- Sharding >
- Sharding Concepts >
- Sharded Cluster Architectures >
- Production Cluster Architecture
Production Cluster Architecture¶
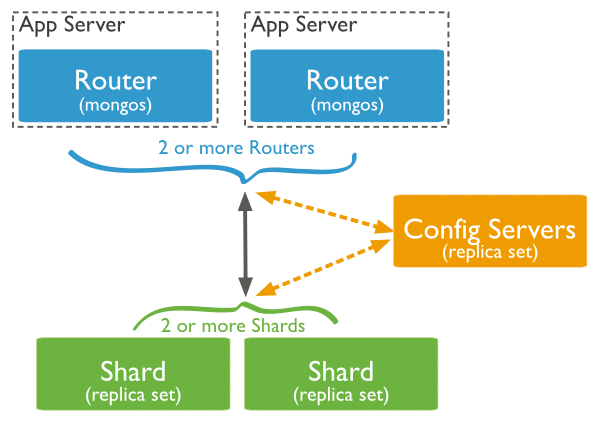
In a production cluster, you must ensure that data is redundant and that your systems are highly available. To that end, a production cluster must have the following components:
- Config Servers
Changed in version 3.2: Starting in MongoDB 3.2, config servers for sharded clusters can be deployed as a replica set. The replica set config servers must run the WiredTiger storage engine. MongoDB 3.2 deprecates the use of three mirrored mongod instances for config servers.
A single sharded cluster must have exclusive use of its config servers. If you have multiple sharded clusters, each cluster must have its own replica set config servers.
- Two or More Replica Sets As Shards
These replica sets are the shards. For information on replica sets, see Replication.
- One or More Query Routers (mongos)
The mongos instances are the routers for the cluster. Typically, deployments have one mongos instance on each application server.
You may also deploy a group of mongos instances and use a proxy/load balancer between the application and the mongos. In these deployments, you must configure the load balancer for client affinity so that every connection from a single client reaches the same mongos.
Because cursors and other resources are specific to an single mongos instance, each client must interact with only one mongos instance.
See also
Thank you for your feedback!
We're sorry! You can Report a Problem to help us improve this page.
