter scheduler, as described in the next section. In the default configuration, this scheduler considers hosts that meet all the following criteria:
Are in the requested availability zone (AvailabilityZoneFilter).
Have sufficient RAM available (RamFilter).
Are capable of servicing the request (ComputeFilter).
Filter Scheduler
The Filter Scheduler supports filtering and weighting to make informed decisions on where a new instance should be created. This Scheduler supports only working with Compute Nodes.
Filtering
During its work, Filter Scheduler first makes a dictionary of unfiltered hosts, then filters them using filter properties and finally chooses hosts for the requested number of instances (each time it chooses the most weighed host and appends it to the list of selected hosts).
If it turns up, that it can’t find candidates for the next instance, it means that there are no more appropriate hosts where the instance could be scheduled.
If we speak about filtering and weighting, their work is quite flexible in the Filter Scheduler. There are a lot of filtering strategies for the Scheduler to support. Also you can even implement your own algorithm of filtering.
There are some standard filter classes to use (nova.scheduler.filters):
AllHostsFilter - frankly speaking, this filter does no operation. It passes all the available hosts.
ImagePropertiesFilter - filters hosts based on properties defined on the instance’s image. It passes hosts that can support the specified image properties contained in the instance.
AvailabilityZoneFilter - filters hosts by availability zone. It passes hosts matching the availability zone specified in the instance properties.
ComputeCapabilitiesFilter - checks that the capabilities provided by the host Compute service satisfy any extra specifications associated with the instance type. It passes hosts that can create the specified instance type.
The extra specifications can have a scope at the beginning of the key string of a key/value pair. The scope format is scope:key and can be nested, i.e. key_string := scope:key_string. Example like capabilities:cpu_info: features is valid scope format. A key string without any : is non-scope format. Each filter defines its valid scope, and not all filters accept non-scope format.
The extra specifications can have an operator at the beginning of the value string of a key/value pair. If there is no operator specified, then a default operator of s== is used. Valid operators are:
* = (equal to or greater than as a number; same as vcpus case)* == (equal to as a number)* != (not equal to as a number)* >= (greater than or equal to as a number)* <= (less than or equal to as a number)* s== (equal to as a string)* s!= (not equal to as a string)* s>= (greater than or equal to as a string)* s> (greater than as a string)* s<= (less than or equal to as a string)* s< (less than as a string)* <in> (substring)* <or> (find one of these)Examples are: ">= 5", "s== 2.1.0", "<in> gcc", and "<or> fpu <or> gpu"
class RamFilter(filters.BaseHostFilter):
"""Ram Filter with over subscription flag"""
def host_passes(self, host_state, filter_properties):
"""Only return hosts with sufficient available RAM."""
instance_type = filter_properties.get('instance_type')
requested_ram = instance_type['memory_mb']
free_ram_mb = host_state.free_ram_mb
total_usable_ram_mb = host_state.total_usable_ram_mb
used_ram_mb = total_usable_ram_mb - free_ram_mb
return total_usable_ram_mb * FLAGS.ram_allocation_ratio - used_ram_mb >= requested_ramHere ram_allocation_ratio means the virtual RAM to physical RAM allocation ratio (it is 1.5 by default). Really, nice and simple.
Next standard filter to describe is AvailabilityZoneFilter and it isn’t difficult too. This filter just looks at the availability zone of compute node and availability zone from the properties of the request. Each Compute service has its own availability zone. So deployment engineers have an option to run scheduler with availability zones support and can configure availability zones on each compute host. This classes method host_passes returns True if availability zone mentioned in request is the same on the current compute host.
The ImagePropertiesFilter filters hosts based on the architecture, hypervisor type, and virtual machine mode specified in the instance. E.g., an instance might require a host that supports the arm architecture on a qemu compute host. The ImagePropertiesFilter will only pass hosts that can satisfy this request. These instance properties are populated from properties define on the instance’s image. E.g. an image can be decorated with these properties using glance image-update img-uuid --property architecture=arm --property hypervisor_type=qemu Only hosts that satisfy these requirements will pass the ImagePropertiesFilter.
ComputeCapabilitiesFilter checks if the host satisfies any extra_specs specified on the instance type. The extra_specs can contain key/value pairs. The key for the filter is either non-scope format (i.e. no : contained), or scope format in capabilities scope (i.e. capabilities:xxx:yyy). One example of capabilities scope is capabilities:cpu_info:features, which will match host’s cpu features capabilities. The ComputeCapabilitiesFilter will only pass hosts whose capabilities satisfy the requested specifications. All hosts are passed if no extra_specs are specified.
ComputeFilter is quite simple and passes any host whose Compute service is enabled and operational.
Now we are going to IsolatedHostsFilter. There can be some special hosts reserved for specific images. These hosts are called isolated. So the images to run on the isolated hosts are also called isolated. This Scheduler checks if image_isolated flag named in instance specifications is the same that the host has.
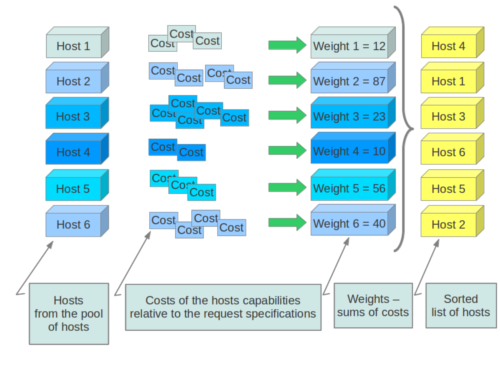
Weights
Filter Scheduler uses so-called weights during its work.
The Filter Scheduler weights hosts based on the config option scheduler_weight_classes, this defaults to nova.scheduler.weights.all_weighers, which selects the only weigher available – the RamWeigher. Hosts are then weighted and sorted with the largest weight winning.
Filter Scheduler finds local list of acceptable hosts by repeated filtering and weighing. Each time it chooses a host, it virtually consumes resources on it, so subsequent selections can adjust accordingly. It is useful if the customer asks for the same large amount of instances, because weight is computed for each instance requested.
In the end Filter Scheduler sorts selected hosts by their weight and provisions instances on them.
The request flow for provisioning an instance goes like this:
The dashboard or CLI gets the user credentials and authenticates with the Identity Service via REST API.
The Identity Service authenticates the user with the user credentials, and then generates and sends back an auth-token which will be used for sending the request to other components through REST-call.
The dashboard or CLI converts the new instance request specified in launch instance or nova-boot form to a REST API request and sends it to
nova-api.nova-apireceives the request and sends a request to the Identity Service for validation of the auth-token and access permission.The Identity Service validates the token and sends updated authentication headers with roles and permissions.
nova-apichecks for conflicts withnova-database.nova-apicreates initial database entry for a new instance.nova-apisends the rpc.call request tonova-schedulerexpecting to get updated instance entry with host ID specified.nova-schedulerpicks up the request from the queue.nova-schedulerinteracts withnova-databaseto find an appropriate host via filtering and weighing.nova-schedulerreturns the updated instance entry with the appropriate host ID after filtering and weighing.nova-schedulersends the rpc.cast request tonova-computefor launching an instance on the appropriate host.nova-computepicks up the request from the queue.nova-computesends the rpc.call request tonova-conductorto fetch the instance information such as host ID and flavor (RAM, CPU, Disk).nova-conductorpicks up the request from the queue.nova-conductorinteracts withnova-database.nova-conductorreturns the instance information.nova-computepicks up the instance information from the queue.nova-computeperforms the REST call by passing the auth-token toglance-api. Then,nova-computeuses the Image ID to retrieve the Image URI from the Image Service, and loads the image from the image storage.glance-apivalidates the auth-token with keystone.nova-computegets the image metadata.nova-computeperforms the REST-call by passing the auth-token to Network API to allocate and configure the network so that the instance gets the IP address.neutron-servervalidates the auth-token with keystone.nova-computeretrieves the network info.nova-computeperforms the REST call by passing the auth-token to Volume API to attach volumes to the instance.cinder-apivalidates the auth-token with keystone.nova-computeretrieves the block storage info.nova-computegenerates data for the hypervisor driver and executes the request on the hypervisor (via libvirt or API).
Block Storage and OpenStack Compute
OpenStack provides two classes of block storage, "ephemeral" storage and persistent "volumes". Ephemeral storage exists only for the life of an instance, it will persist across reboots of the guest operating system but when the instance is deleted so is the associated storage. All instances have some ephemeral storage. Volumes are persistent virtualized block devices independent of any particular instance. Volumes may be attached to a single instance at a time, but may be detached or reattached to a different instance while retaining all data, much like a USB drive.
Ephemeral Storage
Ephemeral storage is associated with a single unique instance. Its size is defined by the flavor of the instance.
Data on ephemeral storage ceases to exist when the instance it is associated with is terminated. Rebooting the VM or restarting the host server, however, will not destroy ephemeral data. In the typical use case an instance's root filesystem is stored on ephemeral storage. This is often an unpleasant surprise for people unfamiliar with the cloud model of computing.
In addition to the ephemeral root volume all flavors except the smallest, m1.tiny, provide an additional ephemeral block device varying from 20G for the m1.small through 160G for the m1.xlarge by default - these sizes are configurable. This is presented as a raw block device with no partition table or filesystem. Cloud aware operating system images may discover, format, and mount this device. For example the cloud-init package included in Ubuntu's stock cloud images will format this space as an ext3 filesystem and mount it on /mnt. It is important to note this a feature of the guest operating system. OpenStack only provisions the raw storage.
Volume Storage
Volume storage is independent of any particular instance and is persistent. Volumes are user created and within quota and availability limits may be of any arbitrary size.
When first created volumes are raw block devices with no partition table and no filesystem. They must be attached to an instance to be partitioned and/or formatted. Once this is done they may be used much like an external disk drive. Volumes may attached to only one instance at a time, but may be detached and reattached to either the same or different instances.
It is possible to configure a volume so that it is bootable and provides a persistent virtual instance similar to traditional non-cloud based virtualization systems. In this use case the resulting instance may still have ephemeral storage depending on the flavor selected, but the root filesystem (and possibly others) will be on the persistent volume and thus state will be maintained even if the instance is shutdown. Details of this configuration are discussed in theOpenStack End User Guide.
Volumes do not provide concurrent access from multiple instances. For that you need either a traditional network filesystem like NFS or CIFS or a cluster filesystem such as GlusterFS. These may be built within an OpenStack cluster or provisioned outside of it, but are not features provided by the OpenStack software.
The OpenStack Block Storage service works via the interaction of a series of daemon processes named cinder-* that reside persistently on the host machine or machines. The binaries can all be run from a single node, or spread across multiple nodes. They can also be run on the same node as other OpenStack services.
The current services available in OpenStack Block Storage are:
cinder-api - The cinder-api service is a WSGI app that authenticates and routes requests throughout the Block Storage system. It supports the OpenStack API's only, although there is a translation that can be done via Nova's EC2 interface which calls in to the cinderclient.
cinder-scheduler - The cinder-scheduler is responsible for scheduling/routing requests to the appropriate volume service. As of Grizzly; depending upon your configuration this may be simple round-robin scheduling to the running volume services, or it can be more sophisticated through the use of the Filter Scheduler. The Filter Scheduler is the default in Grizzly and enables filter on things like Capacity, Availability Zone, Volume Types and Capabilities as well as custom filters.
cinder-volume - The cinder-volume service is responsible for managing Block Storage devices, specifically the back-end devices themselves.
cinder-backup - The cinder-backup service provides a means to back up a Cinder Volume to OpenStack Object Store (SWIFT).
Introduction to OpenStack Block Storage
OpenStack Block Storage provides persistent High Performance Block Storage resources that can be consumed by OpenStack Compute instances. This includes secondary attached storage similar to Amazon's Elastic Block Storage (EBS). In addition images can be written to a Block Storage device and specified for OpenStack Compute to use a bootable persistent instance.
There are some differences from Amazon's EBS that one should be aware of. OpenStack Block Storage is not a shared storage solution like NFS, but currently is designed so that the device is attached and in use by a single instance at a time.
Backend Storage Devices
OpenStack Block Storage requires some form of back-end storage that the service is built on. The default implementation is to use LVM on a local Volume Group named "cinder-volumes". In addition to the base driver implementation, OpenStack Block Storage also provides the means to add support for other storage devices to be utilized such as external Raid Arrays or other Storage appliances.
Users and Tenants (Projects)
The OpenStack Block Storage system is designed to be used by many different cloud computing consumers or customers, basically tenants on a shared system, using role-based access assignments. Roles control the actions that a user is allowed to perform. In the default configuration, most actions do not require a particular role, but this is configurable by the system administrator editing the appropriate policy.json file that maintains the rules. A user's access to particular volumes is limited by tenant, but the username and password are assigned per user. Key pairs granting access to a volume are enabled per user, but quotas to control resource consumption across available hardware resources are per tenant.
For tenants, quota controls are available to limit the:
Number of volumes which may be created
Number of snapshots which may be created
Total number of Giga Bytes allowed per tenant (shared between snapshots and volumes)
Volumes Snapshots and Backups
This introduction provides a high level overview of the two basic resources offered by the OpenStack Block Storage service. The first is Volumes and the second is Snapshots which are derived from Volumes.
Volumes
Volumes are allocated block storage resources that can be attached to instances as secondary storage or they can be used as the root store to boot instances. Volumes are persistent R/W Block Storage devices most commonly attached to the compute node via iSCSI.
Snapshots
A Snapshot in OpenStack Block Storage is a read-only point in time copy of a Volume. The Snapshot can be created from a Volume that is currently in use (via the use of '--force True') or in an available state. The Snapshot can then be used to create a new volume via create from snapshot.
Backups
A Backup is an archived copy of a Volume currently stored in Object Storage (Swift).
Managing Volumes
Cinder is the OpenStack service that allows you to give extra block level storage to your OpenStack Compute instances. You may recognize this as a similar offering from Amazon EC2 known as Elastic Block Storage (EBS). The default Cinder implementation is an iSCSI solution that employs the use of Logical Volume Manager (LVM) for Linux. Note that a volume may only be attached to one instance at a time. This is not a ‘shared storage’ solution like a SAN of NFS on which multiple servers can attach to. It's also important to note that Cinder also includes a number of drivers to allow you to use a number of other vendor's back-end storage devices in addition to or instead of the base LVM implementation.
Here is brief walk-through of a simple create/attach sequence, keep in mind this requires proper configuration of both OpenStack Compute via cinder.conf and OpenStack Block Storage via cinder.conf.
The volume is created via cinder create; which creates an LV into the volume group (VG) "cinder-volumes"
The volume is attached to an instance via nova volume-attach; which creates a unique iSCSI IQN that will be exposed to the compute node
The compute node which run the concerned instance has now an active ISCSI session; and a new local storage (usually a /dev/sdX disk)
libvirt uses that local storage as a storage for the instance; the instance get a new disk (usually a /dev/vdX disk)
Block Storage Capabilities
OpenStack provides persistent block level storage devices for use with OpenStack compute instances.
The block storage system manages the creation, attaching and detaching of the block devices to servers. Block storage volumes are fully integrated into OpenStack Compute and the Dashboard allowing for cloud users to manage their own storage needs.
In addition to using simple Linux server storage, it has unified storage support for numerous storage platforms including Ceph, NetApp, Nexenta, SolidFire, and Zadara.
Block storage is appropriate for performance sensitive scenarios such as database storage, expandable file systems, or providing a server with access to raw block level storage.
Snapshot management provides powerful functionality for backing up data stored on block storage volumes. Snapshots can be restored or used to create a new block storage volume.
- cinder usage
- cinder optional arguments
- cinder absolute-limits command
- cinder availability-zone-list command
- cinder backup-create command
- cinder backup-delete command
- cinder backup-list command
- cinder backup-restore command
- cinder backup-show command
- cinder create command
- cinder credentials command
- cinder delete command
- cinder encryption-type-create command
- cinder encryption-type-delete command
- cinder encryption-type-list command
- cinder encryption-type-show command
- cinder endpoints command
- cinder extend command
- cinder extra-specs-list command
- cinder force-delete command
- cinder list command
- cinder list-extensions command
- cinder metadata command
- cinder metadata-show command
- cinder metadata-update-all command
- cinder migrate command
- cinder qos-associate command
- cinder qos-create command
- cinder qos-delete command
- cinder qos-disassociate command
- cinder qos-disassociate-all command
- cinder qos-get-association command
- cinder qos-key command
- cinder qos-list command
- cinder qos-show command
- cinder quota-class-show command
- cinder quota-class-update command
- cinder quota-defaults command
- cinder quota-show command
- cinder quota-update command
- cinder quota-usage command
- cinder rate-limits command
- cinder readonly-mode-update command
- cinder rename command
- cinder reset-state command
- cinder service-disable command
- cinder service-enable command
- cinder service-list command
- cinder show command
- cinder snapshot-create command
- cinder snapshot-delete command
- cinder snapshot-list command
- cinder snapshot-metadata command
- cinder snapshot-metadata-show command
- cinder snapshot-metadata-update-all command
- cinder snapshot-rename command
- cinder snapshot-reset-state command
- cinder snapshot-show command
- cinder transfer-accept command
- cinder transfer-create command
- cinder transfer-delete command
- cinder transfer-list command
- cinder transfer-show command
- cinder type-create command
- cinder type-delete command
- cinder type-key command
- cinder type-list command
- cinder upload-to-image command
The cinder client is the command-line interface (CLI) for the OpenStack Block Storage API and its extensions. This chapter documents cinder version 1.0.8.
For help on a specific cinder command, enter:
$ cinder help COMMANDusage: cinder [--version] [--debug] [--os-username <auth-user-name>]
[--os-password <auth-password>]
[--os-tenant-name <auth-tenant-name>]
[--os-tenant-id <auth-tenant-id>] [--os-auth-url <auth-url>]
[--os-region-name <region-name>] [--service-type <service-type>]
[--service-name <service-name>]
[--volume-service-name <volume-service-name>]
[--endpoint-type <endpoint-type>]
[--os-volume-api-version <volume-api-ver>]
[--os-cacert <ca-certificate>] [--retries <retries>]
<subcommand> ...
Subcommands
- absolute-limits
Print a list of absolute limits for a user
- availability-zone-list
List all the availability zones.
- backup-create
Creates a backup.
- backup-delete
Remove a backup.
- backup-list
List all the backups.
- backup-restore
Restore a backup.
- backup-show
Show details about a backup.
- create
Add a new volume.
- credentials
Show user credentials returned from auth.
- delete
Remove volume(s).
- encryption-type-create
Create a new encryption type for a volume type (Admin Only).
- encryption-type-delete
Delete the encryption type for a volume type (Admin Only).
- encryption-type-list
List encryption type information for all volume types (Admin Only).
- encryption-type-show
Show the encryption type information for a volume type (Admin Only).
- endpoints
Discover endpoints that get returned from the authenticate services.
- extend
Attempt to extend the size of an existing volume.
- extra-specs-list
Print a list of current 'volume types and extra specs' (Admin Only).
- force-delete
Attempt forced removal of volume(s), regardless of the state(s).
- list
List all the volumes.
- metadata
Set or Delete metadata on a volume.
- metadata-show
Show metadata of given volume.
- metadata-update-all
Update all metadata of a volume.
- migrate
Migrate the volume to the new host.
- qos-associate
Associate qos specs with specific volume type.
- qos-create
Create a new qos specs.
- qos-delete
Delete a specific qos specs.
- qos-disassociate
Disassociate qos specs from specific volume type.
- qos-disassociate-all
Disassociate qos specs from all of its associations.
- qos-get-association
Get all associations of specific qos specs.
- qos-key
Set or unset specifications for a qos spec.
- qos-list
Get full list of qos specs.
- qos-show
Get a specific qos specs.
- quota-class-show
List the quotas for a quota class.
- quota-class-update
Update the quotas for a quota class.
- quota-defaults
List the default quotas for a tenant.
- quota-show
List the quotas for a tenant.
- quota-update
Update the quotas for a tenant.
- quota-usage
List the quota usage for a tenant.
- rate-limits
Print a list of rate limits for a user
- readonly-mode-update
Update volume read-only access mode read_only.
- rename
Rename a volume.
- reset-state
Explicitly update the state of a volume.
- service-disable
Disable the service.
- service-enable
Enable the service.
- service-list
List all the services. Filter by host & service binary.
- show
Show details about a volume.
- snapshot-create
Add a new snapshot.
- snapshot-delete
Remove a snapshot.
- snapshot-list
List all the snapshots.
- snapshot-metadata
Set or Delete metadata of a snapshot.
- snapshot-metadata-show
Show metadata of given snapshot.
- snapshot-metadata-update-all
Update all metadata of a snapshot.
- snapshot-rename
Rename a snapshot.
- snapshot-reset-state
Explicitly update the state of a snapshot.
- snapshot-show
Show details about a snapshot.
- transfer-accept
Accepts a volume transfer.
- transfer-create
Creates a volume transfer.
- transfer-delete
Undo a transfer.
- transfer-list
List all the transfers.
- transfer-show
Show details about a transfer.
- type-create
Create a new volume type.
- type-delete
Delete a specific volume type.
- type-key
Set or unset extra_spec for a volume type.
- type-list
Print a list of available 'volume types'.
- upload-to-image
Upload volume to image service as image.
- bash-completion
Print arguments for bash_completion.
- help
Display help about this program or one of its subcommands.
- list-extensions
List all the os-api extensions that are available.
- --version
show program's version number and exit
- --debug
Print debugging output
- --os-username <auth-user-name>
Defaults to
env[OS_USERNAME].- --os-password <auth-password>
Defaults to
env[OS_PASSWORD].- --os-tenant-name <auth-tenant-name>
Defaults to
env[OS_TENANT_NAME].- --os-tenant-id <auth-tenant-id>
Defaults to
env[OS_TENANT_ID].- --os-auth-url <auth-url>
Defaults to
env[OS_AUTH_URL].- --os-region-name <region-name>
Defaults to
env[OS_REGION_NAME].- --service-type <service-type>
Defaults to volume for most actions
- --service-name <service-name>
Defaults to
env[CINDER_SERVICE_NAME]- --volume-service-name <volume-service-name>
Defaults to
env[CINDER_VOLUME_SERVICE_NAME]- --endpoint-type <endpoint-type>
Defaults to
env[CINDER_ENDPOINT_TYPE]or publicURL.- --os-volume-api-version <volume-api-ver>
Accepts 1 or 2,defaults to
env[OS_VOLUME_API_VERSION].- --os-cacert <ca-certificate>
Specify a CA bundle file to use in verifying a TLS (https) server certificate. Defaults to
env[OS_CACERT]- --retries <retries>
Number of retries.
usage: cinder absolute-limits
Print a list of absolute limits for a user
usage: cinder availability-zone-list
List all the availability zones.
usage: cinder backup-create [--container <container>]
[--display-name <display-name>]
[--display-description <display-description>]
<volume>
Creates a backup.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to backup.
Optional arguments
- --container <container>
Optional Backup container name. (Default=None)
- --display-name <display-name>
Optional backup name. (Default=None)
- --display-description <display-description>
Optional backup description. (Default=None)
usage: cinder backup-delete <backup>
Remove a backup.
Positional arguments
- <backup>
Name or ID of the backup to delete.
usage: cinder backup-restore [--volume-id <volume>] <backup>
Restore a backup.
Positional arguments
- <backup>
ID of the backup to restore.
Optional arguments
- --volume-id <volume>
Optional ID(or name) of the volume to restore to.
usage: cinder backup-show <backup>
Show details about a backup.
Positional arguments
- <backup>
Name or ID of the backup.
usage: cinder create [--snapshot-id <snapshot-id>]
[--source-volid <source-volid>] [--image-id <image-id>]
[--display-name <display-name>]
[--display-description <display-description>]
[--volume-type <volume-type>]
[--availability-zone <availability-zone>]
[--metadata [<key=value> [<key=value> ...]]]
<size>
Add a new volume.
Positional arguments
- <size>
Size of volume in GB
Optional arguments
- --snapshot-id <snapshot-id>
Create volume from snapshot id (Optional, Default=None)
- --source-volid <source-volid>
Create volume from volume id (Optional, Default=None)
- --image-id <image-id>
Create volume from image id (Optional, Default=None)
- --display-name <display-name>
Volume name (Optional, Default=None)
- --display-description <display-description>
Volume description (Optional, Default=None)
- --volume-type <volume-type>
Volume type (Optional, Default=None)
- --availability-zone <availability-zone>
Availability zone for volume (Optional, Default=None)
- --metadata [<key=value> [<key=value> ...]]
Metadata key=value pairs (Optional, Default=None)
usage: cinder delete <volume> [<volume> ...]
Remove volume(s).
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume(s) to delete.
usage: cinder encryption-type-create [--cipher <cipher>]
[--key_size <key_size>]
[--control_location <control_location>]
<volume_type> <provider>
Create a new encryption type for a volume type (Admin Only).
Positional arguments
- <volume_type>
Name or ID of the volume type
- <provider>
Class providing encryption support (e.g. LuksEncryptor)
Optional arguments
- --cipher <cipher>
Encryption algorithm/mode to use (e.g., aes-xts- plain64) (Optional, Default=None)
- --key_size <key_size>
Size of the encryption key, in bits (e.g., 128, 256) (Optional, Default=None)
- --control_location <control_location>
Notional service where encryption is performed (e.g., front-end=Nova). Values: 'front-end', 'back-end' (Optional, Default=None)
usage: cinder encryption-type-delete <volume_type>
Delete the encryption type for a volume type (Admin Only).
Positional arguments
- <volume_type>
Name or ID of the volume type
usage: cinder encryption-type-list
List encryption type information for all volume types (Admin Only).
usage: cinder encryption-type-show <volume_type>
Show the encryption type information for a volume type (Admin Only).
Positional arguments
- <volume_type>
Name or ID of the volume type
usage: cinder endpoints
Discover endpoints that get returned from the authenticate services.
usage: cinder extend <volume> <new-size>
Attempt to extend the size of an existing volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to extend.
- <new-size>
New size of volume in GB
usage: cinder extra-specs-list
Print a list of current 'volume types and extra specs' (Admin Only).
usage: cinder force-delete <volume> [<volume> ...]
Attempt forced removal of volume(s), regardless of the state(s).
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume(s) to delete.
usage: cinder list [--all-tenants [<0|1>]] [--display-name <display-name>]
[--status <status>]
[--metadata [<key=value> [<key=value> ...]]]
List all the volumes.
Optional arguments
- --all-tenants [<0|1>]
Display information from all tenants (Admin only).
- --display-name <display-name>
Filter results by display-name
- --status <status>
Filter results by status
- --metadata [<key=value> [<key=value> ...]]
Filter results by metadata
usage: cinder list-extensions
List all the os-api extensions that are available.
usage: cinder metadata <volume> <action> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Set or Delete metadata on a volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to update metadata on.
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'unset'
- <key=value>
Metadata to set/unset (only key is necessary on unset)
usage: cinder metadata-show <volume>
Show metadata of given volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
ID of volume
usage: cinder metadata-update-all <volume> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Update all metadata of a volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
ID of the volume to update metadata on.
- <key=value>
Metadata entry/entries to update.
usage: cinder migrate [--force-host-copy <True|False>] <volume> <host>
Migrate the volume to the new host.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
ID of the volume to migrate
- <host>
Destination host
Optional arguments
- --force-host-copy <True|False>
Optional flag to force the use of the generic host- based migration mechanism, bypassing driver optimizations (Default=False).
usage: cinder qos-associate <qos_specs> <volume_type_id>
Associate qos specs with specific volume type.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of qos_specs.
- <volume_type_id>
ID of volume type to be associated with.
usage: cinder qos-create <name> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Create a new qos specs.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of the new QoS specs
- <key=value>
Specifications for QoS
usage: cinder qos-delete [--force <True|False>] <qos_specs>
Delete a specific qos specs.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of the qos_specs to delete.
Optional arguments
- --force <True|False>
Optional flag that indicates whether to delete specified qos specs even if it is in-use.
usage: cinder qos-disassociate <qos_specs> <volume_type_id>
Disassociate qos specs from specific volume type.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of qos_specs.
- <volume_type_id>
ID of volume type to be associated with.
usage: cinder qos-disassociate-all <qos_specs>
Disassociate qos specs from all of its associations.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of qos_specs to be operate on.
usage: cinder qos-get-association <qos_specs>
Get all associations of specific qos specs.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of the qos_specs.
usage: cinder qos-key <qos_specs> <action> key=value [key=value ...]
Set or unset specifications for a qos spec.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of qos specs
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'unset'
- key=value
QoS specs to set/unset (only key is necessary on unset)
usage: cinder qos-show <qos_specs>
Get a specific qos specs.
Positional arguments
- <qos_specs>
ID of the qos_specs to show.
usage: cinder quota-class-show <class>
List the quotas for a quota class.
Positional arguments
- <class>
Name of quota class to list the quotas for.
usage: cinder quota-class-update [--volumes <volumes>]
[--snapshots <snapshots>]
[--gigabytes <gigabytes>]
[--volume-type <volume_type_name>]
<class>
Update the quotas for a quota class.
Positional arguments
- <class>
Name of quota class to set the quotas for.
Optional arguments
- --volumes <volumes>
New value for the "volumes" quota.
- --snapshots <snapshots>
New value for the "snapshots" quota.
- --gigabytes <gigabytes>
New value for the "gigabytes" quota.
- --volume-type <volume_type_name>
Volume type (Optional, Default=None)
usage: cinder quota-defaults <tenant_id>
List the default quotas for a tenant.
Positional arguments
- <tenant_id>
UUID of tenant to list the default quotas for.
usage: cinder quota-show <tenant_id>
List the quotas for a tenant.
Positional arguments
- <tenant_id>
UUID of tenant to list the quotas for.
usage: cinder quota-update [--volumes <volumes>] [--snapshots <snapshots>]
[--gigabytes <gigabytes>]
[--volume-type <volume_type_name>]
<tenant_id>
Update the quotas for a tenant.
Positional arguments
- <tenant_id>
UUID of tenant to set the quotas for.
Optional arguments
- --volumes <volumes>
New value for the "volumes" quota.
- --snapshots <snapshots>
New value for the "snapshots" quota.
- --gigabytes <gigabytes>
New value for the "gigabytes" quota.
- --volume-type <volume_type_name>
Volume type (Optional, Default=None)
usage: cinder quota-usage <tenant_id>
List the quota usage for a tenant.
Positional arguments
- <tenant_id>
UUID of tenant to list the quota usage for.
usage: cinder readonly-mode-update <volume> <True|true|False|false>
Update volume read-only access mode read_only.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
ID of the volume to update.
- <True|true|False|false>
Flag to indicate whether to update volume to read-only access mode.
usage: cinder rename [--display-description <display-description>]
<volume> [<display-name>]
Rename a volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to rename.
- <display-name>
New display-name for the volume.
Optional arguments
- --display-description <display-description>
Optional volume description. (Default=None)
usage: cinder reset-state [--state <state>] <volume> [<volume> ...]
Explicitly update the state of a volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to modify.
Optional arguments
- --state <state>
Indicate which state to assign the volume. Options include available, error, creating, deleting, error_deleting. If no state is provided, available will be used.
usage: cinder service-disable <hostname> <binary>
Disable the service.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
- <binary>
Service binary.
usage: cinder service-enable <hostname> <binary>
Enable the service.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
- <binary>
Service binary.
usage: cinder service-list [--host <hostname>] [--binary <binary>]
List all the services. Filter by host & service binary.
Optional arguments
- --host <hostname>
Name of host.
- --binary <binary>
Service binary.
usage: cinder show <volume>
Show details about a volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume.
usage: cinder snapshot-create [--force <True|False>]
[--display-name <display-name>]
[--display-description <display-description>]
<volume>
Add a new snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to snapshot
Optional arguments
- --force <True|False>
Optional flag to indicate whether to snapshot a volume even if it's attached to an instance. (Default=False)
- --display-name <display-name>
Optional snapshot name. (Default=None)
- --display-description <display-description>
Optional snapshot description. (Default=None)
usage: cinder snapshot-delete <snapshot>
Remove a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
Name or ID of the snapshot to delete.
usage: cinder snapshot-list [--all-tenants [<0|1>]]
[--display-name <display-name>]
[--status <status>] [--volume-id <volume-id>]
List all the snapshots.
Optional arguments
- --all-tenants [<0|1>]
Display information from all tenants (Admin only).
- --display-name <display-name>
Filter results by display-name
- --status <status>
Filter results by status
- --volume-id <volume-id>
Filter results by volume-id
usage: cinder snapshot-metadata <snapshot> <action> <key=value>
[<key=value> ...]
Set or Delete metadata of a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
ID of the snapshot to update metadata on.
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'unset'
- <key=value>
Metadata to set/unset (only key is necessary on unset)
usage: cinder snapshot-metadata-show <snapshot>
Show metadata of given snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
ID of snapshot
usage: cinder snapshot-metadata-update-all <snapshot> <key=value>
[<key=value> ...]
Update all metadata of a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
ID of the snapshot to update metadata on.
- <key=value>
Metadata entry/entries to update.
usage: cinder snapshot-rename [--display-description <display-description>]
<snapshot> [<display-name>]
Rename a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
Name or ID of the snapshot.
- <display-name>
New display-name for the snapshot.
Optional arguments
- --display-description <display-description>
Optional snapshot description. (Default=None)
usage: cinder snapshot-reset-state [--state <state>]
<snapshot> [<snapshot> ...]
Explicitly update the state of a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
Name or ID of the snapshot to modify.
Optional arguments
- --state <state>
Indicate which state to assign the snapshot. Options include available, error, creating, deleting, error_deleting. If no state is provided, available will be used.
usage: cinder snapshot-show <snapshot>
Show details about a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
Name or ID of the snapshot.
usage: cinder transfer-accept <transfer> <auth_key>
Accepts a volume transfer.
Positional arguments
- <transfer>
ID of the transfer to accept.
- <auth_key>
Auth key of the transfer to accept.
usage: cinder transfer-create [--display-name <display-name>] <volume>
Creates a volume transfer.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to transfer.
Optional arguments
- --display-name <display-name>
Optional transfer name. (Default=None)
usage: cinder transfer-delete <transfer>
Undo a transfer.
Positional arguments
- <transfer>
Name or ID of the transfer to delete.
usage: cinder transfer-show <transfer>
Show details about a transfer.
Positional arguments
- <transfer>
Name or ID of the transfer to accept.
usage: cinder type-create <name>
Create a new volume type.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of the new volume type
usage: cinder type-delete <id>
Delete a specific volume type.
Positional arguments
- <id>
Unique ID of the volume type to delete
usage: cinder type-key <vtype> <action> [<key=value> [<key=value> ...]]
Set or unset extra_spec for a volume type.
Positional arguments
- <vtype>
Name or ID of the volume type
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'unset'
- <key=value>
Extra_specs to set/unset (only key is necessary on unset)
usage: cinder upload-to-image [--force <True|False>]
[--container-format <container-format>]
[--disk-format <disk-format>]
<volume> <image-name>
Upload volume to image service as image.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume to upload to an image
- <image-name>
Name for created image
Optional arguments
- --force <True|False>
Optional flag to indicate whether to upload a volume even if it's attached to an instance. (Default=False)
- --container-format <container-format>
Optional type for container format (Default=bare)
- --disk-format <disk-format>
Optional type for disk format (Default=raw)
A volume is a detachable block storage device, similar to a USB hard drive. You can attach a volume to only one instance. To create and manage volumes, you use a combination of nova and cinder client commands.
This example creates a
my-new-volume volume based on an
image.
As an administrator, you can migrate a volume with its data from one location to another in a manner that is transparent to users and workloads. You can migrate only detached volumes with no snapshots.
Possible use cases for data migration:
Bring down a physical storage device for maintenance without disrupting workloads.
Modify the properties of a volume.
Free up space in a thinly-provisioned back end.
Migrate a volume, as follows:
$ cinder migratevolumeIDdestinationHost--force-host-copy=True|False
Where --force-host-copy=True forces
the generic host-based migration mechanism and bypasses
any driver optimizations.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If the volume is in use or has snapshots, the specified host destination cannot accept the volume. If the user is not an administrator, the migration fails. |
List images, and note the ID of the image to use for your volume:
$ nova image-list
+--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------------------------------------+ | ID | Name | Status | Server | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------------------------------------+ | 397e713c-b95b-4186-ad46-6126863ea0a9 | cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec | ACTIVE | | | df430cc2-3406-4061-b635-a51c16e488ac | cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec-kernel | ACTIVE | | | 3cf852bd-2332-48f4-9ae4-7d926d50945e | cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec-ramdisk | ACTIVE | | | 7e5142af-1253-4634-bcc6-89482c5f2e8a | myCirrosImage | ACTIVE | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | | 89bcd424-9d15-4723-95ec-61540e8a1979 | mysnapshot | ACTIVE | f51ebd07-c33d-4951-8722-1df6aa8afaa4 | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------------------------------------+
List the availability zones, and note the ID of the availability zone in which to create your volume:
$ nova availability-zone-list
+-----------------------+----------------------------------------+ | Name | Status | +-----------------------+----------------------------------------+ | internal | available | | |- devstack | | | | |- nova-conductor | enabled :-) 2013-07-25T16:50:44.000000 | | | |- nova-consoleauth | enabled :-) 2013-07-25T16:50:44.000000 | | | |- nova-scheduler | enabled :-) 2013-07-25T16:50:44.000000 | | | |- nova-cert | enabled :-) 2013-07-25T16:50:44.000000 | | | |- nova-network | enabled :-) 2013-07-25T16:50:44.000000 | | nova | available | | |- devstack | | | | |- nova-compute | enabled :-) 2013-07-25T16:50:39.000000 | +-----------------------+----------------------------------------+
Create a volume with 8 GB of space. Specify the availability zone and image:
$ cinder create 8 --display-name my-new-volume --image-id 397e713c-b95b-4186-ad46-6126863ea0a9 --availability-zone nova
+---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | attachments | [] | | availability_zone | nova | | bootable | false | | created_at | 2013-07-25T17:02:12.472269 | | display_description | None | | display_name | my-new-volume | | id | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | | image_id | 397e713c-b95b-4186-ad46-6126863ea0a9 | | metadata | {} | | size | 8 | | snapshot_id | None | | source_volid | None | | status | creating | | volume_type | None | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+To verify that your volume was created successfully, list the available volumes:
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | available | my-new-volume | 8 | None | true | | | bd7cf584-45de-44e3-bf7f-f7b50bf235e3 | available | my-bootable-vol | 8 | None | true | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
If your volume was created successfully, its status is
available. If its status iserror, you might have exceeded your quota.
Attach your volume to a server:
$ nova volume-attach 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 /dev/vdb
+----------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +----------+--------------------------------------+ | device | /dev/vdb | | serverId | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | | id | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | | volumeId | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | +----------+--------------------------------------+
Note the ID of your volume.
Show information for your volume:
$ cinder show 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8
+------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | attachments | [{u'device': u'/dev/vdb', u'server_id': u'84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5', u'id': u'573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8', u'volume_id': u'573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8'}] | | availability_zone | nova | | bootable | true | | created_at | 2013-07-25T17:02:12.000000 | | display_description | None | | display_name | my-new-volume | | id | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | | metadata | {} | | os-vol-host-attr:host | devstack | | os-vol-tenant-attr:tenant_id | 66265572db174a7aa66eba661f58eb9e | | size | 8 | | snapshot_id | None | | source_volid | None | | status | in-use | | volume_image_metadata | {u'kernel_id': u'df430cc2-3406-4061-b635-a51c16e488ac', u'image_id': u'397e713c-b95b-4186-ad46-6126863ea0a9', u'ramdisk_id': u'3cf852bd-2332-48f4-9ae4-7d926d50945e', u'image_name': u'cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec'} | | volume_type | None | +------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+The output shows that the volume is attached to the server with ID
84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5, is in the nova availability zone, and is bootable.
To resize your volume, you must first detach it from the server.
To detach the volume from your server, pass the server ID and volume ID to the command:
$ nova volume-detach 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8
The volume-detach command does not return any output.
List volumes:
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | available | my-new-volume | 8 | None | true | | | bd7cf584-45de-44e3-bf7f-f7b50bf235e3 | available | my-bootable-vol | 8 | None | true | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
Note that the volume is now available.
Resize the volume by passing the volume ID and the new size (a value greater than the old one) as parameters:
$ cinder extend
573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f810The extend command does not return any output.
To delete your volume, you must first detach it from the server.
To detach the volume from your server and check for the list of existing volumes, see steps 1 and 2 mentioned in the section called “Resize a volume”.
Delete the volume:
$ cinder delete my-new-volume
The delete command does not return any output.
List the volumes again, and note that the status of your volume is
deleting:$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 573e024d-5235-49ce-8332-be1576d323f8 | deleting | my-new-volume | 8 | None | true | | | bd7cf584-45de-44e3-bf7f-f7b50bf235e3 | available | my-bootable-vol | 8 | None | true | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
When the volume is fully deleted, it disappears from the list of volumes:
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | bd7cf584-45de-44e3-bf7f-f7b50bf235e3 | available | my-bootable-vol | 8 | None | true | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+-----------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
You can transfer a volume from one owner to another by using the cinder transfer* commands. The volume donor, or original owner, creates a transfer request and sends the created transfer ID and authorization key to the volume recipient. The volume recipient, or new owner, accepts the transfer by using the ID and key.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The procedure for volume transfer is intended for tenants (both the volume donor and recipient) within the same cloud. |
Use cases include:
Create a custom bootable volume or a volume with a large data set and transfer it to the end customer.
For bulk import of data to the cloud, the data ingress system creates a new Block Storage volume, copies data from the physical device, and transfers device ownership to the end user.
While logged in as the volume donor, list available volumes:
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 72bfce9f-cacf-477a-a092-bf57a7712165 | error | None | 1 | None | false | | | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | available | None | 1 | None | false | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
As the volume donor, request a volume transfer authorization code for a specific volume:
$ cinder transfer-create
volumeIDThe volume must be in an ‘available’ state or the request will be denied. If the transfer request is valid in the database (that is, it has not expired or been deleted), the volume is placed in an
awaiting transferstate. For example:$ cinder transfer-create a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f
+------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------+--------------------------------------+ | auth_key | b2c8e585cbc68a80 | | created_at | 2013-10-14T15:20:10.121458 | | id | 6e4e9aa4-bed5-4f94-8f76-df43232f44dc | | name | None | | volume_id | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | +------------+--------------------------------------+
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note Optionally, you can specify a name for the transfer by using the
--display-nameparameter.displayNameSend the volume transfer ID and authorization key to the new owner (for example, by email).
View pending transfers:
$ cinder transfer-list
+--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+------+ | ID | VolumeID | Name | +--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+------+ | 6e4e9aa4-bed5-4f94-8f76-df43232f44dc | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | None | +--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+------+
After the volume recipient, or new owner, accepts the transfer, you can see that the transfer is no longer available:
$ cinder transfer-list
+----+-----------+------+ | ID | Volume ID | Name | +----+-----------+------+ +----+-----------+------+
As the volume recipient, you must first obtain the transfer ID and authorization key from the original owner.
Display the transfer request details using the ID:
$ cinder transfer-show
transferIDFor example:
$ cinder transfer-show 6e4e9aa4-bed5-4f94-8f76-df43232f44dc
+------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------+--------------------------------------+ | created_at | 2013-10-14T15:20:10.000000 | | id | 6e4e9aa4-bed5-4f94-8f76-df43232f44dc | | name | None | | volume_id | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | +------------+--------------------------------------+
Accept the request:
$ cinder transfer-accept
transferIDauthKeyFor example:
$ cinder transfer-accept 6e4e9aa4-bed5-4f94-8f76-df43232f44dc b2c8e585cbc68a80
+-----------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +-----------+--------------------------------------+ | id | 6e4e9aa4-bed5-4f94-8f76-df43232f44dc | | name | None | | volume_id | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | +-----------+--------------------------------------+
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note If you do not have a sufficient quota for the transfer, the transfer is refused.
List available volumes and their statuses:
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-------------------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-------------------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 72bfce9f-cacf-477a-a092-bf57a7712165 | error | None | 1 | None | false | | | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | awaiting-transfer | None | 1 | None | false | | +--------------------------------------+-------------------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
Find the matching transfer ID:
$ cinder transfer-list
+--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+------+ | ID | VolumeID | Name | +--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+------+ | a6da6888-7cdf-4291-9c08-8c1f22426b8a | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | None | +--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+------+
Delete the volume:
$ cinder transfer-delete
transferIDFor example:
$ cinder transfer-delete a6da6888-7cdf-4291-9c08-8c1f22426b8a
The transfer list is now empty and the volume is again available for transfer:
$ cinder transfer-list
+----+-----------+------+ | ID | Volume ID | Name | +----+-----------+------+ +----+-----------+------+
$ cinder list
+--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 72bfce9f-cacf-477a-a092-bf57a7712165 | error | None | 1 | None | false | | | a1cdace0-08e4-4dc7-b9dc-457e9bcfe25f | available | None | 1 | None | false | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
To give multiple users shared, secure access to the same data, you can set a volume to read-only access.
Run this command to set a volume to read-only access:
$ cinder readonly-mode-updateVOLUMEBOOLEAN
Where VOLUME is the ID of the
target volume and BOOLEAN is a flag
that enables read-only or read/write access to the
volume.
Valid values for BOOLEAN
are:
true. Sets the read-only flag in the volume. When you attach the volume to an instance, the instance checks for this flag to determine whether to restrict volume access to read-only.false. Sets the volume to read/write access.
- nova usage
- nova optional arguments
- nova absolute-limits command
- nova add-fixed-ip command
- nova add-secgroup command
- nova agent-create command
- nova agent-delete command
- nova agent-list command
- nova agent-modify command
- nova aggregate-add-host command
- nova aggregate-create command
- nova aggregate-delete command
- nova aggregate-details command
- nova aggregate-list command
- nova aggregate-remove-host command
- nova aggregate-set-metadata command
- nova aggregate-update command
- nova availability-zone-list command
- nova backup command
- nova baremetal-interface-add command
- nova baremetal-interface-list command
- nova baremetal-interface-remove command
- nova baremetal-node-create command
- nova baremetal-node-delete command
- nova baremetal-node-list command
- nova baremetal-node-show command
- nova boot command
- nova cell-capacities command
- nova cell-show command
- nova clear-password command
- nova cloudpipe-configure command
- nova cloudpipe-create command
- nova cloudpipe-list command
- nova console-log command
- nova credentials command
- nova delete command
- nova diagnostics command
- nova dns-create command
- nova dns-create-private-domain command
- nova dns-create-public-domain command
- nova dns-delete command
- nova dns-delete-domain command
- nova dns-domains command
- nova dns-list command
- nova endpoints command
- nova evacuate command
- nova fixed-ip-get command
- nova fixed-ip-reserve command
- nova fixed-ip-unreserve command
- nova flavor-access-add command
- nova flavor-access-list command
- nova flavor-access-remove command
- nova flavor-create command
- nova flavor-delete command
- nova flavor-key command
- nova flavor-list command
- nova flavor-show command
- nova floating-ip-associate command
- nova floating-ip-bulk-create command
- nova floating-ip-bulk-delete command
- nova floating-ip-bulk-list command
- nova floating-ip-create command
- nova floating-ip-delete command
- nova floating-ip-disassociate command
- nova floating-ip-list command
- nova floating-ip-pool-list command
- nova force-delete command
- nova get-password command
- nova get-rdp-console command
- nova get-spice-console command
- nova get-vnc-console command
- nova host-action command
- nova host-describe command
- nova host-evacuate command
- nova host-list command
- nova host-meta command
- nova host-servers-migrate command
- nova host-update command
- nova hypervisor-list command
- nova hypervisor-servers command
- nova hypervisor-show command
- nova hypervisor-stats command
- nova hypervisor-uptime command
- nova image-create command
- nova image-delete command
- nova image-list command
- nova image-meta command
- nova image-show command
- nova instance-action command
- nova instance-action-list command
- nova interface-attach command
- nova interface-detach command
- nova interface-list command
- nova keypair-add command
- nova keypair-delete command
- nova keypair-list command
- nova keypair-show command
- nova list command
- nova list-extensions command
- nova list-secgroup command
- nova live-migration command
- nova lock command
- nova meta command
- nova migrate command
- nova migration-list command
- nova net command
- nova net-create command
- nova net-delete command
- nova net-list command
- nova network-associate-host command
- nova network-associate-project command
- nova network-create command
- nova network-disassociate command
- nova network-list command
- nova network-show command
- nova pause command
- nova quota-class-show command
- nova quota-class-update command
- nova quota-defaults command
- nova quota-delete command
- nova quota-show command
- nova quota-update command
- nova rate-limits command
- nova reboot command
- nova rebuild command
- nova refresh-network command
- nova remove-fixed-ip command
- nova remove-secgroup command
- nova rename command
- nova rescue command
- nova reset-network command
- nova reset-state command
- nova resize command
- nova resize-confirm command
- nova resize-revert command
- nova restore command
- nova resume command
- nova root-password command
- nova scrub command
- nova secgroup-add-group-rule command
- nova secgroup-add-rule command
- nova secgroup-create command
- nova secgroup-delete command
- nova secgroup-delete-group-rule command
- nova secgroup-delete-rule command
- nova secgroup-list command
- nova secgroup-list-rules command
- nova secgroup-update command
- nova service-disable command
- nova service-enable command
- nova service-list command
- nova shelve command
- nova shelve-offload command
- nova show command
- nova ssh command
- nova start command
- nova stop command
- nova suspend command
- nova unlock command
- nova unpause command
- nova unrescue command
- nova unshelve command
- nova usage command
- nova usage-list command
- nova volume-attach command
- nova volume-create command
- nova volume-delete command
- nova volume-detach command
- nova volume-list command
- nova volume-show command
- nova volume-snapshot-create command
- nova volume-snapshot-delete command
- nova volume-snapshot-list command
- nova volume-snapshot-show command
- nova volume-type-create command
- nova volume-type-delete command
- nova volume-type-list command
- nova volume-update command
- nova x509-create-cert command
- nova x509-get-root-cert command
The nova client is the command-line interface (CLI) for the OpenStack Compute API and its extensions. This chapter documents nova version 2.17.0.
For help on a specific nova command, enter:
$ nova help COMMANDusage: nova [--version] [--debug] [--os-cache] [--timings]
[--timeout <seconds>] [--os-auth-token OS_AUTH_TOKEN]
[--os-username <auth-user-name>] [--os-password <auth-password>]
[--os-tenant-name <auth-tenant-name>]
[--os-tenant-id <auth-tenant-id>] [--os-auth-url <auth-url>]
[--os-region-name <region-name>] [--os-auth-system <auth-system>]
[--service-type <service-type>] [--service-name <service-name>]
[--volume-service-name <volume-service-name>]
[--endpoint-type <endpoint-type>]
[--os-compute-api-version <compute-api-ver>]
[--os-cacert <ca-certificate>] [--insecure]
[--bypass-url <bypass-url>]
<subcommand> ...
Subcommands
- absolute-limits
Print a list of absolute limits for a user
- add-fixed-ip
Add new IP address on a network to server.
- add-floating-ip
DEPRECATED, use floating-ip-associate instead.
- add-secgroup
Add a Security Group to a server.
- agent-create
Create new agent build.
- agent-delete
Delete existing agent build.
- agent-list
List all builds.
- agent-modify
Modify existing agent build.
- aggregate-add-host
Add the host to the specified aggregate.
- aggregate-create
Create a new aggregate with the specified details.
- aggregate-delete
Delete the aggregate.
- aggregate-details
Show details of the specified aggregate.
- aggregate-list
Print a list of all aggregates.
- aggregate-remove-host
Remove the specified host from the specified aggregate.
- aggregate-set-metadata
Update the metadata associated with the aggregate.
- aggregate-update
Update the aggregate's name and optionally availability zone.
- availability-zone-list
List all the availability zones.
- backup
Backup a server by creating a 'backup' type snapshot.
- boot
Boot a new server.
- clear-password
Clear password for a server.
- cloudpipe-configure
Update the VPN IP/port of a cloudpipe instance.
- cloudpipe-create
Create a cloudpipe instance for the given project.
- cloudpipe-list
Print a list of all cloudpipe instances.
- console-log
Get console log output of a server.
- credentials
Show user credentials returned from auth.
- delete
Immediately shut down and delete specified server(s).
- diagnostics
Retrieve server diagnostics.
- dns-create
Create a DNS entry for domain, name and ip.
- dns-create-private-domain
Create the specified DNS domain.
- dns-create-public-domain
Create the specified DNS domain.
- dns-delete
Delete the specified DNS entry.
- dns-delete-domain
Delete the specified DNS domain.
- dns-domains
Print a list of available dns domains.
- dns-list
List current DNS entries for domain and ip or domain and name.
- endpoints
Discover endpoints that get returned from the authenticate services.
- evacuate
Evacuate server from failed host to specified one.
- fixed-ip-get
Retrieve info on a fixed ip.
- fixed-ip-reserve
Reserve a fixed IP.
- fixed-ip-unreserve
Unreserve a fixed IP.
- flavor-access-add
Add flavor access for the given tenant.
- flavor-access-list
Print access information about the given flavor.
- flavor-access-remove
Remove flavor access for the given tenant.
- flavor-create
Create a new flavor
- flavor-delete
Delete a specific flavor
- flavor-key
Set or unset extra_spec for a flavor.
- flavor-list
Print a list of available 'flavors' (sizes of servers).
- flavor-show
Show details about the given flavor.
- floating-ip-associate
Associate a floating IP address to a server.
- floating-ip-bulk-create
Bulk create floating ips by range.
- floating-ip-bulk-delete
Bulk delete floating ips by range.
- floating-ip-bulk-list
List all floating ips.
- floating-ip-create
Allocate a floating IP for the current tenant.
- floating-ip-delete
De-allocate a floating IP.
- floating-ip-disassociate
Disassociate a floating IP address from a server.
- floating-ip-list
List floating ips for this tenant.
- floating-ip-pool-list
List all floating ip pools.
- get-password
Get password for a server.
- get-rdp-console
Get a rdp console to a server.
- get-spice-console
Get a spice console to a server.
- get-vnc-console
Get a vnc console to a server.
- host-action
Perform a power action on a host.
- host-describe
Describe a specific host.
- host-list
List all hosts by service.
- host-update
Update host settings.
- hypervisor-list
List hypervisors.
- hypervisor-servers
List servers belonging to specific hypervisors.
- hypervisor-show
Display the details of the specified hypervisor.
- hypervisor-stats
Get hypervisor statistics over all compute nodes.
- hypervisor-uptime
Display the uptime of the specified hypervisor.
- image-create
Create a new image by taking a snapshot of a running server.
- image-delete
Delete specified image(s).
- image-list
Print a list of available images to boot from.
- image-meta
Set or Delete metadata on an image.
- image-show
Show details about the given image.
- interface-attach
Attach a network interface to a server.
- interface-detach
Detach a network interface from a server.
- interface-list
List interfaces attached to a server.
- keypair-add
Create a new key pair for use with servers.
- keypair-delete
Delete keypair given by its name.
- keypair-list
Print a list of keypairs for a user
- keypair-show
Show details about the given keypair.
- list
List active servers.
- list-secgroup
List Security Group(s) of a server.
- live-migration
Migrate running server to a new machine.
- lock
Lock a server.
- meta
Set or Delete metadata on a server.
- migrate
Migrate a server. The new host will be selected by the scheduler.
- network-associate-host
Associate host with network.
- network-associate-project
Associate project with network.
- network-create
Create a network.
- network-disassociate
Disassociate host and/or project from the given network.
- network-list
Print a list of available networks.
- network-show
Show details about the given network.
- pause
Pause a server.
- quota-class-show
List the quotas for a quota class.
- quota-class-update
Update the quotas for a quota class.
- quota-defaults
List the default quotas for a tenant.
- quota-delete
Delete quota for a tenant/user so their quota will Revert back to default.
- quota-show
List the quotas for a tenant/user.
- quota-update
Update the quotas for a tenant/user.
- rate-limits
Print a list of rate limits for a user
- reboot
Reboot a server.
- rebuild
Shutdown, re-image, and re-boot a server.
- refresh-network
Refresh server network information.
- remove-fixed-ip
Remove an IP address from a server.
- remove-floating-ip
DEPRECATED, use floating-ip-disassociate instead.
- remove-secgroup
Remove a Security Group from a server.
- rename
Rename a server.
- rescue
Rescue a server.
- reset-network
Reset network of a server.
- reset-state
Reset the state of a server.
- resize
Resize a server.
- resize-confirm
Confirm a previous resize.
- resize-revert
Revert a previous resize (and return to the previous VM).
- resume
Resume a server.
- root-password
Change the root password for a server.
- scrub
Delete data associated with the project.
- secgroup-add-group-rule
Add a source group rule to a security group.
- secgroup-add-rule
Add a rule to a security group.
- secgroup-create
Create a security group.
- secgroup-delete
Delete a security group.
- secgroup-delete-group-rule
Delete a source group rule from a security group.
- secgroup-delete-rule
Delete a rule from a security group.
- secgroup-list
List security groups for the current tenant.
- secgroup-list-rules
List rules for a security group.
- secgroup-update
Update a security group.
- service-disable
Disable the service.
- service-enable
Enable the service.
- service-list
Show a list of all running services. Filter by host & binary.
- shelve
Shelve a server.
- shelve-offload
Remove a shelved server from the compute node.
- show
Show details about the given server.
- ssh
SSH into a server.
- start
Start a server.
- stop
Stop a server.
- suspend
Suspend a server.
- unlock
Unlock a server.
- unpause
Unpause a server.
- unrescue
Unrescue a server.
- unshelve
Unshelve a server.
- usage
Show usage data for a single tenant.
- usage-list
List usage data for all tenants.
- volume-attach
Attach a volume to a server.
- volume-create
Add a new volume.
- volume-delete
Remove volume(s).
- volume-detach
Detach a volume from a server.
- volume-list
List all the volumes.
- volume-show
Show details about a volume.
- volume-snapshot-create
Add a new snapshot.
- volume-snapshot-delete
Remove a snapshot.
- volume-snapshot-list
List all the snapshots.
- volume-snapshot-show
Show details about a snapshot.
- volume-type-create
Create a new volume type.
- volume-type-delete
Delete a specific flavor
- volume-type-list
Print a list of available 'volume types'.
- volume-update
Update volume attachment.
- x509-create-cert
Create x509 cert for a user in tenant.
- x509-get-root-cert
Fetch the x509 root cert.
- bash-completion
Prints all of the commands and options to stdout so that the nova.bash_completion script doesn't have to hard code them.
- help
Display help about this program or one of its subcommands.
- force-delete
Force delete a server.
- restore
Restore a soft-deleted server.
- net
Show a network
- net-create
Create a network
- net-delete
Delete a network
- net-list
List networks
- baremetal-interface-add
Add a network interface to a baremetal node.
- baremetal-interface-list
List network interfaces associated with a baremetal node.
- baremetal-interface-remove
Remove a network interface from a baremetal node.
- baremetal-node-create
Create a baremetal node.
- baremetal-node-delete
Remove a baremetal node and any associated interfaces.
- baremetal-node-list
Print list of available baremetal nodes.
- baremetal-node-show
Show information about a baremetal node.
- host-evacuate
Evacuate all instances from failed host to specified one.
- instance-action
Show an action.
- instance-action-list
List actions on a server.
- migration-list
Print a list of migrations.
- host-servers-migrate
Migrate all instances of the specified host to other available hosts.
- cell-capacities
Get cell capacities for all cells or a given cell.
- cell-show
Show details of a given cell.
- host-meta
Set or Delete metadata on all instances of a host.
- list-extensions
List all the os-api extensions that are available.
- --version
show program's version number and exit
- --debug
Print debugging output
- --os-cache
Use the auth token cache. Defaults to False if
env[OS_CACHE]is not set.- --timings
Print call timing info
- --timeout <seconds>
Set HTTP call timeout (in seconds)
- --os-auth-token OS_AUTH_TOKEN
Defaults to
env[OS_AUTH_TOKEN]- --os-username <auth-user-name>
Defaults to
env[OS_USERNAME].- --os-password <auth-password>
Defaults to
env[OS_PASSWORD].- --os-tenant-name <auth-tenant-name>
Defaults to
env[OS_TENANT_NAME].- --os-tenant-id <auth-tenant-id>
Defaults to
env[OS_TENANT_ID].- --os-auth-url <auth-url>
Defaults to
env[OS_AUTH_URL].- --os-region-name <region-name>
Defaults to
env[OS_REGION_NAME].- --os-auth-system <auth-system>
Defaults to
env[OS_AUTH_SYSTEM].- --service-type <service-type>
Defaults to compute for most actions
- --service-name <service-name>
Defaults to
env[NOVA_SERVICE_NAME]- --volume-service-name <volume-service-name>
Defaults to
env[NOVA_VOLUME_SERVICE_NAME]- --endpoint-type <endpoint-type>
Defaults to
env[NOVA_ENDPOINT_TYPE]or publicURL.- --os-compute-api-version <compute-api-ver>
Accepts 1.1 or 3, defaults to
env[OS_COMPUTE_API_VERSION].- --os-cacert <ca-certificate>
Specify a CA bundle file to use in verifying a TLS (https) server certificate. Defaults to
env[OS_CACERT]- --insecure
Explicitly allow novaclient to perform "insecure" SSL (https) requests. The server's certificate will not be verified against any certificate authorities. This option should be used with caution.
- --bypass-url <bypass-url>
Use this API endpoint instead of the Service Catalog
usage: nova absolute-limits [--tenant [<tenant>]] [--reserved]
Print a list of absolute limits for a user
Optional arguments
- --tenant [<tenant>]
Display information from single tenant (Admin only).
- --reserved
Include reservations count.
usage: nova add-fixed-ip <server> <network-id>
Add new IP address on a network to server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <network-id>
Network ID.
usage: nova add-secgroup <server> <secgroup>
Add a Security Group to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <secgroup>
Name of Security Group.
usage: nova agent-create <os> <architecture> <version> <url> <md5hash>
<hypervisor>
Create new agent build.
Positional arguments
- <os>
type of os.
- <architecture>
type of architecture
- <version>
version
- <url>
url
- <md5hash>
md5 hash
- <hypervisor>
type of hypervisor.
usage: nova agent-delete <id>
Delete existing agent build.
Positional arguments
- <id>
id of the agent-build
usage: nova agent-list [--hypervisor <hypervisor>]
List all builds.
Optional arguments
- --hypervisor <hypervisor>
type of hypervisor.
usage: nova agent-modify <id> <version> <url> <md5hash>
Modify existing agent build.
Positional arguments
- <id>
id of the agent-build
- <version>
version
- <url>
url
- <md5hash>
md5hash
usage: nova aggregate-add-host <aggregate> <host>
Add the host to the specified aggregate.
Positional arguments
- <aggregate>
Name or ID of aggregate.
- <host>
The host to add to the aggregate.
usage: nova aggregate-create <name> [<availability-zone>]
Create a new aggregate with the specified details.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of aggregate.
- <availability-zone>
The availability zone of the aggregate (optional).
usage: nova aggregate-delete <aggregate>
Delete the aggregate.
Positional arguments
- <aggregate>
Name or ID of aggregate to delete.
usage: nova aggregate-details <aggregate>
Show details of the specified aggregate.
Positional arguments
- <aggregate>
Name or ID of aggregate.
usage: nova aggregate-remove-host <aggregate> <host>
Remove the specified host from the specified aggregate.
Positional arguments
- <aggregate>
Name or ID of aggregate.
- <host>
The host to remove from the aggregate.
usage: nova aggregate-set-metadata <aggregate> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Update the metadata associated with the aggregate.
Positional arguments
- <aggregate>
Name or ID of aggregate to update.
- <key=value>
Metadata to add/update to aggregate
usage: nova aggregate-update <aggregate> <name> [<availability-zone>]
Update the aggregate's name and optionally availability zone.
Positional arguments
- <aggregate>
Name or ID of aggregate to update.
- <name>
Name of aggregate.
- <availability-zone>
The availability zone of the aggregate.
usage: nova availability-zone-list
List all the availability zones.
usage: nova backup <server> <name> <backup-type> <rotation>
Backup a server by creating a 'backup' type snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <name>
Name of the backup image.
- <backup-type>
The backup type, like "daily" or "weekly".
- <rotation>
Int parameter representing how many backups to keep around.
usage: nova baremetal-interface-add [--datapath_id <datapath_id>]
[--port_no <port_no>]
<node> <address>
Add a network interface to a baremetal node.
Positional arguments
- <node>
ID of node
- <address>
MAC address of interface
Optional arguments
- --datapath_id <datapath_id>
OpenFlow Datapath ID of interface
- --port_no <port_no>
OpenFlow port number of interface
usage: nova baremetal-interface-list <node>
List network interfaces associated with a baremetal node.
Positional arguments
- <node>
ID of node
usage: nova baremetal-interface-remove <node> <address>
Remove a network interface from a baremetal node.
Positional arguments
- <node>
ID of node
- <address>
MAC address of interface
usage: nova baremetal-node-create [--pm_address <pm_address>]
[--pm_user <pm_user>]
[--pm_password <pm_password>]
[--terminal_port <terminal_port>]
<service_host> <cpus> <memory_mb> <local_gb>
<prov_mac_address>
Create a baremetal node.
Positional arguments
- <service_host>
Name of nova compute host which will control this baremetal node
- <cpus>
Number of CPUs in the node
- <memory_mb>
Megabytes of RAM in the node
- <local_gb>
Gigabytes of local storage in the node
- <prov_mac_address>
MAC address to provision the node
Optional arguments
- --pm_address <pm_address>
Power management IP for the node
- --pm_user <pm_user>
Username for the node's power management
- --pm_password <pm_password>
Password for the node's power management
- --terminal_port <terminal_port>
ShellInABox port?
usage: nova baremetal-node-delete <node>
Remove a baremetal node and any associated interfaces.
Positional arguments
- <node>
ID of the node to delete.
usage: nova baremetal-node-list
Print list of available baremetal nodes.
usage: nova baremetal-node-show <node>
Show information about a baremetal node.
Positional arguments
- <node>
ID of node
usage: nova boot [--flavor <flavor>] [--image <image>]
[--image-with <key=value>] [--boot-volume <volume_id>]
[--snapshot <snapshot_id>] [--num-instances <number>]
[--meta <key=value>] [--file <dst-path=src-path>]
[--key-name <key-name>] [--user-data <user-data>]
[--availability-zone <availability-zone>]
[--security-groups <security-groups>]
[--block-device-mapping <dev-name=mapping>]
[--block-device key1=value1[,key2=value2...]]
[--swap <swap_size>]
[--ephemeral size=<size>[,format=<format>]]
[--hint <key=value>]
[--nic <net-id=net-uuid,v4-fixed-ip=ip-addr,port-id=port-uuid>]
[--config-drive <value>] [--poll]
<name>
Boot a new server.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name for the new server
Optional arguments
- --flavor <flavor>
Name or ID of flavor (see 'nova flavor-list').
- --image <image>
Name or ID of image (see 'nova image-list').
- --image-with <key=value>
Image metadata property (see 'nova image-show').
- --boot-volume <volume_id>
Volume ID to boot from.
- --snapshot <snapshot_id>
Snapshot ID to boot from (will create a volume).
- --num-instances <number>
boot multiple servers at a time (limited by quota).
- --meta <key=value>
Record arbitrary key/value metadata to /meta.js on the new server. Can be specified multiple times.
- --file <dst-path=src-path>
Store arbitrary files from <src-path> locally to <dst- path> on the new server. You may store up to 5 files.
- --key-name <key-name>
Key name of keypair that should be created earlier with the command keypair-add
- --user-data <user-data>
user data file to pass to be exposed by the metadata server.
- --availability-zone <availability-zone>
The availability zone for server placement.
- --security-groups <security-groups>
Comma separated list of security group names.
- --block-device-mapping <dev-name=mapping>
Block device mapping in the format <dev- name>=<id>:<type>:<size(GB)>:<delete-on-terminate>.
- --block-device
key1=value1[,key2=value2...] Block device mapping with the keys: id=image_id, snapshot_id or volume_id, source=source type (image, snapshot, volume or blank), dest=destination type of the block device (volume or local), bus=device's bus, device=name of the device (e.g. vda, xda, ...), size=size of the block device in GB, format=device will be formatted (e.g. swap, ext3, ntfs, ...), bootindex=integer used for ordering the boot disks, type=device type (e.g. disk, cdrom, ...) and shutdown=shutdown behaviour (either preserve or remove).
- --swap <swap_size>
Create and attach a local swap block device of <swap_size> MB.
- --ephemeral
size=<size>[,format=<format>] Create and attach a local ephemeral block device of <size> GB and format it to <format>.
- --hint <key=value>
Send arbitrary key/value pairs to the scheduler for custom use.
- --nic <net-id=net-uuid,v4-fixed-ip=ip-addr,port-id=port-uuid>
Create a NIC on the server. Specify option multiple times to create multiple NICs. net-id: attach NIC to network with this UUID (required if no port-id), v4 -fixed-ip: IPv4 fixed address for NIC (optional), port-id: attach NIC to port with this UUID (required if no net-id)
- --config-drive <value>
Enable config drive
- --poll
Blocks while server builds so progress can be reported.
usage: nova cell-capacities [--cell <cell-name>]
Get cell capacities for all cells or a given cell.
Optional arguments
- --cell <cell-name>
Name of the cell to get the capacities.
usage: nova cell-show <cell-name>
Show details of a given cell.
Positional arguments
- <cell-name>
Name of the cell.
usage: nova clear-password <server>
Clear password for a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova cloudpipe-configure <ip address> <port>
Update the VPN IP/port of a cloudpipe instance.
Positional arguments
- <ip address>
New IP Address.
- <port>
New Port.
usage: nova cloudpipe-create <project_id>
Create a cloudpipe instance for the given project.
Positional arguments
- <project_id>
UUID of the project to create the cloudpipe for.
usage: nova console-log [--length <length>] <server>
Get console log output of a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --length <length>
Length in lines to tail.
usage: nova credentials [--wrap <integer>]
Show user credentials returned from auth.
Optional arguments
- --wrap <integer>
wrap PKI tokens to a specified length, or 0 to disable
usage: nova delete <server> [<server> ...]
Immediately shut down and delete specified server(s).
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server(s).
usage: nova diagnostics <server>
Retrieve server diagnostics.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova dns-create [--type <type>] <ip> <name> <domain>
Create a DNS entry for domain, name and ip.
Positional arguments
- <ip>
ip address
- <name>
DNS name
- <domain>
DNS domain
Optional arguments
- --type <type>
dns type (e.g. "A")
usage: nova dns-create-private-domain
[--availability-zone <availability-zone>]
<domain>
Create the specified DNS domain.
Positional arguments
- <domain>
DNS domain
Optional arguments
- --availability-zone <availability-zone>
Limit access to this domain to servers in the specified availability zone.
usage: nova dns-create-public-domain [--project <project>] <domain>
Create the specified DNS domain.
Positional arguments
- <domain>
DNS domain
Optional arguments
- --project <project>
Limit access to this domain to users of the specified project.
usage: nova dns-delete <domain> <name>
Delete the specified DNS entry.
Positional arguments
- <domain>
DNS domain
- <name>
DNS name
usage: nova dns-delete-domain <domain>
Delete the specified DNS domain.
Positional arguments
- <domain>
DNS domain
usage: nova dns-list [--ip <ip>] [--name <name>] <domain>
List current DNS entries for domain and ip or domain and name.
Positional arguments
- <domain>
DNS domain
Optional arguments
- --ip <ip>
ip address
- --name <name> DNS
name
usage: nova endpoints
Discover endpoints that get returned from the authenticate services.
usage: nova evacuate [--password <password>] [--on-shared-storage]
<server> <host>
Evacuate server from failed host to specified one.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <host>
Name or ID of target host.
Optional arguments
- --password <password>
Set the provided password on the evacuated server. Not applicable with on-shared-storage flag
- --on-shared-storage
Specifies whether server files are located on shared storage
usage: nova fixed-ip-get <fixed_ip>
Retrieve info on a fixed ip.
Positional arguments
- <fixed_ip>
Fixed IP Address.
usage: nova fixed-ip-reserve <fixed_ip>
Reserve a fixed IP.
Positional arguments
- <fixed_ip>
Fixed IP Address.
usage: nova fixed-ip-unreserve <fixed_ip>
Unreserve a fixed IP.
Positional arguments
- <fixed_ip>
Fixed IP Address.
usage: nova flavor-access-add <flavor> <tenant_id>
Add flavor access for the given tenant.
Positional arguments
- <flavor>
Flavor name or ID to add access for the given tenant.
- <tenant_id>
Tenant ID to add flavor access for.
usage: nova flavor-access-list [--flavor <flavor>] [--tenant <tenant_id>]
Print access information about the given flavor.
Optional arguments
- --flavor <flavor>
Filter results by flavor name or ID.
- --tenant <tenant_id>
Filter results by tenant ID.
usage: nova flavor-access-remove <flavor> <tenant_id>
Remove flavor access for the given tenant.
Positional arguments
- <flavor>
Flavor name or ID to remove access for the given tenant.
- <tenant_id>
Tenant ID to remove flavor access for.
usage: nova flavor-create [--ephemeral <ephemeral>] [--swap <swap>]
[--rxtx-factor <factor>] [--is-public <is-public>]
<name> <id> <ram> <disk> <vcpus>
Create a new flavor
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of the new flavor
- <id>
Unique ID (integer or UUID) for the new flavor. If specifying 'auto', a UUID will be generated as id
- <ram>
Memory size in MB
- <disk>
Disk size in GB
- <vcpus>
Number of vcpus
Optional arguments
- --ephemeral <ephemeral>
Ephemeral space size in GB (default 0)
- --swap <swap>
Swap space size in MB (default 0)
- --rxtx-factor <factor>
RX/TX factor (default 1)
- --is-public <is-public>
Make flavor accessible to the public (default true)
usage: nova flavor-delete <flavor>
Delete a specific flavor
Positional arguments
- <flavor>
Name or ID of the flavor to delete
usage: nova flavor-key <flavor> <action> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Set or unset extra_spec for a flavor.
Positional arguments
- <flavor>
Name or ID of flavor
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'unset'
- <key=value>
Extra_specs to set/unset (only key is necessary on unset)
usage: nova flavor-list [--extra-specs] [--all]
Print a list of available 'flavors' (sizes of servers).
Optional arguments
- --extra-specs
Get extra-specs of each flavor.
- --all
Display all flavors (Admin only).
usage: nova flavor-show <flavor>
Show details about the given flavor.
Positional arguments
- <flavor>
Name or ID of flavor
usage: nova floating-ip-associate [--fixed-address <fixed_address>]
<server> <address>
Associate a floating IP address to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <address>
IP Address.
Optional arguments
- --fixed-address <fixed_address>
Fixed IP Address to associate with.
usage: nova floating-ip-bulk-create [--pool <pool>] [--interface <interface>]
<range>
Bulk create floating ips by range.
Positional arguments
- <range>
Address range to create
Optional arguments
- --pool <pool>
Pool for new Floating IPs
- --interface <interface>
Interface for new Floating IPs
usage: nova floating-ip-bulk-delete <range>
Bulk delete floating ips by range.
Positional arguments
- <range>
Address range to delete
usage: nova floating-ip-bulk-list [--host <host>]
List all floating ips.
Optional arguments
- --host <host>
Filter by host
usage: nova floating-ip-create [<floating-ip-pool>]
Allocate a floating IP for the current tenant.
Positional arguments
- <floating-ip-pool>
Name of Floating IP Pool. (Optional)
usage: nova floating-ip-delete <address>
De-allocate a floating IP.
Positional arguments
- <address>
IP of Floating Ip.
usage: nova floating-ip-disassociate <server> <address>
Disassociate a floating IP address from a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <address>
IP Address.
usage: nova force-delete <server>
Force delete a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova get-password <server> [<private-key>]
Get password for a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <private-key>
Private key (used locally to decrypt password) (Optional). When specified, the command displays the clear (decrypted) VM password. When not specified, the ciphered VM password is displayed.
usage: nova get-rdp-console <server> <console-type>
Get a rdp console to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <console-type>
Type of rdp console ("rdp-html5").
usage: nova get-spice-console <server> <console-type>
Get a spice console to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <console-type>
Type of spice console ("spice-html5").
usage: nova get-vnc-console <server> <console-type>
Get a vnc console to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <console-type>
Type of vnc console ("novnc" or "xvpvnc").
usage: nova host-action [--action <action>] <hostname>
Perform a power action on a host.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
Optional arguments
- --action <action> A
power action: startup, reboot, or shutdown.
usage: nova host-describe <hostname>
Describe a specific host.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
usage: nova host-evacuate [--target_host <target_host>] [--on-shared-storage]
<host>
Evacuate all instances from failed host to specified one.
Positional arguments
- <host>
Name of host.
Optional arguments
- --target_host <target_host>
Name of target host.
- --on-shared-storage
Specifies whether all instances files are on shared storage
usage: nova host-list [--zone <zone>]
List all hosts by service.
Optional arguments
- --zone <zone>
Filters the list, returning only those hosts in the availability zone <zone>.
usage: nova host-meta <host> <action> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Set or Delete metadata on all instances of a host.
Positional arguments
- <host>
Name of host.
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'delete'
- <key=value>
Metadata to set or delete (only key is necessary on delete)
usage: nova host-servers-migrate <host>
Migrate all instances of the specified host to other available hosts.
Positional arguments
- <host>
Name of host.
usage: nova host-update [--status <enable|disable>]
[--maintenance <enable|disable>]
<hostname>
Update host settings.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
Optional arguments
- --status <enable|disable>
Either enable or disable a host.
- --maintenance <enable|disable>
Either put or resume host to/from maintenance.
usage: nova hypervisor-list [--matching <hostname>]
List hypervisors.
Optional arguments
- --matching <hostname>
List hypervisors matching the given <hostname>.
usage: nova hypervisor-servers <hostname>
List servers belonging to specific hypervisors.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
The hypervisor hostname (or pattern) to search for.
usage: nova hypervisor-show <hypervisor>
Display the details of the specified hypervisor.
Positional arguments
- <hypervisor>
Name or ID of the hypervisor to show the details of.
usage: nova hypervisor-stats
Get hypervisor statistics over all compute nodes.
usage: nova hypervisor-uptime <hypervisor>
Display the uptime of the specified hypervisor.
Positional arguments
- <hypervisor>
Name or ID of the hypervisor to show the uptime of.
usage: nova image-create [--show] [--poll] <server> <name>
Create a new image by taking a snapshot of a running server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <name>
Name of snapshot.
Optional arguments
- --show
Print image info.
- --poll
Blocks while server snapshots so progress can be reported.
usage: nova image-delete <image> [<image> ...]
Delete specified image(s).
Positional arguments
- <image>
Name or ID of image(s).
usage: nova image-list [--limit <limit>]
Print a list of available images to boot from.
Optional arguments
- --limit <limit>
number of images to return per request
usage: nova image-meta <image> <action> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Set or Delete metadata on an image.
Positional arguments
- <image>
Name or ID of image
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'delete'
- <key=value>
Metadata to add/update or delete (only key is necessary on delete)
usage: nova image-show <image>
Show details about the given image.
Positional arguments
- <image>
Name or ID of image
usage: nova instance-action <server> <request_id>
Show an action.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or UUID of the server to show an action for.
- <request_id>
Request ID of the action to get.
usage: nova instance-action-list <server>
List actions on a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or UUID of the server to list actions for.
usage: nova interface-attach [--port-id <port_id>] [--net-id <net_id>]
[--fixed-ip <fixed_ip>]
<server>
Attach a network interface to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --port-id <port_id>
Port ID.
- --net-id <net_id>
Network ID
- --fixed-ip <fixed_ip>
Requested fixed IP.
usage: nova interface-detach <server> <port_id>
Detach a network interface from a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <port_id>
Port ID.
usage: nova interface-list <server>
List interfaces attached to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova keypair-add [--pub-key <pub-key>] <name>
Create a new key pair for use with servers.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of key.
Optional arguments
- --pub-key <pub-key>
Path to a public ssh key.
usage: nova keypair-delete <name>
Delete keypair given by its name.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Keypair name to delete.
usage: nova keypair-show <keypair>
Show details about the given keypair.
Positional arguments
- <keypair>
Name or ID of keypair
usage: nova list [--reservation-id <reservation-id>] [--ip <ip-regexp>]
[--ip6 <ip6-regexp>] [--name <name-regexp>]
[--instance-name <name-regexp>] [--status <status>]
[--flavor <flavor>] [--image <image>] [--host <hostname>]
[--all-tenants [<0|1>]] [--tenant [<tenant>]] [--deleted]
[--fields <fields>] [--minimal]
List active servers.
Optional arguments
- --reservation-id <reservation-id>
Only return servers that match reservation-id.
- --ip <ip-regexp>
Search with regular expression match by IP address (Admin only).
- --ip6 <ip6-regexp>
Search with regular expression match by IPv6 address (Admin only).
- --name <name-regexp>
Search with regular expression match by name
- --instance-name <name-regexp>
Search with regular expression match by server name (Admin only).
- --status <status>
Search by server status
- --flavor <flavor>
Search by flavor name or ID
- --image <image>
Search by image name or ID
- --host <hostname>
Search servers by hostname to which they are assigned (Admin only).
- --all-tenants [<0|1>]
Display information from all tenants (Admin only).
- --tenant [<tenant>]
Display information from single tenant (Admin only).
- --deleted
Only display deleted servers (Admin only).
- --fields <fields>
Comma-separated list of fields to display. Use the show command to see which fields are available.
- --minimal
Get only uuid and name.
usage: nova list-extensions
List all the os-api extensions that are available.
usage: nova list-secgroup <server>
List Security Group(s) of a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova live-migration [--block-migrate] [--disk-over-commit]
<server> [<host>]
Migrate running server to a new machine.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <host>
destination host name.
Optional arguments
- --block-migrate
True in case of block_migration. (Default=False:live_migration)
- --disk-over-commit
Allow overcommit.(Default=False)
usage: nova lock <server>
Lock a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova meta <server> <action> <key=value> [<key=value> ...]
Set or Delete metadata on a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server
- <action>
Actions: 'set' or 'delete'
- <key=value>
Metadata to set or delete (only key is necessary on delete)
usage: nova migrate [--poll] <server>
Migrate a server. The new host will be selected by the scheduler.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --poll
Blocks while server migrates so progress can be reported.
usage: nova migration-list [--host <host>] [--status <status>]
[--cell_name <cell_name>]
Print a list of migrations.
Optional arguments
- --host <host>
Fetch migrations for the given host.
- --status <status>
Fetch migrations for the given status.
- --cell_name <cell_name>
Fetch migrations for the given cell_name.
usage: nova net <network_id>
Show a network
Positional arguments
- <network_id>
ID of network
usage: nova net-create <network_label> <cidr>
Create a network
Positional arguments
- <network_label>
Network label (ex. my_new_network)
- <cidr>
IP block to allocate from (ex. 172.16.0.0/24 or 2001:DB8::/64)
usage: nova net-delete <network_id>
Delete a network
Positional arguments
- <network_id>
ID of network
usage: nova network-associate-host <network> <host>
Associate host with network.
Positional arguments
- <network>
uuid of network
- <host>
Name of host
usage: nova network-associate-project <network>
Associate project with network.
Positional arguments
- <network>
uuid of network
usage: nova network-create [--fixed-range-v4 <x.x.x.x/yy>]
[--fixed-range-v6 CIDR_V6] [--vlan <vlan id>]
[--vpn <vpn start>] [--gateway GATEWAY]
[--gateway-v6 GATEWAY_V6] [--bridge <bridge>]
[--bridge-interface <bridge interface>]
[--multi-host <'T'|'F'>] [--dns1 <DNS Address>]
[--dns2 <DNS Address>] [--uuid <network uuid>]
[--fixed-cidr <x.x.x.x/yy>]
[--project-id <project id>] [--priority <number>]
<network_label>
Create a network.
Positional arguments
- <network_label>
Label for network
Optional arguments
- --fixed-range-v4 <x.x.x.x/yy>
IPv4 subnet (ex: 10.0.0.0/8)
- --fixed-range-v6
CIDR_V6 IPv6 subnet (ex: fe80::/64
- --vlan <vlan id>
vlan id
- --vpn <vpn start>
vpn start
- --gateway GATEWAY
gateway
- --gateway-v6
GATEWAY_V6 ipv6 gateway
- --bridge <bridge>
VIFs on this network are connected to this bridge
- --bridge-interface <bridge interface>
the bridge is connected to this interface
- --multi-host <'T'|'F'>
Multi host
- --dns1 <DNS Address>
First DNS
- --dns2 <DNS Address>
Second DNS
- --uuid <network uuid>
Network UUID
- --fixed-cidr <x.x.x.x/yy>
IPv4 subnet for fixed IPS (ex: 10.20.0.0/16)
- --project-id <project id>
Project id
- --priority <number>
Network interface priority
usage: nova network-disassociate [--host-only [<0|1>]]
[--project-only [<0|1>]]
<network>
Disassociate host and/or project from the given network.
Positional arguments
- <network>
uuid of network
Optional arguments
- --host-only [<0|1>]
- --project-only [<0|1>]
usage: nova network-show <network>
Show details about the given network.
Positional arguments
- <network>
uuid or label of network
usage: nova pause <server>
Pause a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova quota-class-show <class>
List the quotas for a quota class.
Positional arguments
- <class>
Name of quota class to list the quotas for.
usage: nova quota-class-update [--instances <instances>] [--cores <cores>]
[--ram <ram>] [--floating-ips <floating-ips>]
[--metadata-items <metadata-items>]
[--injected-files <injected-files>]
[--injected-file-content-bytes <injected-file-content-bytes>]
[--injected-file-path-bytes <injected-file-path-bytes>]
[--key-pairs <key-pairs>]
[--security-groups <security-groups>]
[--security-group-rules <security-group-rules>]
<class>
Update the quotas for a quota class.
Positional arguments
- <class>
Name of quota class to set the quotas for.
Optional arguments
- --instances <instances>
New value for the "instances" quota.
- --cores <cores>
New value for the "cores" quota.
- --ram <ram>
New value for the "ram" quota.
- --floating-ips <floating-ips>
New value for the "floating-ips" quota.
- --metadata-items <metadata-items>
New value for the "metadata-items" quota.
- --injected-files <injected-files>
New value for the "injected-files" quota.
- --injected-file-content-bytes <injected-file-content-bytes>
New value for the "injected-file-content-bytes" quota.
- --injected-file-path-bytes <injected-file-path-bytes>
New value for the "injected-file-path-bytes" quota.
- --key-pairs <key-pairs>
New value for the "key-pairs" quota.
- --security-groups <security-groups>
New value for the "security-groups" quota.
- --security-group-rules <security-group-rules>
New value for the "security-group-rules" quota.
usage: nova quota-defaults [--tenant <tenant-id>]
List the default quotas for a tenant.
Optional arguments
- --tenant <tenant-id> ID
of tenant to list the default quotas for.
usage: nova quota-delete [--tenant <tenant-id>] [--user <user-id>]
Delete quota for a tenant/user so their quota will Revert back to default.
Optional arguments
- --tenant <tenant-id> ID
of tenant to delete quota for.
- --user <user-id> ID
of user to delete quota for.
usage: nova quota-show [--tenant <tenant-id>] [--user <user-id>]
List the quotas for a tenant/user.
Optional arguments
- --tenant <tenant-id> ID
of tenant to list the quotas for.
- --user <user-id> ID
of user to list the quotas for.
usage: nova quota-update [--user <user-id>] [--instances <instances>]
[--cores <cores>] [--ram <ram>]
[--floating-ips <floating-ips>]
[--fixed-ips <fixed-ips>]
[--metadata-items <metadata-items>]
[--injected-files <injected-files>]
[--injected-file-content-bytes <injected-file-content-bytes>]
[--injected-file-path-bytes <injected-file-path-bytes>]
[--key-pairs <key-pairs>]
[--security-groups <security-groups>]
[--security-group-rules <security-group-rules>]
[--force]
<tenant-id>
Update the quotas for a tenant/user.
Positional arguments
- <tenant-id>
ID of tenant to set the quotas for.
Optional arguments
- --user <user-id> ID
of user to set the quotas for.
- --instances <instances>
New value for the "instances" quota.
- --cores <cores>
New value for the "cores" quota.
- --ram <ram>
New value for the "ram" quota.
- --floating-ips <floating-ips>
New value for the "floating-ips" quota.
- --fixed-ips <fixed-ips>
New value for the "fixed-ips" quota.
- --metadata-items <metadata-items>
New value for the "metadata-items" quota.
- --injected-files <injected-files>
New value for the "injected-files" quota.
- --injected-file-content-bytes <injected-file-content-bytes>
New value for the "injected-file-content-bytes" quota.
- --injected-file-path-bytes <injected-file-path-bytes>
New value for the "injected-file-path-bytes" quota.
- --key-pairs <key-pairs>
New value for the "key-pairs" quota.
- --security-groups <security-groups>
New value for the "security-groups" quota.
- --security-group-rules <security-group-rules>
New value for the "security-group-rules" quota.
- --force
Whether force update the quota even if the already used and reserved exceeds the new quota
usage: nova reboot [--hard] [--poll] <server>
Reboot a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --hard
Perform a hard reboot (instead of a soft one).
- --poll
Blocks while server is rebooting.
usage: nova rebuild [--rebuild-password <rebuild-password>] [--poll]
[--minimal] [--preserve-ephemeral]
<server> <image>
Shutdown, re-image, and re-boot a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <image>
Name or ID of new image.
Optional arguments
- --rebuild-password <rebuild-password>
Set the provided password on the rebuild server.
- --poll
Blocks while server rebuilds so progress can be reported.
- --minimal
Skips flavor/image lookups when showing servers
- --preserve-ephemeral
Preserve the default ephemeral storage partition on rebuild.
usage: nova refresh-network <server>
Refresh server network information.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of a server for which the network cache should be refreshed from neutron (Admin only).
usage: nova remove-fixed-ip <server> <address>
Remove an IP address from a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <address>
IP Address.
usage: nova remove-secgroup <server> <secgroup>
Remove a Security Group from a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <secgroup>
Name of Security Group.
usage: nova rename <server> <name>
Rename a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name (old name) or ID of server.
- <name>
New name for the server.
usage: nova rescue <server>
Rescue a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova reset-network <server>
Reset network of a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova reset-state [--active] <server>
Reset the state of a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --active
Request the server be reset to "active" state instead of "error" state (the default).
usage: nova resize [--poll] <server> <flavor>
Resize a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <flavor>
Name or ID of new flavor.
Optional arguments
- --poll
Blocks while servers resizes so progress can be reported.
usage: nova resize-confirm <server>
Confirm a previous resize.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova resize-revert <server>
Revert a previous resize (and return to the previous VM).
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova restore <server>
Restore a soft-deleted server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova resume <server>
Resume a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova root-password <server>
Change the root password for a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova scrub <project_id>
Delete data associated with the project.
Positional arguments
- <project_id>
The ID of the project.
usage: nova secgroup-add-group-rule <secgroup> <source-group> <ip-proto>
<from-port> <to-port>
Add a source group rule to a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
- <source-group>
ID or name of source group.
- <ip-proto>
IP protocol (icmp, tcp, udp).
- <from-port>
Port at start of range.
- <to-port>
Port at end of range.
usage: nova secgroup-add-rule <secgroup> <ip-proto> <from-port> <to-port>
<cidr>
Add a rule to a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
- <ip-proto>
IP protocol (icmp, tcp, udp).
- <from-port>
Port at start of range.
- <to-port>
Port at end of range.
- <cidr>
CIDR for address range.
usage: nova secgroup-create <name> <description>
Create a security group.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of security group.
- <description>
Description of security group.
usage: nova secgroup-delete <secgroup>
Delete a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
usage: nova secgroup-delete-group-rule <secgroup> <source-group> <ip-proto>
<from-port> <to-port>
Delete a source group rule from a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
- <source-group>
ID or name of source group.
- <ip-proto>
IP protocol (icmp, tcp, udp).
- <from-port>
Port at start of range.
- <to-port>
Port at end of range.
usage: nova secgroup-delete-rule <secgroup> <ip-proto> <from-port> <to-port>
<cidr>
Delete a rule from a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
- <ip-proto>
IP protocol (icmp, tcp, udp).
- <from-port>
Port at start of range.
- <to-port>
Port at end of range.
- <cidr>
CIDR for address range.
usage: nova secgroup-list [--all-tenants [<0|1>]]
List security groups for the current tenant.
Optional arguments
- --all-tenants [<0|1>]
Display information from all tenants (Admin only).
usage: nova secgroup-list-rules <secgroup>
List rules for a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
usage: nova secgroup-update <secgroup> <name> <description>
Update a security group.
Positional arguments
- <secgroup>
ID or name of security group.
- <name>
Name of security group.
- <description>
Description of security group.
usage: nova service-disable [--reason <reason>] <hostname> <binary>
Disable the service.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
- <binary>
Service binary.
Optional arguments
- --reason <reason>
Reason for disabling service.
usage: nova service-enable <hostname> <binary>
Enable the service.
Positional arguments
- <hostname>
Name of host.
- <binary>
Service binary.
usage: nova service-list [--host <hostname>] [--binary <binary>]
Show a list of all running services. Filter by host & binary.
Optional arguments
- --host <hostname>
Name of host.
- --binary <binary>
Service binary.
usage: nova shelve <server>
Shelve a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova shelve-offload <server>
Remove a shelved server from the compute node.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova show [--minimal] <server>
Show details about the given server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --minimal
Skips flavor/image lookups when showing servers
usage: nova ssh [--port PORT] [--private] [--ipv6] [--login <login>]
[-i IDENTITY] [--extra-opts EXTRA]
<server>
SSH into a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
Optional arguments
- --port PORT
Optional flag to indicate which port to use for ssh. (Default=22)
- --private
Optional flag to indicate whether to only use private address attached to an instance. (Default=False). If no public address is found try private address
- --ipv6
Optional flag to indicate whether to use an IPv6 address attached to a server. (Defaults to IPv4 address)
- --login <login>
Login to use.
- -i IDENTITY, --identity IDENTITY
Private key file, same as the -i option to the ssh command.
- --extra-opts EXTRA
Extra options to pass to ssh. see: man ssh
usage: nova start <server>
Start a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova stop <server>
Stop a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova suspend <server>
Suspend a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova unlock <server>
Unlock a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova unpause <server>
Unpause a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova unrescue <server>
Unrescue a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova unshelve <server>
Unshelve a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
usage: nova usage [--start <start>] [--end <end>] [--tenant <tenant-id>]
Show usage data for a single tenant.
Optional arguments
- --start <start>
Usage range start date ex 2012-01-20 (default: 4 weeks ago)
- --end <end>
Usage range end date, ex 2012-01-20 (default: tomorrow)
- --tenant <tenant-id> UUID
or name of tenant to get usage for.
usage: nova usage-list [--start <start>] [--end <end>]
List usage data for all tenants.
Optional arguments
- --start <start>
Usage range start date ex 2012-01-20 (default: 4 weeks ago)
- --end <end>
Usage range end date, ex 2012-01-20 (default: tomorrow)
usage: nova volume-attach <server> <volume> [<device>]
Attach a volume to a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <volume>
ID of the volume to attach.
- <device>
Name of the device e.g. /dev/vdb. Use "auto" for autoassign (if supported)
usage: nova volume-create [--snapshot-id <snapshot-id>]
[--image-id <image-id>]
[--display-name <display-name>]
[--display-description <display-description>]
[--volume-type <volume-type>]
[--availability-zone <availability-zone>]
<size>
Add a new volume.
Positional arguments
- <size>
Size of volume in GB
Optional arguments
- --snapshot-id <snapshot-id>
Optional snapshot id to create the volume from. (Default=None)
- --image-id <image-id>
Optional image id to create the volume from. (Default=None)
- --display-name <display-name>
Optional volume name. (Default=None)
- --display-description <display-description>
Optional volume description. (Default=None)
- --volume-type <volume-type>
Optional volume type. (Default=None)
- --availability-zone <availability-zone>
Optional Availability Zone for volume. (Default=None)
usage: nova volume-delete <volume> [<volume> ...]
Remove volume(s).
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume(s) to delete.
usage: nova volume-detach <server> <volume>
Detach a volume from a server.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <volume>
Attachment ID of the volume.
usage: nova volume-list [--all-tenants [<0|1>]]
List all the volumes.
Optional arguments
- --all-tenants [<0|1>]
Display information from all tenants (Admin only).
usage: nova volume-show <volume>
Show details about a volume.
Positional arguments
- <volume>
Name or ID of the volume.
usage: nova volume-snapshot-create [--force <True|False>]
[--display-name <display-name>]
[--display-description <display-description>]
<volume-id>
Add a new snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <volume-id>
ID of the volume to snapshot
Optional arguments
- --force <True|False>
Optional flag to indicate whether to snapshot a volume even if its attached to a server. (Default=False)
- --display-name <display-name>
Optional snapshot name. (Default=None)
- --display-description <display-description>
Optional snapshot description. (Default=None)
usage: nova volume-snapshot-delete <snapshot>
Remove a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
Name or ID of the snapshot to delete.
usage: nova volume-snapshot-show <snapshot>
Show details about a snapshot.
Positional arguments
- <snapshot>
Name or ID of the snapshot.
usage: nova volume-type-create <name>
Create a new volume type.
Positional arguments
- <name>
Name of the new flavor
usage: nova volume-type-delete <id>
Delete a specific flavor
Positional arguments
- <id>
Unique ID of the volume type to delete
usage: nova volume-update <server> <volume> <volume>
Update volume attachment.
Positional arguments
- <server>
Name or ID of server.
- <volume>
Attachment ID of the volume.
- <volume>
ID of the volume to attach.
usage: nova x509-create-cert [<private-key-filename>] [<x509-cert-filename>]
Create x509 cert for a user in tenant.
Positional arguments
- <private-key-filename>
Filename for the private key [Default: pk.pem]
- <x509-cert-filename>
Filename for the X.509 certificate [Default: cert.pem]
You can use the nova client to list images, set and delete image metadata, delete images, and take a snapshot of a running instance to create an image.
The safest approach is to shut down the instance before you take a snapshot.
You cannot create a snapshot from an instance that has an attached volume. Detach the volume, create the image, and re-mount the volume.
To create an image
Write any buffered data to disk.
For more information, see the Taking Snapshots in the OpenStack Operations Guide.
To create the image, list instances to get the server ID:
$ nova list
+--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+ | ID | Name | Status | Task State | Power State | Networks | +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+ | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | myCirrosServer | ACTIVE | None | Running | private=10.0.0.3 | +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+
In this example, the server is named
myCirrosServer. Use this server to create a snapshot, as follows:$ nova image-create myCirrosServer myCirrosImage
The command creates a qemu snapshot and automatically uploads the image to your repository. Only the tenant that creates the image has access to it.
Get details for your image to check its status:
$ nova image-show
IMAGE+-------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +-------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | metadata owner_id | 66265572db174a7aa66eba661f58eb9e | | minDisk | 0 | | metadata instance_type_name | m1.small | | metadata instance_type_id | 5 | | metadata instance_type_memory_mb | 2048 | | id | 7e5142af-1253-4634-bcc6-89482c5f2e8a | | metadata instance_type_root_gb | 20 | | metadata instance_type_rxtx_factor | 1 | | metadata ramdisk_id | 3cf852bd-2332-48f4-9ae4-7d926d50945e | | metadata image_state | available | | metadata image_location | snapshot | | minRam | 0 | | metadata instance_type_vcpus | 1 | | status | ACTIVE | | updated | 2013-07-22T19:46:42Z | | metadata instance_type_swap | 0 | | metadata instance_type_vcpu_weight | None | | metadata base_image_ref | 397e713c-b95b-4186-ad46-6126863ea0a9 | | progress | 100 | | metadata instance_type_flavorid | 2 | | OS-EXT-IMG-SIZE:size | 14221312 | | metadata image_type | snapshot | | metadata user_id | 376744b5910b4b4da7d8e6cb483b06a8 | | name | myCirrosImage | | created | 2013-07-22T19:45:58Z | | metadata instance_uuid | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | | server | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | | metadata kernel_id | df430cc2-3406-4061-b635-a51c16e488ac | | metadata instance_type_ephemeral_gb | 0 | +-------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
The image status changes from
SAVINGtoACTIVE. Only the tenant who creates the image has access to it.
To launch an instance from your image
To launch an instance from your image, include the image ID and flavor ID, as follows:
$ nova boot newServer --image 7e5142af-1253-4634-bcc6-89482c5f2e8a --flavor 3
+-------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +-------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | OS-EXT-STS:task_state | scheduling | | image | myCirrosImage | | OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | building | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:instance_name | instance-00000007 | | flavor | m1.medium | | id | d7efd3e4-d375-46d1-9d57-372b6e4bdb7f | | security_groups | [{u'name': u'default'}] | | user_id | 376744b5910b4b4da7d8e6cb483b06a8 | | OS-DCF:diskConfig | MANUAL | | accessIPv4 | | | accessIPv6 | | | progress | 0 | | OS-EXT-STS:power_state | 0 | | OS-EXT-AZ:availability_zone | nova | | config_drive | | | status | BUILD | | updated | 2013-07-22T19:58:33Z | | hostId | | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:host | None | | key_name | None | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:hypervisor_hostname | None | | name | newServer | | adminPass | jis88nN46RGP | | tenant_id | 66265572db174a7aa66eba661f58eb9e | | created | 2013-07-22T19:58:33Z | | metadata | {} | +-------------------------------------+--------------------------------------+
You cannot create a snapshot from an instance that has an attached volume. Detach the volume, create the image, and re-mount the volume.
Make sure the version of qemu you are using is version 0.14 or greater. Older versions of qemu result in an "
unknown option -s" error message in thenova-compute.log.Examine the
/var/log/nova-api.logand/var/log/nova-compute.loglog files for error messages.
You can boot instances from a volume instead of an image. Use
the nova boot
--block-device parameter to define how
volumes are attached to an instance when you create it. You can
use the --block-device parameter with
existing or new volumes that you create from a source image,
volume, or snapshot.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
To attach a volume to a running instance, see Manage volumes. |
Use this procedure to create a volume from an image, and use it to boot an instance.
You can create a volume from an existing image, volume, or snapshot.
List available images:
$ nova image-list +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------+ | ID | Name | Status | Server | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------+ | e0b7734d-2331-42a3-b19e-067adc0da17d | cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec | ACTIVE | | | 75bf193b-237b-435e-8712-896c51484de9 | cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec-kernel | ACTIVE | | | 19eee81c-f972-44e1-a952-1dceee148c47 | cirros-0.3.2-x86_64-uec-ramdisk | ACTIVE | | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------+--------+--------+
To create a bootable volume from an image and launch an instance from this volume, use the
--block-deviceparameter.For example:
$ nova boot --flavor
FLAVOR--block-device source=SOURCE,id=ID,dest=DEST,size=SIZE,shutdown=PRESERVE,bootindex=INDEXNAMEThe parameters are:
Parameter Description --flavorFLAVORThe flavor ID or name.
--block-devicesource=SOURCE,id=ID,dest=DEST,size=SIZE,shutdown=PRESERVE,bootindex=INDEXSOURCE: The type of object used to create the block device. Valid values arevolume,snapshot,imageandblank.ID: The ID of the source object.DEST: The type of the target virtual device. Valid values arevolumeandlocal.SIZE: The size of the volume that will be created.PRESERVE: What to do with the volume when the instance is terminated.preservewill not delete the volume,removewill.INDEX: Used to order the boot disks. Use0to boot from this volume.
NAMEThe name for the server.
-
Create a bootable volume from an image, before the instance boots. The volume is not deleted when the instance is terminated:
$ nova boot --flavor 2 \ --block-device source=image,id=e0b7734d-2331-42a3-b19e-067adc0da17d,dest=volume,size=10,shutdown=preserve,bootindex=0 \ myInstanceFromVolume +--------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +--------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+ | OS-EXT-STS:task_state | scheduling | | image | Attempt to boot from volume - no image supplied | | OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | building | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:instance_name | instance-00000003 | | OS-SRV-USG:launched_at | None | | flavor | m1.small | | id | 2e65c854-dba9-4f68-8f08-fe332e546ecc | | security_groups | [{u'name': u'default'}] | | user_id | 352b37f5c89144d4ad0534139266d51f | | OS-DCF:diskConfig | MANUAL | | accessIPv4 | | | accessIPv6 | | | progress | 0 | | OS-EXT-STS:power_state | 0 | | OS-EXT-AZ:availability_zone | nova | | config_drive | | | status | BUILD | | updated | 2014-02-02T13:29:54Z | | hostId | | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:host | None | | OS-SRV-USG:terminated_at | None | | key_name | None | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:hypervisor_hostname | None | | name | myInstanceFromVolume | | adminPass | TzjqyGsRcJo9 | | tenant_id | f7ac731cc11f40efbc03a9f9e1d1d21f | | created | 2014-02-02T13:29:53Z | | os-extended-volumes:volumes_attached | [] | | metadata | {} | +--------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------+ List volumes to see the bootable volume and its attached
myInstanceFromVolumeinstance:$ cinder list +--------------------------------------+--------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+--------------------------------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+--------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+--------------------------------------+ | 2fff50ab-1a9c-4d45-ae60-1d054d6bc868 | in-use | | 10 | None | true | 2e65c854-dba9-4f68-8f08-fe332e546ecc | +--------------------------------------+--------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+--------------------------------------+
Use the --block-device parameter to
attach an existing, non-bootable volume to a new
instance.
Create a volume:
$ cinder create --display-name my-volume 8 +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | attachments | [] | | availability_zone | nova | | bootable | false | | created_at | 2014-02-04T21:25:18.730961 | | display_description | None | | display_name | my-volume | | id | 3195a5a7-fd0d-4ac3-b919-7ba6cbe11d46 | | metadata | {} | | size | 8 | | snapshot_id | None | | source_volid | None | | status | creating | | volume_type | None | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+List volumes:
$ cinder list +--------------------------------------+---------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Bootable | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+ | 3195a5a7-fd0d-4ac3-b919-7ba6cbe11d46 | available | my-volume | 8 | None | false | | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+----------+-------------+
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note The volume is not bootable because it was not created from an image.
The volume is also entirely empty: It has no partition table and no file system.
-
Run this command to create an instance and boot it with the volume that is attached to this instance. An image is used as boot source:
$ nova boot --flavor 2 --image e0b7734d-2331-42a3-b19e-067adc0da17d \ --block-device source=volume,id=3195a5a7-fd0d-4ac3-b919-7ba6cbe11d46,dest=volume,shutdown=preserve \ myInstanceWithVolume +--------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +--------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | OS-EXT-STS:task_state | scheduling | | image | e0b7734d-2331-42a3-b19e-067adc0da17d | | OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | building | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:instance_name | instance-00000003 | | flavor | m1.small | | id | 8ed8b0f9-70de-4662-a16c-0b51ce7b17b4 | | security_groups | [{u'name': u'default'}] | | user_id | 352b37f5c89144d4ad0534139266d51f | | OS-DCF:diskConfig | MANUAL | | accessIPv4 | | | accessIPv6 | | | progress | 0 | | OS-EXT-STS:power_state | 0 | | OS-EXT-AZ:availability_zone | nova | | config_drive | | | status | BUILD | | updated | 2013-10-16T01:43:26Z | | hostId | | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:host | None | | OS-SRV-USG:terminated_at | None | | key_name | None | | OS-EXT-SRV-ATTR:hypervisor_hostname | None | | name | myInstanceWithVolume | | adminPass | BULD33uzYwhq | | tenant_id | f7ac731cc11f40efbc03a9f9e1d1d21f | | created | 2013-10-16T01:43:25Z | | os-extended-volumes:volumes_attached | [{u'id': u'3195a5a7-fd0d-4ac3-b919-7ba6cbe11d46'}] | | metadata | {} | +--------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------+ List volumes:
$ nova volume-list
Note that the volume is attached to a server:
+--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+--------------------------------------+ | ID | Status | Display Name | Size | Volume Type | Attached to | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+--------------------------------------+ | 3195a5a7-fd0d-4ac3-b919-7ba6cbe11d46 | in-use | my-volume | 8 | None | 8ed8b0f9-70de-4662-a16c-0b51ce7b17b4 | +--------------------------------------+-----------+--------------+------+-------------+--------------------------------------+
Use the nova boot
--swap parameter to attach a swap disk on
boot or the nova boot
--ephemeral parameter to attach an
ephemeral disk on boot. When you terminate the instance, both
disks are deleted.
Boot an instance with a 512 MB swap disk and 2 GB ephemeral disk:
$ nova boot --flavorFLAVOR--imageIMAGE_ID--swap 512 --ephemeral size=2NAME
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
The flavor defines the maximum swap and ephemeral disk size. You cannot exceed these maximum values. |
When you no longer need an instance, you can delete it.
List all instances:
$ nova list +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+ | ID | Name | Status | Task State | Power State | Networks | +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+ | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | myCirrosServer | ACTIVE | None | Running | private=10.0.0.3 | | 8a99547e-7385-4ad1-ae50-4ecfaaad5f42 | myInstanceFromVolume | ACTIVE | None | Running | private=10.0.0.4 | | d7efd3e4-d375-46d1-9d57-372b6e4bdb7f | newServer | ERROR | None | NOSTATE | | +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+
Run the nova delete command to delete the instance. The following example shows deletion of the
newServerinstance, which is inERRORstate:$ nova delete newServer
The command does not notify that your server was deleted.
To verify that the server was deleted, run the nova list command:
$ nova list +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+ | ID | Name | Status | Task State | Power State | Networks | +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+ | 84c6e57d-a6b1-44b6-81eb-fcb36afd31b5 | myCirrosServer | ACTIVE | None | Running | private=10.0.0.3 | | 8a99547e-7385-4ad1-ae50-4ecfaaad5f42 | myInstanceFromVolume | ACTIVE | None | Running | private=10.0.0.4 | +--------------------------------------+----------------------+--------+------------+-------------+------------------+
The deleted instance does not appear in the list.